Classes Of Functional Groups
Organic Chemistry deals mostly with carbon and hydrogens, also called hydrocarbons, but those groups which replace hydrogen and bonds with carbon to give a characteristic nature, unique of their own, to the hydrocarbon they are attached to, are called functional groups. All the compounds belonging to a functional group undergo reactions in a similar pattern and are known to have similar physical and chemical properties.
Characteristics Of Functional Groups
In organic chemistry, we encounter a number of special substituent groups which are attached to the hydrocarbon backbone. These groups impart certain characteristics to the molecule of which it is a part of and thus, become the highlight of that particular molecule.
IUPAC Nomenclature
In Chemistry, IUPAC stands for International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry which suggested a systematic naming approach for the organic and inorganic compounds, as in the beginning stage of nomenclature one single chemical compound was named in many ways by which lead to confusion. The need for this approach aroused as the number of chemical compounds newly discovered were increasing (approximately 32 million compounds) and the basic concept of nomenclature i.e. the trivial nomenclature and the derived system of nomenclature failed to overcome the challenge. It is an important task to name a chemical compound systematically and unambiguously which reduces lots of confusion about the newly reported compounds.
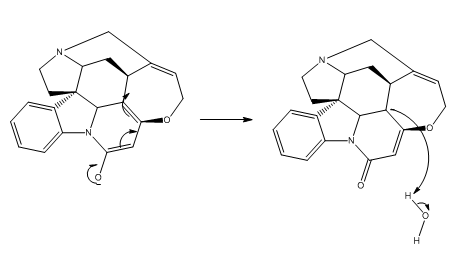
The green pathway: the electrons flow from the negatively charged oxygen atom to the C-O bond, the C=c bond to the C-C bond, the C=C bond to the carbon atom, and the carbon atom to the hydrogen atom than the oxygen atom
(A) I dont understand why is the proton transfer from the hydrogen atom to the oxygen atom needed
(B) I do not understand why cant the electron flow directly from the O - to the oxygen atom in H2O?

Negative charge on electronegative atom is more reasonable (stable) than electropositive atom.
The less stable ion is faster in reaction so the formation of O-H is slower and C-H is faster.
Lowest energy product is more stable than highest energy product.
In organic reactions, the mechanism leads to the formation of lowest energy products.
Therefore, the direction of electron flow to H2O is results the formation of O-H bond and electron flow to C-O, C=C is leads to the formation of C-H bond.
C-H bond has lowest energy and lowest electronegativity difference than O-H bond therefor, the direction of electron flow through C-O, C=C and C-C in the reaction.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images









