Q16. Match the following basic kinematic equations to their respective integrated form at constant acceleration: < < v = vo + act 1. v = s = so + vot + act² S v² = v² + 2ac (s − so) 2. a = dv dt ds dt 3. ads - vdv
Q16. Match the following basic kinematic equations to their respective integrated form at constant acceleration: < < v = vo + act 1. v = s = so + vot + act² S v² = v² + 2ac (s − so) 2. a = dv dt ds dt 3. ads - vdv
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:**Title: Matching Kinematic Equations with Their Integrated Forms**
**Question 16:** Match the following basic kinematic equations to their respective integrated form at constant acceleration:
1. **\( v = v_0 + a_c t \)**
2. **\( v^2 = v_0^2 + 2a_c (s - s_0) \)**
3. **\( s = s_0 + v_0 t + \frac{1}{2} a_c t^2 \)**
**Integrated Forms:**
1. **\( v = \frac{ds}{dt} \)**
2. **\( a = \frac{dv}{dt} \)**
3. **\( a\, ds = v\, dv \)**
### Explanation of Diagrams:
- **Equation 1:** Represents the relationship between velocity (\(v\)), initial velocity (\(v_0\)), acceleration (\(a_c\)), and time (\(t\)). It's a linear relation describing how velocity changes over time.
- **Equation 2:** Relates the square of velocity to initial velocity squared, acceleration, and the change in position (\(s\)). It is derived from the work-energy principle and links kinetic energy with distance.
- **Equation 3:** Describes position (\(s\)) over time with constant acceleration. It integrates initial position, initial velocity, and acceleration, providing a quadratic relationship between position and time.
![**Q24.** The buoyancy force on the 580-kg balloon is \( F = 6 \, \text{kN} \), and the air force acting on the balloon is \( \mathbf{F}_{\text{air}} = \left\{ C_1 \cdot t \, \mathbf{i} - C_2 \cdot \sqrt{t} \, \mathbf{j} \right\} \, \text{N} \), when \( t \) is time in seconds, constants \( C_1 = 24 \) and \( C_2 = 240 \). If the balloon starts from rest, determine its speed after 28 seconds. Neglect the size of the balloon but don’t neglect its weight. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point, and proper SI unit. Take \( g = 9.81 \, \text{m/s}^2 \).
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram shows a hot air balloon with colored stripes. It includes the following labels:
- An upward arrow labeled \( F = 6 \, \text{kN} \) indicating the buoyancy force.
- A leftward arrow labeled \( \mathbf{F}_{\text{air}} \) indicating the air force.
- Coordinate axes labeled \( x \) and \( y \).
**Your Answer:**
Answer: [Your calculation here] units](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F73e7c7d8-a37c-4d1e-af6f-0c5c8d6d1088%2Fed34a5dc-e204-44d3-a7e9-09d1b8aae6c6%2Fx4r1ok9_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Q24.** The buoyancy force on the 580-kg balloon is \( F = 6 \, \text{kN} \), and the air force acting on the balloon is \( \mathbf{F}_{\text{air}} = \left\{ C_1 \cdot t \, \mathbf{i} - C_2 \cdot \sqrt{t} \, \mathbf{j} \right\} \, \text{N} \), when \( t \) is time in seconds, constants \( C_1 = 24 \) and \( C_2 = 240 \). If the balloon starts from rest, determine its speed after 28 seconds. Neglect the size of the balloon but don’t neglect its weight. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point, and proper SI unit. Take \( g = 9.81 \, \text{m/s}^2 \).
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram shows a hot air balloon with colored stripes. It includes the following labels:
- An upward arrow labeled \( F = 6 \, \text{kN} \) indicating the buoyancy force.
- A leftward arrow labeled \( \mathbf{F}_{\text{air}} \) indicating the air force.
- Coordinate axes labeled \( x \) and \( y \).
**Your Answer:**
Answer: [Your calculation here] units
Expert Solution
Step 1
as per guideline i have to answer only first question of yours .please repost rest .
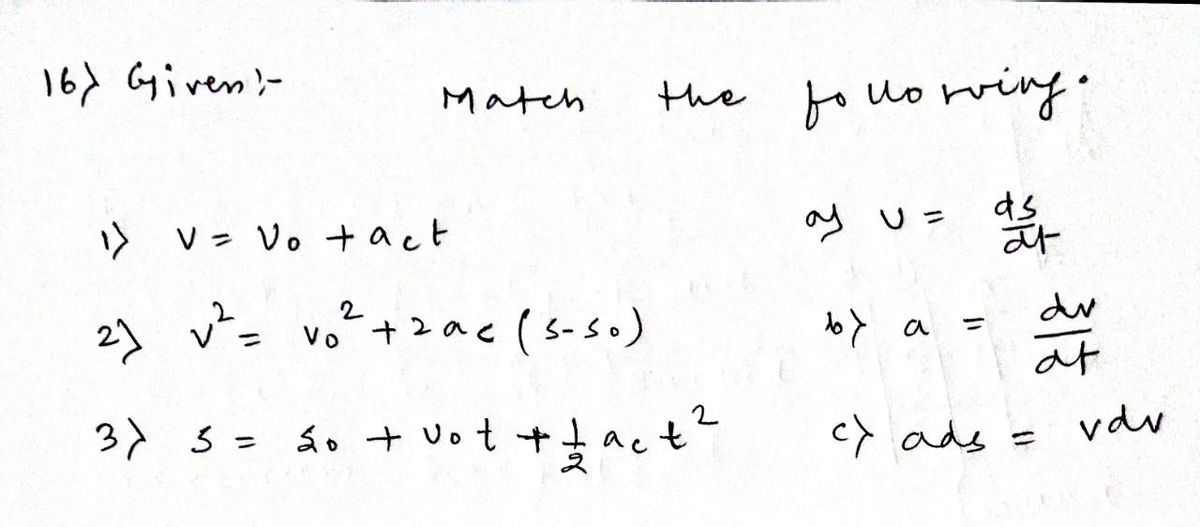
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY