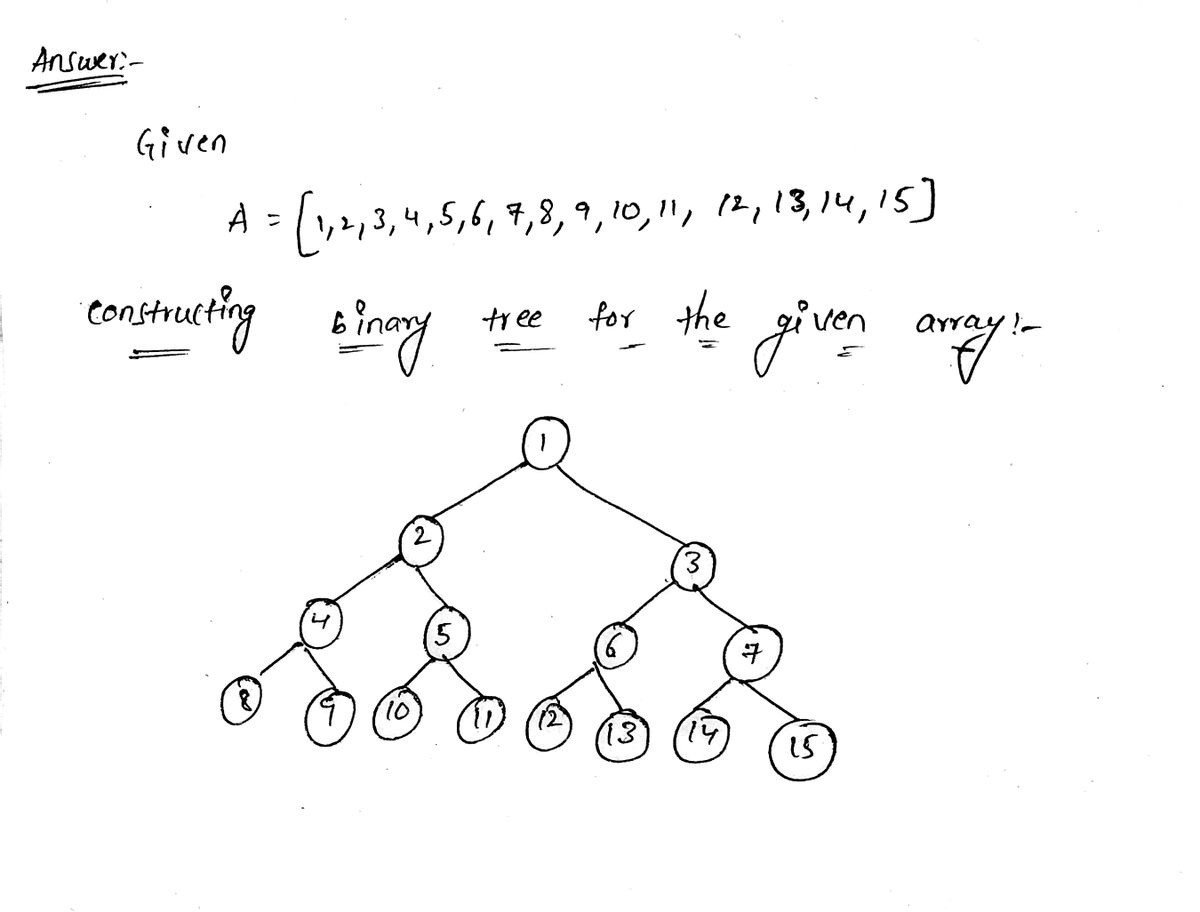
Suppose we want to use the Heapsort algorithm to sort a large list of numbers. Our first step is to convert the input list to a heap, and then run BUILD-MAX-HEAP, which applies MAX-HEAPIFY on all the nodes in the heap, starting at the bottom and moving towards the top. (Think about why we do it bottom-up instead of top-down.) An example is provided on pg. 157 of the textbook. In this example, A = [4,1,3,2,16,9,10,14,8,7]. The end result of BUILD- MAX-HEAP is [16,14,10,8,7,9,3,2,4,1]. I strongly encourage you to go through this example, step by step. A total of 7 swaps are made by BUILD-MAX-HEAP. You can check that the seven swaps occur in this order: (14,2), (10,3), (16,1), (7,1), (16,4), (14,4), (8,4). Here is another way to see this: 2 goes down one level, 3 goes down one level, 1 goes down two levels, and 4 goes down three levels. Adding the underlined numbers, we see that the total number of swaps is 1+1+2+3 = 7. %3D Suppose A = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. Determine BUILD-MAX-HEAP(A), and also determine the total number of swaps.
