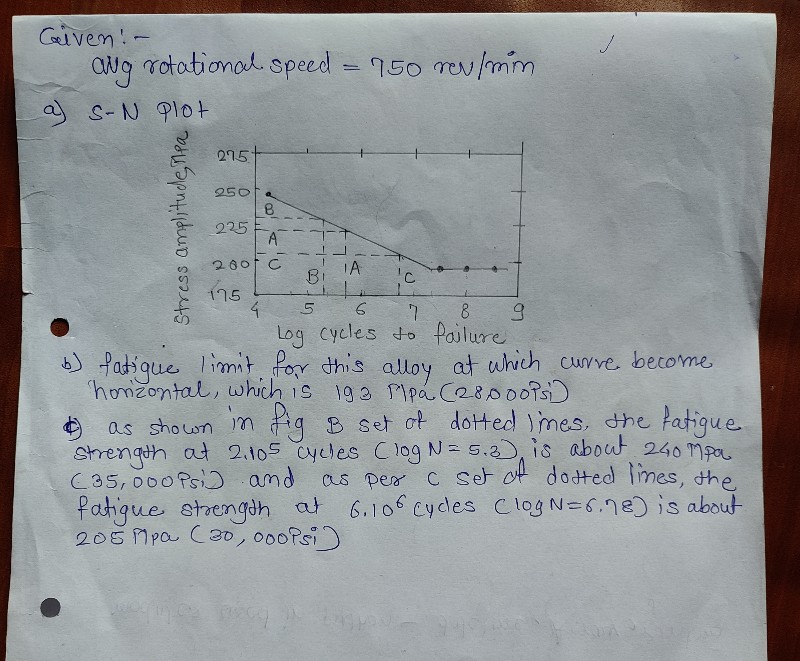
Table 3 shows the fatigue data for a ductile cast iron to be used for an automobile axle that rotates at an average rotational speed of 750 revolutions per minute: Table 3: Fatigue data of a ductile cast iron Cycles to Failure Stress Amplitude (MPa) 248 236 224 213 201 193 193 193 1 X 105 3 X 105 1 X 106 3 X 106 1 X 10² 3 X 10² 1 X 108 3 X 108 a) Make an S-N plot (stress amplitude versus logarithm cycles to failure). b) What is the fatigue limit for this alloy? c) Determine the fatigue lifetimes at stress amplitudes of 230 MPa and 175 MPa?
Design Against Fluctuating Loads
Machine elements are subjected to varieties of loads, some components are subjected to static loads, while some machine components are subjected to fluctuating loads, whose load magnitude tends to fluctuate. The components of a machine, when rotating at a high speed, are subjected to a high degree of load, which fluctuates from a high value to a low value. For the machine elements under the action of static loads, static failure theories are applied to know the safe and hazardous working conditions and regions. However, most of the machine elements are subjected to variable or fluctuating stresses, due to the nature of load that fluctuates from high magnitude to low magnitude. Also, the nature of the loads is repetitive. For instance, shafts, bearings, cams and followers, and so on.
Design Against Fluctuating Load
Stress is defined as force per unit area. When there is localization of huge stresses in mechanical components, due to irregularities present in components and sudden changes in cross-section is known as stress concentration. For example, groves, keyways, screw threads, oil holes, splines etc. are irregularities.
C and D
c) Determine the fatigue lifetimes at stress amplitudes of 230 MPa and 175 MPa?
d) Estimate the maximum lifetime of continuous driving that are allowable for the following 250
MPa and 150 MPa stress levels.

Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









