As we will learn, many antioxidants–compounds that prevent unwanted radical oxidation reactions from occurring–are phenols, compounds that contain an OH group bonded directly to a benzene ring.
a.) Explain why homolysis of the O–H bond in phenol requires
considerably less energy than homolysis of the O–H bond in ethanol
(362 kJ/mol vs. 438 kJ/mol).
b.) Why is the C–O bond in phenol shorter than the C–O bond in ethanol?

Resonance structure:
The representation of delocalized electrons in a molecule by means of different structures gives rise to what is called resonance structures.
If a compound has a greater number of resonance structures, it has a greater stability and vice versa.
Answer to (a)-
The homolysis of bond in phenol gives phenoxide ion ( fig-1 ) and in the case of ethanol, it gives the ethanolate ion ( fig - 2 ).
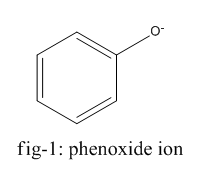
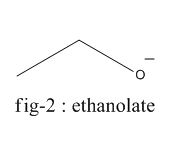
Phenoxide ion is highly stable by resonance and can be represented by the following diagram (fig-3) whereas ethanolate ion cannot undergo resonance.
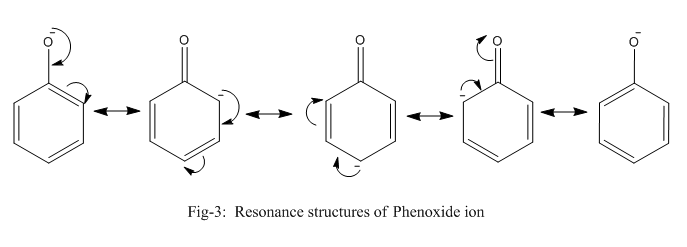
Thus, even after breaking the bond between oxygen and hydrogen, phenol is stable which is not the case of ethanol. Thus, the bond in ethanol is stronger and requires more energy to break than phenol which requires comparatively lesser energy.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images









