Mars, r-0.58 m, 0-140° Earth, r-0.49 m, 0-20° Mercury, r-0.26 m, 0-42° Neptune, r-3.30 m, 6--15° Saturn, r=1.70 m, -138° 9. OSU has been given a large model of the solar system which consists of hollow Styrofoam spheres of different sizes representing the Sun and planets. The planets are all connected to the center of the sun by means of steel rods of varying lengths and at varying angles relative to the x-axis as shown above. The steel rods are all 0.5 cm in diameter and are made of steel having a density of 7.88 g/cm'. We'd like the position of the Sun. Find the center of mass of the model (direction and angle) relative to the Sun in the center of the model. The Styrofoam spheres are so much lighter in comparison to the rods, that their mass can be neglected. Hint: calculate the center of mass for the x and y dimensions separately, to suspend the model from it's center of mass, but it doesn't look like the center of mass coincides with then combine them to get the final answer. Pluto, r=3.53 m, 116° Uranus, r-2.65 m, 0-65° Jupiter, r-0.95 m, 0=-6: Venus, r-0.36 m, 0-120°
Fluid Pressure
The term fluid pressure is coined as, the measurement of the force per unit area of a given surface of a closed container. It is a branch of physics that helps to study the properties of fluid under various conditions of force.
Gauge Pressure
Pressure is the physical force acting per unit area on a body; the applied force is perpendicular to the surface of the object per unit area. The air around us at sea level exerts a pressure (atmospheric pressure) of about 14.7 psi but this doesn’t seem to bother anyone as the bodily fluids are constantly pushing outwards with the same force but if one swims down into the ocean a few feet below the surface one can notice the difference, there is increased pressure on the eardrum, this is due to an increase in hydrostatic pressure.
OSU has been given a large model of the solar system which consists of hollow Styrofoam spheres of different sizes representing the Sun and planets. The planets are all connected to the center of the sun by means of steel rods of varying lengths and at varying angles relative to the x-axis as shown above. The steel rods are all 0.5 cm in diameter and are made of steel having a density of 7.88 g/cm3. We’d like to suspend the model from it’s center of mass, but it doesn’t look like the center of mass coincides with the position of the Sun.
Find the center of mass of the model (direction and angle) relative to the Sun in the center of the model. The Styrofoam spheres are so much lighter in comparison to the rods, that their mass can be neglected. Hint: calculate the center of mass for the x and y dimensions separately, then combine them to get the final answer

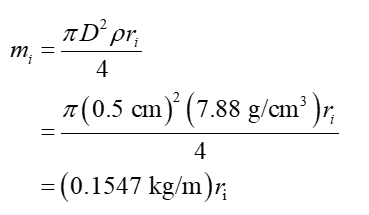
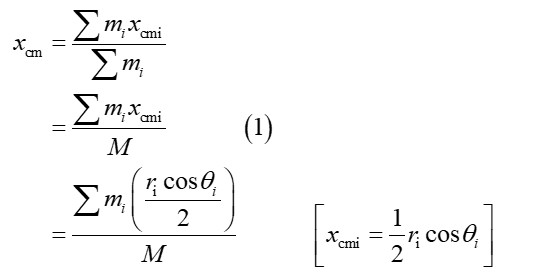
The center of mass of a rod with uniform density is at its geometric center.
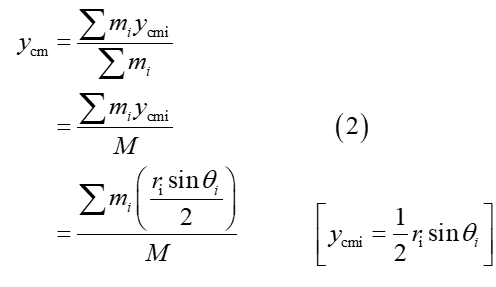
|
Planet |
ri (m) |
mi (kg) |
θi (°) |
mixi (kg.m) |
miyi (kg.m) |
|
Mercury |
0.26 |
0.04022 |
-42 |
0.003887 |
-0.00350 |
|
Venus |
0.36 |
0.05569 |
-120 |
-0.005003 |
-0.00869 |
|
Earth |
0.49 |
0.0758 |
20 |
0.017453 |
0.00635 |
|
Mars |
0.58 |
0.08973 |
140 |
-0.019912 |
0.01675 |
|
Jupiter |
0.95 |
0.14697 |
-65 |
0.029539 |
-0.06325 |
|
Saturn |
1.7 |
0.26299 |
-138 |
-0.165941 |
-0.14978 |
|
Uranus |
2.65 |
0.40996 |
65 |
0.229845 |
0.49217 |
|
Neptune |
3.3 |
0.51051 |
-15 |
0.813668 |
-0.21791 |
|
Pluto |
3.53 |
0.54609 |
116 |
-0.421635 |
0.86674 |
|
Total |
2.13795 |
0.481901 |
0.93888 |
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 8 steps with 7 images









