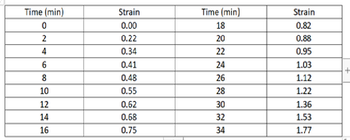
The following creep data were taken on an aluminum alloy at 480 C (900 F) and a constant stress of 2.75 MPa (400 psi). Plot the data as strain versus time, a) then determine the steady-state or minimum creep rate. Note: The initial and instantaneous strain is not included. b) Identify at what time can a secondary creep region occur and at what time would it end to start the tertiary region in a creep curve: (see attachment).
Design Against Fluctuating Loads
Machine elements are subjected to varieties of loads, some components are subjected to static loads, while some machine components are subjected to fluctuating loads, whose load magnitude tends to fluctuate. The components of a machine, when rotating at a high speed, are subjected to a high degree of load, which fluctuates from a high value to a low value. For the machine elements under the action of static loads, static failure theories are applied to know the safe and hazardous working conditions and regions. However, most of the machine elements are subjected to variable or fluctuating stresses, due to the nature of load that fluctuates from high magnitude to low magnitude. Also, the nature of the loads is repetitive. For instance, shafts, bearings, cams and followers, and so on.
Design Against Fluctuating Load
Stress is defined as force per unit area. When there is localization of huge stresses in mechanical components, due to irregularities present in components and sudden changes in cross-section is known as stress concentration. For example, groves, keyways, screw threads, oil holes, splines etc. are irregularities.
- The following creep data were taken on an aluminum alloy at 480 C (900 F) and a constant stress of 2.75 MPa (400 psi). Plot the data as strain versus time,
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Sorry I forgot to add the table. I think the answers will change this time
- The following creep data were taken on an aluminum alloy at 480 C (900 F) and a constant stress of 2.75 MPa (400 psi). Plot the data as strain versus time,