Calculate the pressure exerted by 1.0 mol C2H6 behaving as (a) a perfect gas, (b) a van der Waals gas when it is confined under the fol lowing conditions: (i) at 273.15 K in 22.414 dm3 , (ii) at 1000 K in 100 cm3. Use the data given.

The perfect gas is an ideal gas that obeys the ideal gas law. It defines as the one in which the collision between the molecules is perfectly elastic. The formula for an ideal gas is shown below, where P is pressure, V is volume, n is a number of moles. R is the gas constant whose value is 0.0821 l.atm/k.mol, and T is the temperature in kelvin.
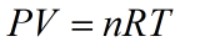
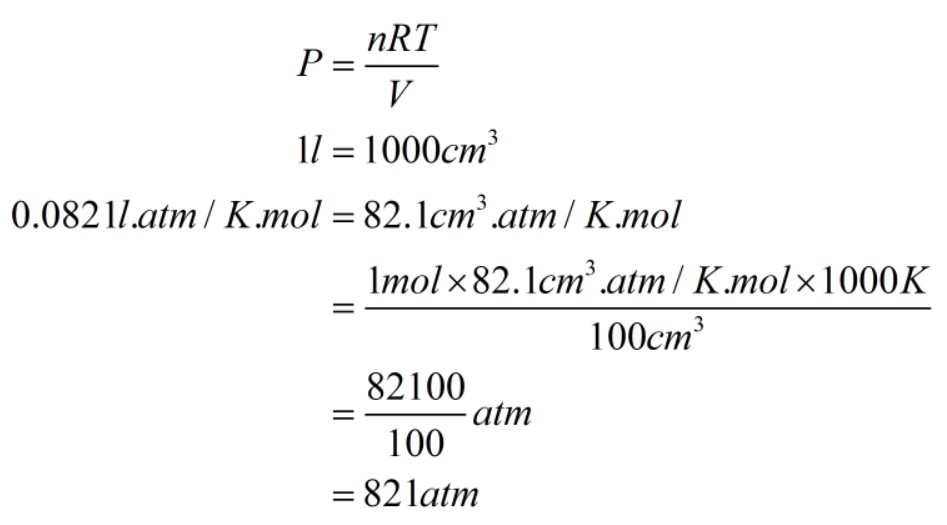
1- The pressure was calculated by substituting values given in the first part. The temperature is given as 273.15 kelvin, and the volume is 22.414 dm3.

Similarly, the second part is calculated where the temperature 1000 kelvin and volume is 100 cm3.
The van der Waal equation which is used in chemistry and thermodynamics is the equation of state which generalizes the perfect gas equation as the real gases can not act ideally. The formula of van der Waal is :
.jpg)
The value of gas constant a and b are calculated form-critical volume and critical temperature. The critical volume is 3b and the formula of critical temperature is mentioned below from where "a" is calculated.
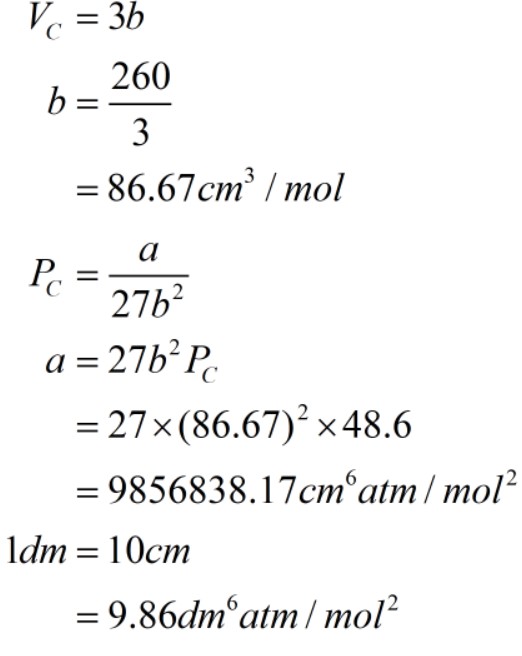
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 7 images