Suppose we want to use the Heapsort algorithm to sort a large list of numbers. Our first step is to convert the input list to a heap, and then run BUILD-MAX-HEAP, which applies MAX-HEAPIFY on all the nodes in the heap, starting at the bottom and moving towards the top. (Think about why we do it bottom-up instead of top-down.) An example is provided on pg. 157 of the textbook. In this example, A = [4,1,3,2,16,9,10,14,8,7]. The end result of BUILD- MAX-HEAP is [16,14,10,8,7,9,3,2,4,1]. I strongly encourage you to go through this example, step by step. A total of 7 swaps are made by BUILD-MAX-HEAP. You can check that the seven swaps occur in this order: (14,2), (10,3), (16,1), (7,1), (16,4), (14,4), (8,4). Here is another way to see this: 2 goes down one level, 3 goes down one level, 1 goes down two levels, and 4 goes down three levels. Adding the underlined numbers, we see that the total number of swaps is 1+1+2+3 = 7. %3D Suppose A = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. Determine BUILD-MAX-HEAP(A), and also determine the total number of swaps.
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1PE
Related questions
Question
![Suppose we want to use the Heapsort algorithm to sort a large list
of numbers.
Our first step is to convert the input list to a heap, and then run
BUILD-MAX-HEAP, which applies MAX-HEAPIFY on all the nodes
in the heap, starting at the bottom and moving towards the top.
(Think about why we do it bottom-up instead of top-down.)
An example is provided on pg. 157 of the textbook. In this
example, A = [4,1,3,2,16,9,10,14,8,7]. The end result of BUILD-
%3D
MAX-HEAP is [16,14,10,8,7,9,3,2,4,1]. I strongly encourage you
to go through this example, step by step.
A total of 7 swaps are made by BUILD-MAX-HEAP. You can
check that the seven swaps occur in this order: (14,2), (10,3),
(16,1), (7,1), (16,4), (14,4), (8,4).
Here is another way to see this: 2 goes down one level, 3 goes
down one level, 1 goes down two levels, and 4 goes down three
levels. Adding the underlined numbers, we see that the total
number of swaps is 1+1+2+3 = 7.
Suppose A = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15].
Determine BUILD-MAX-HEAP(A), and also determine the total
number of swaps.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fe837985f-2989-4a25-a05d-02efdd5ff4d2%2F305b9c7a-f11c-4cf1-915a-ca2993692f23%2F9uoj8kg_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose we want to use the Heapsort algorithm to sort a large list
of numbers.
Our first step is to convert the input list to a heap, and then run
BUILD-MAX-HEAP, which applies MAX-HEAPIFY on all the nodes
in the heap, starting at the bottom and moving towards the top.
(Think about why we do it bottom-up instead of top-down.)
An example is provided on pg. 157 of the textbook. In this
example, A = [4,1,3,2,16,9,10,14,8,7]. The end result of BUILD-
%3D
MAX-HEAP is [16,14,10,8,7,9,3,2,4,1]. I strongly encourage you
to go through this example, step by step.
A total of 7 swaps are made by BUILD-MAX-HEAP. You can
check that the seven swaps occur in this order: (14,2), (10,3),
(16,1), (7,1), (16,4), (14,4), (8,4).
Here is another way to see this: 2 goes down one level, 3 goes
down one level, 1 goes down two levels, and 4 goes down three
levels. Adding the underlined numbers, we see that the total
number of swaps is 1+1+2+3 = 7.
Suppose A = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15].
Determine BUILD-MAX-HEAP(A), and also determine the total
number of swaps.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780078022159
Author:
Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780134444321
Author:
Tony Gaddis
Publisher:
PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780132737968
Author:
Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:
PEARSON

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780078022159
Author:
Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780134444321
Author:
Tony Gaddis
Publisher:
PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780132737968
Author:
Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:
PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780133976892
Author:
Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:
PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781337627900
Author:
Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education