For students who first enrolled in two year public institutions in a recent semester, the proportion who earned a bachelor's degree within six years was 0.386. The president of a certain junior college believes that the proportion of students who enroll in her institution have a higher completion rate (a) State the null and alternative hypotheses in words (b) State the null and alterative hypotheses symbolically (c) Explain what it would mean to make a Type I error (d) Explain what it would mean to make a Type Il error (a) State the null hypothesis in words. Choose the correct answer below OA. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is greater than OB. Among students who first enroll in two-year public institutions, the completion rate is 0.386. OC. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is 0.386. OD. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is less than 0.386. 386 (
For students who first enrolled in two year public institutions in a recent semester, the proportion who earned a bachelor's degree within six years was 0.386. The president of a certain junior college believes that the proportion of students who enroll in her institution have a higher completion rate (a) State the null and alternative hypotheses in words (b) State the null and alterative hypotheses symbolically (c) Explain what it would mean to make a Type I error (d) Explain what it would mean to make a Type Il error (a) State the null hypothesis in words. Choose the correct answer below OA. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is greater than OB. Among students who first enroll in two-year public institutions, the completion rate is 0.386. OC. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is 0.386. OD. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is less than 0.386. 386 (
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:For students who first enrolled in two year public institutions in a recent semester, the proportion who earned a bachelor's degree within six years was 0.386. The president of a certain junior college believes that the
proportion of students who enroll in her institution have a higher completion rate.
(a) State the null and alterative hypotheses in words
(b) State the null and alternative hypotheses symbolically
(c) Explain what it would mean to make a Type 1 error
(d) Explain what it would mean to make a Type Il error
(a) State the null hypothesis in words. Choose the correct answer below
OA. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is greater than 0.386.
OB. Among students who first enroll in two-year public institutions, the completion rate is 0.386.
OC. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is 0.386.
OD. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is less than 0.386.
(C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 1 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Transcribed Image Text:For students who first enrolled in two-year public institutions in a recent semester, the proportion who earned a bachelor's degree within six years was 0.386. The president of a certain junior college believes that the proportion of students who enroll at her institution has a higher completion rate.
**(a) State the null and alternative hypotheses in words.**
* Choose the correct answer below:
- A. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is greater than 0.386. (Correct option selected)
- B. Among students who first enroll in two-year public institutions, the completion rate is 0.386.
- C. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is 0.386.
- D. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is less than 0.386.
**(b) State the hypotheses symbolically.**
- \( H_0: P = 0.386 \)
- \( H_1: P > 0.386 \)
**(c) Explain what it would mean to make a Type I error.**
- The president **rejects** the hypothesis that the proportion of students who earn a bachelor's degree within six years is equal to 0.386 when, in fact, the proportion is equal to 0.386.
**(d) Explain what it would mean to make a Type II error.**
- The president **fails to reject** the hypothesis that the proportion of students who earn a bachelor's degree within six years is equal to 0.386 when, in fact, the proportion is greater.
The exercise involves understanding hypothesis testing, where the null hypothesis (\(H_0\)) assumes a completion rate of 0.386, and the alternative hypothesis (\(H_1\)) proposes a higher completion rate for the junior college. Making a Type I error involves incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis, while a Type II error involves failing to reject the null hypothesis when it is false.
Solution
Follow-up Question
Transcribed Image Text:### Statistical Hypothesis Testing: Understanding Null and Alternative Hypotheses
#### Context
For students who first enrolled in two-year public institutions in a recent semester, the proportion who earned a bachelor's degree within six years was 0.386. The president of a certain junior college believes that the proportion of students enrolling at her institution has a higher completion rate.
#### Tasks
(a) **State the null and alternative hypotheses in words:**
The alternative hypothesis statement is:
- A. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is greater than 0.386.
(b) **State the hypotheses symbolically:**
- Null Hypothesis (H₀): \( P = 0.386 \)
- Alternative Hypothesis (H₁): \( P > 0.386 \)
(c) **Explain what it would mean to make a Type I error:**
A Type I error occurs when the president rejects the null hypothesis that the proportion of students who earn a bachelor's degree within six years is equal to 0.386, when, in fact, the proportion is 0.386.
(d) **Explain what it would mean to make a Type II error:**
A Type II error occurs when the president fails to reject the null hypothesis that the proportion of students who earn a bachelor's degree within six years is equal to 0.386, when, in fact, the proportion is greater than 0.386.
#### Conclusion
Understanding Type I and Type II errors is crucial for interpreting results in hypothesis testing. A Type I error involves rejecting a true null hypothesis, while a Type II error involves failing to reject a false null hypothesis.
Solution
Follow-up Question
![For students who first enrolled in two-year public institutions in a recent semester, the proportion who earned a bachelor's degree within six years was 0.386. The president of a certain junior college believes that the proportion of students who enroll in her institution have a higher completion rate.
(a) State the null and alternative hypotheses in words.
(b) State the null and alternative hypotheses symbolically.
(c) Explain what it would mean to make a Type I error.
(d) Explain what it would mean to make a Type II error.
**Given Information:**
**Null Hypothesis (in words):**
B. Among students who first enroll in two-year public institutions, the completion rate is 0.386.
C. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is 0.386.
D. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is less than 0.386.
**Alternative Hypothesis (in words):**
Choose the correct answer below:
A. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is greater than 0.386.
B. Among students who first enroll in two-year public institutions, the completion rate is 0.386.
C. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is 0.386.
D. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is less than 0.386.
**(b) State the hypotheses symbolically:**
- \( H_0 : p = 0.386 \)
- \( H_1 : p > 0.386 \)
**(c) What would it mean to make a Type I error?**
**(d) What would it mean to make a Type II error?**
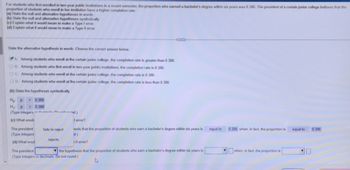
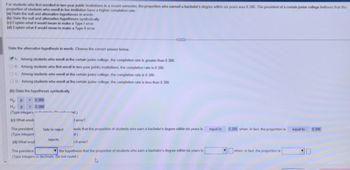
The president [rejects/fails to reject] the hypothesis that the proportion of students who earn a bachelor's degree within six years is [box for input] when, in fact, the proportion is [box for input]. (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.)](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/ac3be618-b645-4bd8-855b-808ff3fc18d4/c783de1b-a1f6-4f9f-be41-2f30a8a62b85/7w1pnr_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:For students who first enrolled in two-year public institutions in a recent semester, the proportion who earned a bachelor's degree within six years was 0.386. The president of a certain junior college believes that the proportion of students who enroll in her institution have a higher completion rate.
(a) State the null and alternative hypotheses in words.
(b) State the null and alternative hypotheses symbolically.
(c) Explain what it would mean to make a Type I error.
(d) Explain what it would mean to make a Type II error.
**Given Information:**
**Null Hypothesis (in words):**
B. Among students who first enroll in two-year public institutions, the completion rate is 0.386.
C. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is 0.386.
D. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is less than 0.386.
**Alternative Hypothesis (in words):**
Choose the correct answer below:
A. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is greater than 0.386.
B. Among students who first enroll in two-year public institutions, the completion rate is 0.386.
C. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is 0.386.
D. Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is less than 0.386.
**(b) State the hypotheses symbolically:**
- \( H_0 : p = 0.386 \)
- \( H_1 : p > 0.386 \)
**(c) What would it mean to make a Type I error?**
**(d) What would it mean to make a Type II error?**
The president [rejects/fails to reject] the hypothesis that the proportion of students who earn a bachelor's degree within six years is [box for input] when, in fact, the proportion is [box for input]. (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.)
Solution
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:**Hypothesis Testing for Junior College Completion Rates**
For students who first enrolled in two-year public institutions in a recent semester, the proportion who earned a bachelor's degree within six years was 0.386. The president of a certain junior college believes that the proportion of students who enroll in her institution have a higher completion rate.
(a) **State the null and alternative hypotheses in words:**
- **Null Hypothesis (H₀):** Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is 0.386.
- **Alternative Hypothesis (H₁):** Among students who enroll at the certain junior college, the completion rate is greater than 0.386.
(b) **State the hypotheses symbolically:**
- H₀: p = 0.386
- H₁: p > 0.386
(c) **Explain what it would mean to make a Type I error:**
A Type I error would mean rejecting the null hypothesis when it is actually true. In this context, it would imply concluding that the junior college’s completion rate is higher than 0.386, when in reality, it is not.
(d) **Explain what it would mean to make a Type II error:**
A Type II error would mean failing to reject the null hypothesis when the alternative hypothesis is true. This would indicate not recognizing that the junior college's completion rate is indeed higher than 0.386, even though it is.
**Note on Diagrams or Graphs:**
There are boxes provided to symbolically denote the null and alternative hypotheses with symbols for correctness verification.
Solution
Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman