Suppose you perform the hypothesis test Ho: µ = 90 versus H1:µ < 90. The population variance, o?, is unknown. The sample size is n = 17. Assume the significance level is 0.01. 1) Should you use z or t to find the critical value? Ot Oz 2) Choose the correct critical region. Reject Ho if z > %a Reject Ho if t > ta Reject Ho if z > %a Reject Ho if t > ta Reject Ho if z > %a Reject Ho if t > to OReject Ho if z > za Reject Ho if t > t: OReject Ho if z < Za Reject Ho if t << - ta - Reject Ho if z < Za Reject Ho if t < ta Reject Ho if z < Reject Ho if t < -ta OReject Ho if z < – zg Reject Ho if t < - tg OReject Ho if z < Za or z > za Reject Ho if t < - ta or t > ta | ta or t > ta Reject Ho if t < - ta or t > ta OReject Ho if z < Za or z > za Reject Ho if t < - O Reject Ho if z < Za or z > z: OReject Ho if z < or z 2 z: O Reject Ho if t < - te or t > ta 3) Identify the critical value. If there are multiple critical values, separate them using commas. If using z, round to 2 decimals; if using t, round to 3 decimals". 4) From our collected data, we find that the test statistic value is 1.52. What decision should you make? Reject Ho O Do Not Reject Ho * Note: If you have an answer such as z 2.50, you must type 2.50 instead of 2.5. %3D
Suppose you perform the hypothesis test Ho: µ = 90 versus H1:µ < 90. The population variance, o?, is unknown. The sample size is n = 17. Assume the significance level is 0.01. 1) Should you use z or t to find the critical value? Ot Oz 2) Choose the correct critical region. Reject Ho if z > %a Reject Ho if t > ta Reject Ho if z > %a Reject Ho if t > ta Reject Ho if z > %a Reject Ho if t > to OReject Ho if z > za Reject Ho if t > t: OReject Ho if z < Za Reject Ho if t << - ta - Reject Ho if z < Za Reject Ho if t < ta Reject Ho if z < Reject Ho if t < -ta OReject Ho if z < – zg Reject Ho if t < - tg OReject Ho if z < Za or z > za Reject Ho if t < - ta or t > ta | ta or t > ta Reject Ho if t < - ta or t > ta OReject Ho if z < Za or z > za Reject Ho if t < - O Reject Ho if z < Za or z > z: OReject Ho if z < or z 2 z: O Reject Ho if t < - te or t > ta 3) Identify the critical value. If there are multiple critical values, separate them using commas. If using z, round to 2 decimals; if using t, round to 3 decimals". 4) From our collected data, we find that the test statistic value is 1.52. What decision should you make? Reject Ho O Do Not Reject Ho * Note: If you have an answer such as z 2.50, you must type 2.50 instead of 2.5. %3D
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Suppose you perform the hypothesis test Ho: µ = 90 versus H1:µ < 90. The population variance, o?, is
unknown. The sample size is n = 17. Assume the significance level is 0.01.
1) Should you use z or t to find the critical value?
Ot
Oz
2) Choose the correct critical region.
Reject Ho if z > %a
Reject Ho if t > ta
Reject Ho if z > %a
Reject Ho if t > ta
Reject Ho if z > %a
Reject Ho if t > to
OReject Ho if z > za
Reject Ho if t > t:
OReject Ho if z <
Za
Reject Ho if t << - ta
-
Reject Ho if z <
Za
Reject Ho if t <
ta
Reject Ho if z <
Reject Ho if t < -ta
OReject Ho if z < – zg
Reject Ho if t < - tg
OReject Ho if z <
Za or z > za
Reject Ho if t < - ta or t > ta
|
ta or t > ta
Reject Ho if t < - ta or t > ta
OReject Ho if z <
Za or z > za
Reject Ho if t <
-
O Reject Ho if z <
Za or z > z:
OReject Ho if z <
- 플
or z 2 z:
O Reject Ho if t < - te or t > ta
3) Identify the critical value. If there are multiple critical values, separate them using commas. If using z,
round to 2 decimals; if using t, round to 3 decimals".
4) From our collected data, we find that the test statistic value is 1.52. What decision should you make?
OReject Ho
O Do Not Reject Ho
* Note: If you have an answer such as z
2.50, you must type 2.50 instead of 2.5.
Expert Solution
Step 1
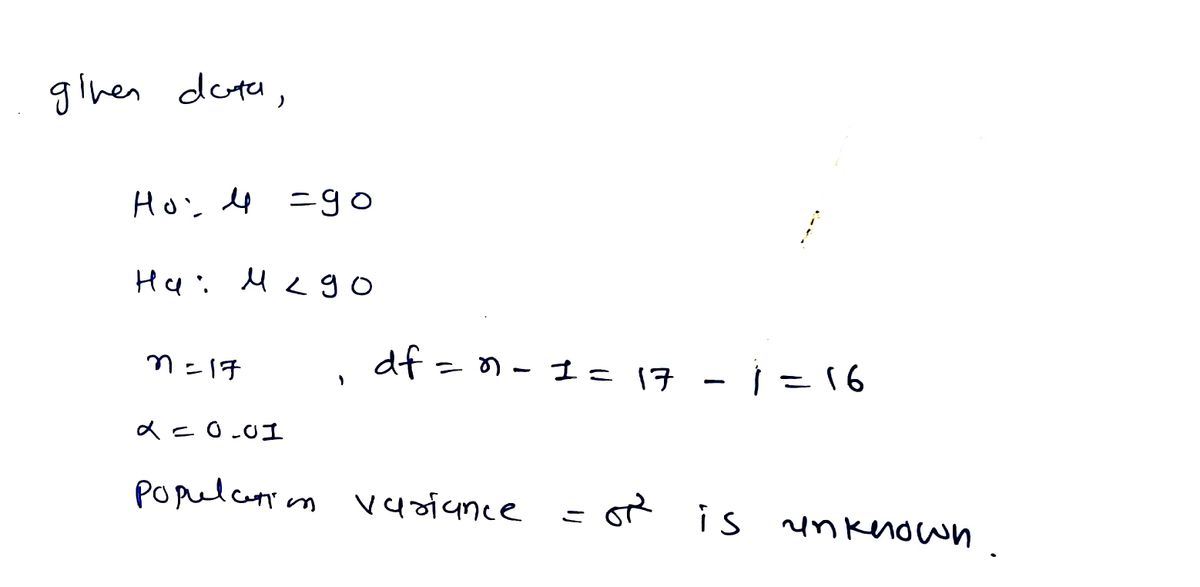
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman