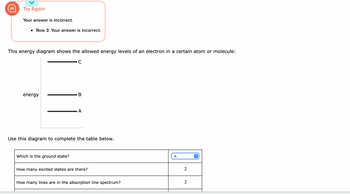
This energy diagram shows the allowed energy levels of an electron in a certain atom or molecule: energy B Which is the ground state? A Use this diagram to complete the table below. How many excited states are there? How many lines are in the absorption line spectrum? Which transition causes the absorption line at the shortest wavelength? Which transition causes the absorption line at the longest wavelength? (pick one) C 0 0 0
Electronic Transitions and Spectroscopy
The term “electronic” connotes electron, and the term “transition” implies transformation. In a molecule, the electrons move from a lower to a higher energy state due to excitation. The two energy states, the ground state and the excited state are the lowest and the highest energy states, respectively. An energy change is observed with this transition, which depicts the various data related to the molecule.
Photoelectron Spectroscopy
Photoelectron spectroscopy (PES) is a part of experimental chemistry. It is a technique used in laboratories that involves projecting intense beams of radiation on a sample element. In response, the element ejects electrons for which the relative energies are measured.

Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images