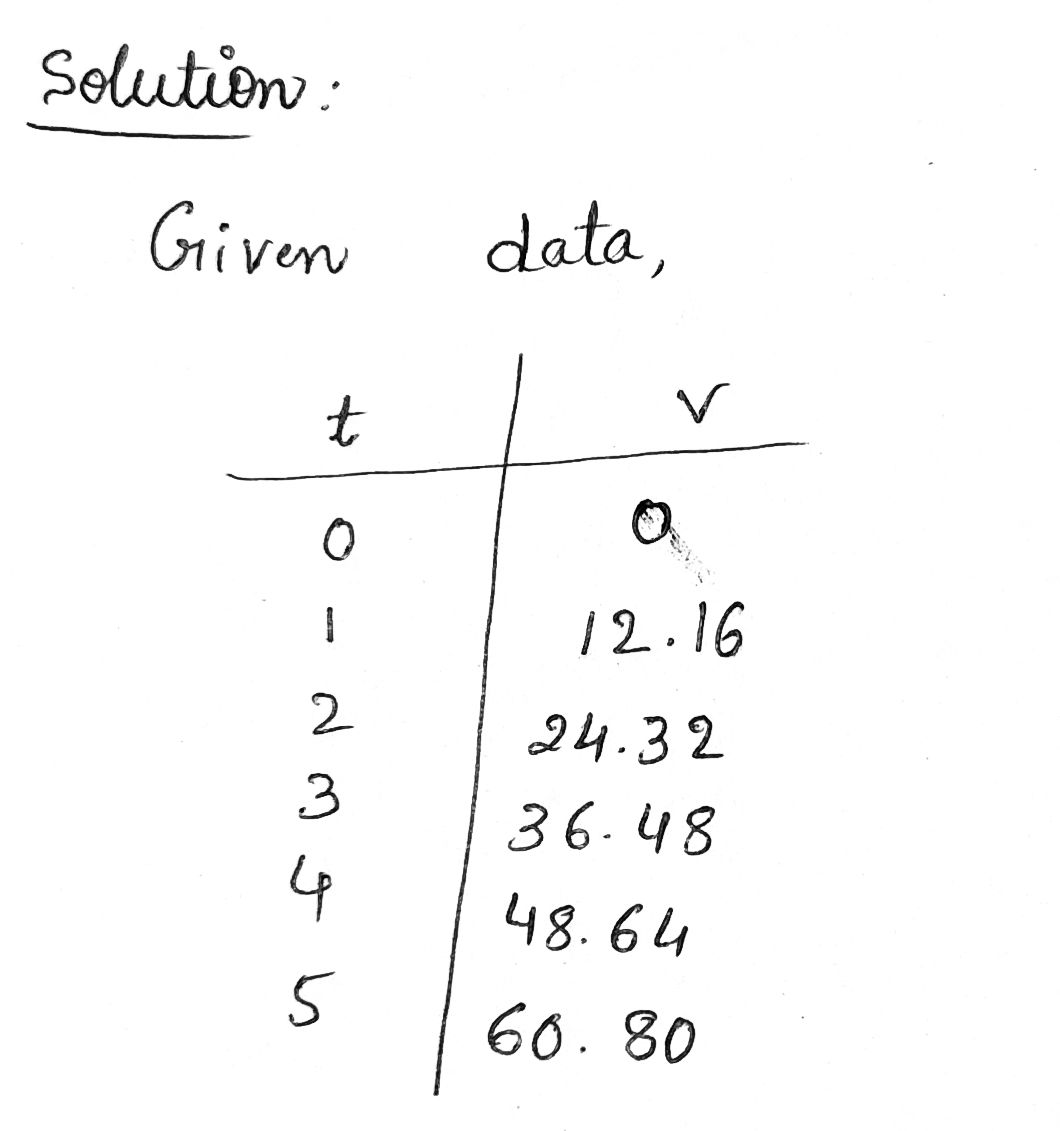
The behavior of objects falling near Earth's surface depends on the mass of Earth. On Mars, a much smaller planet than Earth, things are different. If performed his experiment on Mars, he would have obtained the following table of data. t = seconds V = feet per second 0 12.16 24.32 36.48 48.64 60.80 0 1 2 3 4 5 (a) Show that these data can be modeled by a linear function. For each additional 1 second in time there is ---Select--in speed of Find a formula for the function. V(t) = (b) Calculate V(9). V(9) = Explain in practical terms what your answer means. This means that seconds after the release the velocity of the rock is feet per second. feet per second. (c) Galileo found that the acceleration due to gravity of an object falling near Earth's surface was 32 feet per second per second. Physicists norm denote this number by the letter g. If Galileo had lived on Mars, what value would he have found for g? ft/ser per ser
The behavior of objects falling near Earth's surface depends on the mass of Earth. On Mars, a much smaller planet than Earth, things are different. If performed his experiment on Mars, he would have obtained the following table of data. t = seconds V = feet per second 0 12.16 24.32 36.48 48.64 60.80 0 1 2 3 4 5 (a) Show that these data can be modeled by a linear function. For each additional 1 second in time there is ---Select--in speed of Find a formula for the function. V(t) = (b) Calculate V(9). V(9) = Explain in practical terms what your answer means. This means that seconds after the release the velocity of the rock is feet per second. feet per second. (c) Galileo found that the acceleration due to gravity of an object falling near Earth's surface was 32 feet per second per second. Physicists norm denote this number by the letter g. If Galileo had lived on Mars, what value would he have found for g? ft/ser per ser
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN:9780134463216
Author:Robert F. Blitzer
Publisher:Robert F. Blitzer
ChapterP: Prerequisites: Fundamental Concepts Of Algebra
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1MCCP: In Exercises 1-25, simplify the given expression or perform the indicated operation (and simplify,...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:The behavior of objects falling near Earth's surface depends on the mass of Earth. On Mars, a much smaller planet than Earth, things are different. If Galileo had
performed his experiment on Mars, he would have obtained the following table of data.
t = seconds V = feet per second
0
12.16
24.32
36.48
48.64
60.80
3
0
1
2
3
4
5
(a) Show that these data can be modeled by a linear function.
For each additional 1 second in time there is ---Select--- in speed of
Find a formula for the function.
V(t) =
(b) Calculate V(9).
V(9) =
Explain in practical terms what your answer means.
This means that
seconds after the release the velocity of the rock is
feet per second.
feet per second.
(c) Galileo found that the acceleration due to gravity of an object falling near Earth's surface was 32 feet per second per second. Physicists normally
denote this number by the letter g. If Galileo had lived on Mars, what value would he have found for g?
9=
ft/sec per sec
Expert Solution
Step 1
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Algebra
ISBN:
9780134463216
Author:
Robert F. Blitzer
Publisher:
PEARSON

Contemporary Abstract Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305657960
Author:
Joseph Gallian
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Algebra
ISBN:
9780134463216
Author:
Robert F. Blitzer
Publisher:
PEARSON

Contemporary Abstract Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305657960
Author:
Joseph Gallian
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)
Algebra
ISBN:
9780135163078
Author:
Michael Sullivan
Publisher:
PEARSON

Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth Edition
Algebra
ISBN:
9780980232776
Author:
Gilbert Strang
Publisher:
Wellesley-Cambridge Press

College Algebra (Collegiate Math)
Algebra
ISBN:
9780077836344
Author:
Julie Miller, Donna Gerken
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education