What is the FWHM of this curve?
Q: Based on your radial velocity curve, record the orbital period P in days. This is the time elapsed…
A: 1) The orbital period P is the time elapsed between two subsequent peaks or troughs on the curve.…
Q: Given the following equation for orbital velocity, pe sin 0f + (1 + e cos 0) Ô demonstrate…
A: Given that:v→=μehsinθr^+μh(1+ecosθ)θ^
Q: said 2/3 around the track not halfway around the track?
A:
Q: THE AGNITUL 2: Use the fact that our closest neighboring star (Proxima Centauri) is a a distance of…
A: Given: Radius =98.1×10-3km Distance= 4.24 ly As we know one light year =9.461 ×1015m…
Q: Astronomy) (Part A) White Dwarf Size II. The white dwarf, Sirius B, contains 0.98 solar mass, and…
A: Mass of the dwarf planet = 0.98 solar mass = 1.96 * 1033 gm…
Q: A Spinning Star has a period of rotation of T. Over a period of a million years, its radius…
A: Write the expression for the initial period of the given star, and solve for its initial angular…
Q: V (Volts) 3.0 2.0 1.0 x (m) 1.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 A В С
A:
Q: Given the location marked with the dot on the star's radial velocity curve, at what location (A, B,…
A: The revolution of earth is considered as simple harmonic motion.
Q: If star A has an observed flux that is 1 million times larger than star B, what is the magnitude…
A: Let the flux observed from the star A is BA and the star B is BB. Then Relative brightness can be…
Q: Our galaxy is approximately 100,000 light years in diameter and 2,000 light years thick through the…
A:
Q: For a circular velocity profile of the type (r) = ar¹/9, where a is a constant and r is the radial…
A: Step 1: Step 2: Step 3: Step 4:
Q: Why are the Hll regions around 0 stars generally larger than those around B stars?
A: HII region is the interstellar region where atomic hydrogen is ionized. It is a cloud of partially…
Q: A distant galaxy has an apparent magnitude of 13 and is 5,000 kpc away. What is its absolute…
A: Apparent Magnitude The apparent magnitude of a star or a galaxy is the measure of how bright the…
Q: 2. The Crab pulsar radiates at a luminosity of $1 \times 10^{31} \mathrm{~W}$ and has a period of…
A: (a) To determine the rate at which the period is increasing and how long it will take to double:Step…
Q: Problem 2: A 5.0-mm-diameter proton beam carries a total current of I = 1.5 mA. The current density…
A: Given that:Diameter of the proton beam, D=5.0 mm=5.0×10-3 mRadius of the proton beam, R=5.0…
Q: A 0.0507-kg pair of fuzzy dice is attached to the rearview mirror of a car by a short string. The…
A:
Q: Calculate by how many times Betelgeuse is brighter than the Sun, if its parallax is 0.006 arcsec,…
A: The objective of the question is to calculate how much brighter Betelgeuse is compared to the Sun.…
What is the FWHM of this curve?

