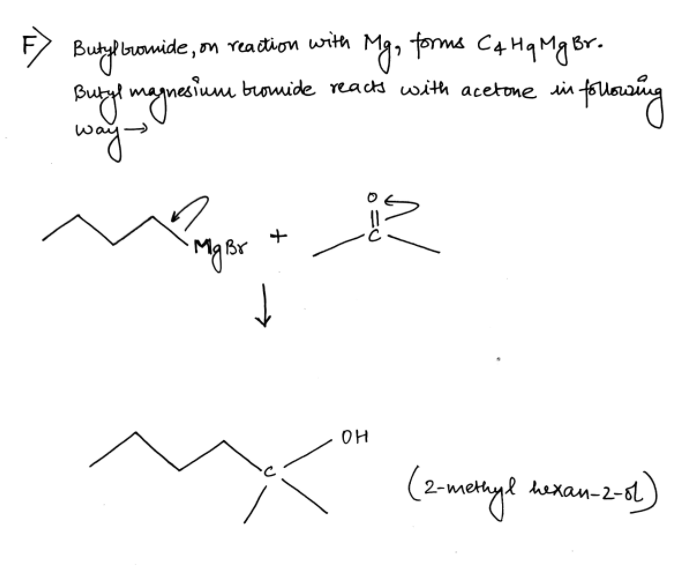
Please answer the question at the bottom, Thanks. LAB NOTES FOR PREPARATION OF BUTYL MAGNESIUM BROMIDE AND ITS SUBSEQUENT CONVERSION TO AN ALCOHOL To the reaction flask were added 2.5967 gram of magnesium turnings, about 20 ml of diglyme, and a solution of 13.5942 gram of butyl bromide in about 25 ml diglyme. The procedure as per the lab manual was initiated. After the required heating time was completed the reaction mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature. Then a solution of 6.1123 gram of acetone in about 15 ml of diglyme was added dropwise as per the lab manual. The rest of the lab manual procedure was completed, ultimately affording 2.5532 gram of an oily, clear and slightly yellow liquid, presumed to be 2-methyl-2- hexanol. Boiling point as measured by distillation was 138 – 141 deg C. About 0.8 ml of the presumed 2-methyl-2-hexanol was placed in an NMR tube to which was added 2 drops of TMS. The tube was capped, then inverted and righted 20 times to thoroughly mix the product and TMS. Subsequently, Proton, Carbon – 13 and DEPT NMR spectra were acquired at the Cumberland Campus using the Anasazi 60MHz FT NMR spectrometer. The IR spectrometer was unavailable. F. Give structure of anticipated product. G. Give structure of obtained product. Structure is attatched. H. Are “F” and “G” the same?
Catalysis and Enzymatic Reactions
Catalysis is the kind of chemical reaction in which the rate (speed) of a reaction is enhanced by the catalyst which is not consumed during the process of reaction and afterward it is removed when the catalyst is not used to make up the impurity in the product. The enzymatic reaction is the reaction that is catalyzed via enzymes.
Lock And Key Model
The lock-and-key model is used to describe the catalytic enzyme activity, based on the interaction between enzyme and substrate. This model considers the lock as an enzyme and the key as a substrate to explain this model. The concept of how a unique distinct key only can have the access to open a particular lock resembles how the specific substrate can only fit into the particular active site of the enzyme. This is significant in understanding the intermolecular interaction between proteins and plays a vital role in drug interaction.
Please answer the question at the bottom, Thanks.
LAB NOTES FOR PREPARATION OF BUTYL MAGNESIUM BROMIDE
AND ITS SUBSEQUENT CONVERSION TO AN ALCOHOL
To the reaction flask were added 2.5967 gram of magnesium turnings, about 20 ml
of diglyme, and a solution of 13.5942 gram of butyl bromide in about 25 ml
diglyme.
The procedure as per the lab manual was initiated. After the required heating time
was completed the reaction mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature.
Then a solution of 6.1123 gram of acetone in about 15 ml of diglyme was added
dropwise as per the lab manual.
The rest of the lab manual procedure was completed, ultimately affording 2.5532
gram of an oily, clear and slightly yellow liquid, presumed to be 2-methyl-2-
hexanol. Boiling point as measured by distillation was 138 – 141 deg C.
About 0.8 ml of the presumed 2-methyl-2-hexanol was placed in an NMR tube to
which was added 2 drops of TMS. The tube was capped, then inverted and righted
20 times to thoroughly mix the product and TMS.
Subsequently, Proton, Carbon – 13 and DEPT NMR spectra were acquired at the
Cumberland Campus using the Anasazi 60MHz FT NMR spectrometer.
The IR spectrometer was unavailable.
F. Give structure of anticipated product.
G. Give structure of obtained product. Structure is attatched.
H. Are “F” and “G” the same?

Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









