The null and alternative hypotheses would be: H0:H0: ? μ p Select an answer > < = ≠ H1:H1: ? p μ Select an answer ≠ > = < The test statistic ? z t = (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.) The p-value = (Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.) The p-value is ? > ≤ αα Based on this, we should Select an answer fail to reject reject accept the null hypothesis. Thus, the final conclusion is that ... The data suggest that the population mean is not significantly less than 45,100 at αα = 0.05, so there is statistically insignificant evidence to conclude that the population mean salary for graduates from your college is less than 45,100. The data suggest that the sample mean is not significantly less than 45,100 at αα = 0.05, so there is statistically insignificant evidence to conclude that the sample mean salary for graduates from your college is less than 42,788. The data suggest that the populaton mean is significantly less than 45,100 at αα = 0.05, so there is statistically significant evidence to conclude that the population mean salary for graduates from your college is less than 45,100.
The average salary for American college graduates is $45,100. You suspect that the average is less for graduates from your college. The 50 randomly selected graduates from your college had an average salary of $42,788 and a standard deviation of $5,940. What can be concluded at the αα = 0.05 level of significance?
- For this study, we should use Select an answer t-test for a population
mean z-test for a population proportion - The null and alternative hypotheses would be:
H0:H0: ? μ p Select an answer > < = ≠
H1:H1: ? p μ Select an answer ≠ > = <
- The test statistic ? z t = (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.)
- The p-value = (Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.)
- The p-value is ? > ≤ αα
- Based on this, we should Select an answer fail to reject reject accept the null hypothesis.
- Thus, the final conclusion is that ...
- The data suggest that the population mean is not significantly less than 45,100 at αα = 0.05, so there is statistically insignificant evidence to conclude that the population mean salary for graduates from your college is less than 45,100.
- The data suggest that the sample mean is not significantly less than 45,100 at αα = 0.05, so there is statistically insignificant evidence to conclude that the sample mean salary for graduates from your college is less than 42,788.
- The data suggest that the populaton mean is significantly less than 45,100 at αα = 0.05, so there is statistically significant evidence to conclude that the population mean salary for graduates from your college is less than 45,100.
Concept:
The one-sample t-test is a statistical technique that used to define whether a sample of data could have been produced by a procedure with a precise mean. The one-sample t-test is used when the population standard deviation is not known.
As the population standard deviation is known, we will use a one-sample t-test.
- For this study, we should use a t-test for a population mean
- The null and alternative hypotheses would be:
H0: μ = 45,100
H1: μ < 45,100
The test statistic t can be calculated as:
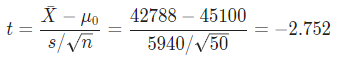
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images