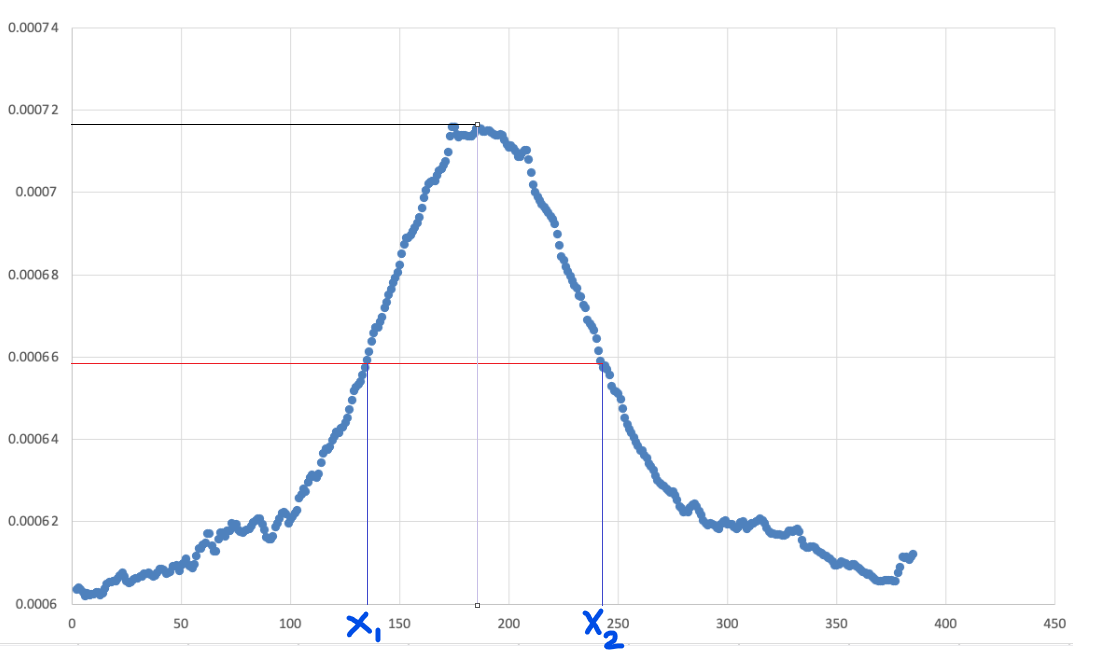
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

- If a star has a radial velocity of 25 km/sec and a transverse velocity of 60 km/sec what is the stars space velocity?If theta dot is the slew rate, what would be the maximum slew rate? How would you differentiate theta dot to get theta double dot?What does a quarter wavelength look like , like theta/4
- The figure below shows the radial velocity of a star plotted as a function of time over the course of 20 days. Where is the planet located in its orbit on day 1 (the start of the graph)? 20 Orbit of star 10- Earth 10+ Time -20 Orbit of planet Radial VelocityQ3.2 The supergiant star has a surface temperature of about 2900 K and emits a power of approximately 4 x 1030 W. Assuming that is a perfect emitter and spherical, find its radius. (hint: Area of the sphere is A = 4πr²)The rate at which a nebular cloud rotates increases as the cloud collapses to form systems of stars and planets. Consider a small segment of a nebular cloud with a mass m of 1.9 x 102" kg, tangential velocity vinitial equal to 6.8 km s-1 located at an orbital distance rinitial = 2.5 x 10* km. After the cloud collapses, the same small segment is located at an orbital distance rinal = 3.2 x 10° km. Calculate the change of the rotational velocity, Ao, for the cloud segment, assuming perfectly circular orbits. Perform your work and report your solution using two significant figures. Δω- 16605 rad s-!
- using the center-of-mass equations or the Carter of Mass Calculator (under Binary-Star Basics, abova), you will investigate a specific binary star system. Assume that Star 1 has m, 3.2 solar masses, Star 2 has m,-0.9 solar masses, and the total separation of the two (R) is 34 All (One AU is Earth's average distance from the Sun) (2) What is the distance, d. (In Au) from Star 1 to the center of mass? AU (b) What is the distance, dy On Au) from Star 2 to the center of mass AU ( what is the ratio of d, tod?For a circular velocity profile of the type (r) = ar¹ ar1/9, where a is a constant and r is the radial distance from the centre of a spiral galaxy, find the ratio (r)/(r), where (r) is the epicyclic frequency and 2(r) is the angular velocity. Enter your answer to 2 decimal places.A supernova in a distant galaxy is observed to be having an absolute magnitude of -19 and an apparent magnitude of 17. Estimate the distance to the galaxy.
- How is the blue color of a reflection nebula related to the blue color of the daytime sky?For a circular velocity profile of the type (r) = αν ar³/6, where a is a constant and is the radial distance from the centre of a spiral galaxy, find the ratio (r)/(r), where (r) is the epicyclic frequency and 2(r) is the angular velocity. Enter your answer to 2 decimal places.Which relationship is correct at constant T and P? delta G is proportianal to deltaS of theuniverse?