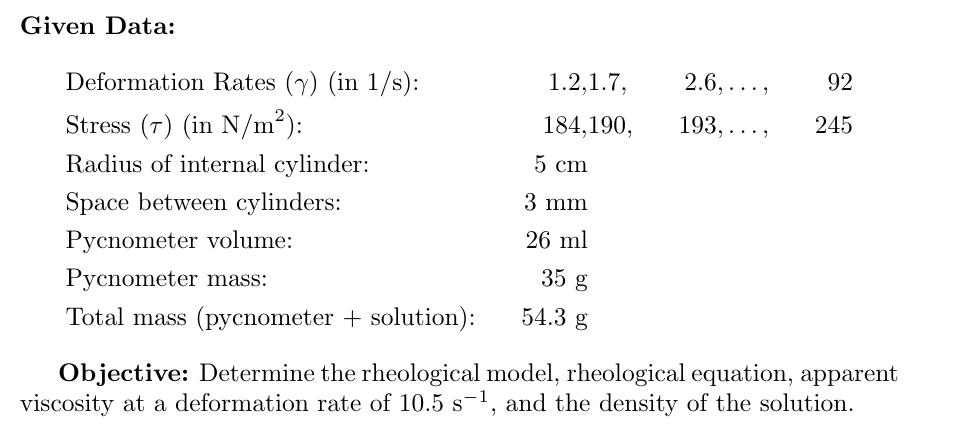
The study of the rheological properties of a solution with an emulsifying additive is carried out in a concentric cylinder viscometer. The radius of the internal cylinder is 5 cm, and the space between both cylinders is 3 mm. Measurements are carried out at 25°C. The equipment software showed the following values: 28 42 62 92 Deformation (1/s) 1.2 1.7 2.6 3.9 5.7 8.5 13 19 Stress (N/m^2) 190 193 203 212 215 219 223 228 233 239 245 184 With the previous data determine: 1. The rheological model (What type of fluid is it?) 2. The rheological equation including the value of the constants of said expression. 3. The value of the apparent viscosity (μ_A = T/y), from the rheological equation, at a deformation of 10.5 s^-1 4. Suppose that you have a sample of the solution under study at 25°C and you need to determine the density using a pycnometer with a volume of 26ml and a mass of 35g. After filling the pycnometer with the solution, the total mass (pycnometer + solution) obtained is 54.3g. Calculate the density of the solution under study in g/m^3.
The study of the rheological properties of a solution with an emulsifying additive is carried out in a concentric cylinder viscometer. The radius of the internal cylinder is 5 cm, and the space between both cylinders is 3 mm. Measurements are carried out at 25°C. The equipment software showed the following values: 28 42 62 92 Deformation (1/s) 1.2 1.7 2.6 3.9 5.7 8.5 13 19 Stress (N/m^2) 190 193 203 212 215 219 223 228 233 239 245 184 With the previous data determine: 1. The rheological model (What type of fluid is it?) 2. The rheological equation including the value of the constants of said expression. 3. The value of the apparent viscosity (μ_A = T/y), from the rheological equation, at a deformation of 10.5 s^-1 4. Suppose that you have a sample of the solution under study at 25°C and you need to determine the density using a pycnometer with a volume of 26ml and a mass of 35g. After filling the pycnometer with the solution, the total mass (pycnometer + solution) obtained is 54.3g. Calculate the density of the solution under study in g/m^3.
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:段階的に解決し、 人工知能を使用せず、 優れた仕事を行います
ご支援ありがとうございました
SOLVE STEP BY STEP IN DIGITAL FORMAT
DON'T USE CHATGPT | DON'T USE CHATGPT DON'T USE CHATGPT
The study of the rheological properties of a solution with an emulsifying additive is carried out in a concentric
cylinder viscometer. The radius of the internal cylinder is 5 cm, and the space between both cylinders is 3 mm.
Measurements are carried out at 25°C. The equipment software showed the following values:
Deformation (1/s) 1.2
Stress (N/m^2) 184
1.7 2.6 3.9 5.7 8.5 13 19 28 42 62 92
190 193 203 212 215 219 223 228 233 239 245
With the previous data determine:
1. The rheological model (What type of fluid is it?)
2. The rheological equation including the value of the constants of said expression.
3. The value of the apparent viscosity (μ_A = T/y), from the rheological equation, at a deformation of 10.5 s^-1
4. Suppose that you have a sample of the solution under study at 25°C and you need to determine the density
using a pycnometer with a volume of 26ml and a mass of 35g. After filling the pycnometer with the solution,
the total mass (pycnometer + solution) obtained is 54.3g. Calculate the density of the solution under study in
g/m^3.
Expert Solution
Step 1: Given data
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY