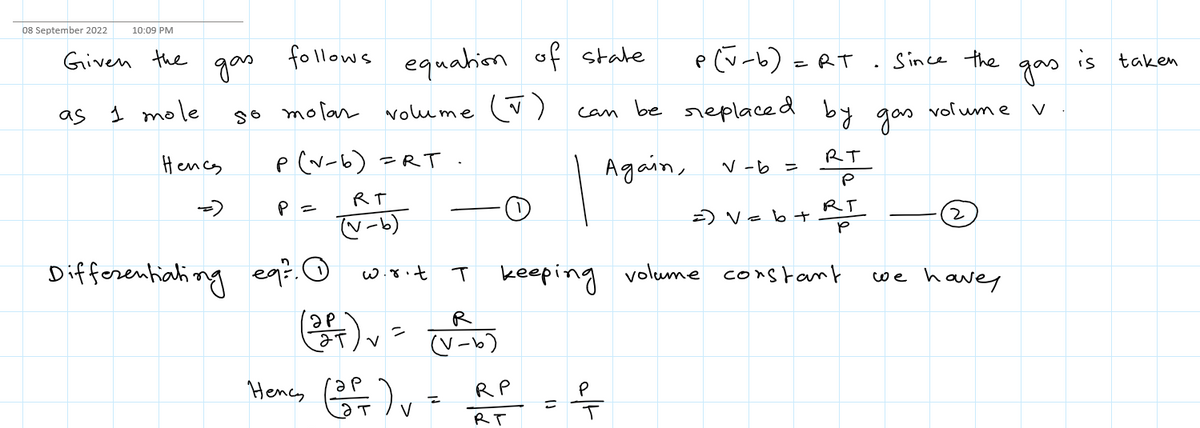
For any gas, =T (7), (7), Suppose you have one mole of a gas that obeys the equation of state, P(V-b) = represents the volume taken up by the molecules in the system, and 3.5 bars and T = 425 K for your gas sample. Hint: Use the equation of state to evaluate the partial derivatives. =RT, where b is the molar volume. Find the value of A if C₂-C=AR when P =
Q: 1.50 moles of a monatomic ideal gas goes isothermally from state 1 to state 2. P1 = 2.8×105 Pa, V1 =…
A:
Q: Calculate the internal energy, Uinternal -in Joules- of 3.2 moles of a monoatomic gas, if Cv,…
A: The solution for this question has been solved below...
Q: A sealed 19 m3 tank is filled with 7,011 moles of ideal oxygen gas (diatomic) at an initial…
A: The objective of this question is to calculate the final pressure of the gas in the tank after it…
Q: What is the molar mass of a gas if 1.30g of the gas has a volume of 255 mL at STP?
A: For ideal gas PV = nRT Where P = Pressure of the gas, V = Volume of the gas, n = number of moles of…
Q: A sample of 3 mol of diatomic gas is measured to have a temperature of 300 K. If the mass of the gas…
A: Given data-
Q: There are lots of examples of ideal gases in the universe, and they exist in many different…
A: " Since you have asked Multiple Question, we will solve the First three parts of the Question for…
Q: A bottle of volume V = 0.15 m³ contains helium gas (a monatomic gas) at a pressure p = 722,266 Pa…
A:
Q: Suppose P (V, T) gives the pressure P (in N/m² ) of a gas at a volume V (in m³) and temperature T…
A: Pressure(P) is defined as force(F) per unit area(A). ⇒P = FA where, Force (F) is…
Q: One mole of oxygen gas is at a pressure of 6 atm and a temperature of 27 °C. (a) If the gas is…
A:
Q: A sample of an ideal gas is compressed and cooled as it is taken from state 1 to state 2. The given…
A: The given values are listed below. P1=94 kPaV1=0.05 m3V2=0.04 m3T1=300 KT2=260 K
Q: Suppose that the average speed (vm) of carbon dioxide molecules (molar mass 44.0 g/mol) in a flame…
A:
Q: A closed 1 L water bottle contains air at standard temperature and pressure. The bottle is left in a…
A:
Q: A gas consists of NO2 molecules at temperature T. What is the r.m.s. speed of the molecules, in m/s?…
A: Given data : The mass of an NO2 molecule, m=1.53×10-26kg Temperature, T=10oC=(10+273)K=283K
Q: P = 25 uc/m³ is distributed uniformly through a certain region. If V = 50 at y = 2 and V=< 90 at y =…
A: Given the volume charge density = 25 micro.C/m3Voltage, V = 50 at y = 2V = 90 at y=5 ɛr= 2
Q: One cubic meter (1 m³) of mono-atomic ideal gas, is initially at room temperature and atmo- spheric…
A: Hello, since your question has multiple sub-parts, we will solve the first three sub-parts for you.…
Q: igure N 4- 3 2- 1 0 ilı. 4 6 8 2 v (m/s) What is the most probable speed? Express your answer with…
A:
Q: Using a numerical integration method such as Simpson’s rule, find the fraction of molecules in a…
A:
Q: Number of molecules in 8.467x10-2 mol C6H6. nificant
A: no of molecules =no of moles of substance(Na)where Na is 6.023x1023 thus,no of…
Q: Consider an ideal gas at temperature T = 578 K and pressure p = 2 atm. Calculate the average volume…
A:
Q: The mean free path λ and the mean collision time T of molecules of a diatomic gas with molecular…
A:
Q: When air expands adiabatically (without gaining or losing heat), its pressure P and volume V are…
A: Given data:
Q: 7. Now suppose that the box contains 1023 gas molecules. Use your formula to calculate the…
A:
Q: The following empirical equation correlates the values of variables in a system in which solid…
A:
Q: The mean free path of a molecule in a gas is 310 nm ▼ What is the mean free path if the gas…
A: Solution Given data Mean free path of molecule in gas λ=310nm=310×10−9mWhat is mean free path if…
Q: λ=kT/21/2σp is the equation of mean free path. What is the relation of mean free path to…
A: Given: The equation of mean free path as λ=kT/21/2σp k is boltzmann constant, T is the temperature,…
Q: The vapor pressure of Substance X is measured at several temperatures: temperature vapor pressure…
A: Given data: The pressure at T1=273-47=226 K is P1=0.0484 atm The pressure at T2=273-35=238 K is…
Q: Suppose that a gas obeys at low pressures the equation PVm = RT + (A+ B/T2)P where A and B are…
A: Given PVm = RT + (A+ B/T2)P where A and B are constants independent of pressure We have to Derive…
Q: Consider a pressure versus volume graph, where the different curves represent different processes…
A:
Q: what is is the mass of air in grams
A: Given data: The volume of automobile tire is: V = 2.5×10-2 m3 The pressure of air in the tire is: P…
Q: An ideal gas that occupies 1.2m³ at a pressure of 1 x 10⁵ Pa and a temperature of 27C is compressed…
A:
Q: The temperature at state A is 20.0ºC, that is 293 K. How many moles of ideal gas is there in the…
A: Here, at A P = 4 atm = 4×105 Pa V = 1 m3 T = 20+273 = 293 K
Q: The volume of an automobile tire is 2.5 × 10−2m3 . the pressure of the air in the tire is 3 atm and…
A: According to ideal gas law - Where P = Pressure V = Volume n = Number of moles T = Temperature…
Q: The volume of an automobile tire is 2.5x10^-2m^3. The pressure of the air in the tire is 3.3 atm and…
A: Given that---- volume of automobile tire = 2.5 × 10 -2. pressure of air in tire 3.3 atm…
Q: How many moles are there in a cubic meter of an ideal gas at 100 degree celsius (C) to 4 digits of…
A: Volume of ideal gas (V) = 1 m3Temperature (T) = 100oC = 100+273.15 k = 373.15 k Pressure (P) = 0.25…

Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

- The tidal lung volume of human breathing, representing the amount of air inhaled and exhaled in a normal breath, is 500 cm³. (Assume atmospheric pressure.) (a) What is the number of molecules of air inhaled with each human breath when the air temperature is 25.0°C? molecules (b) If the molar mass of air is 28.96 g/mol, what is the mass (in g) of air molecules inhaled with each breath? (Assume the air temperature is 25.0°C.) g (c) It has been calculated that all of the air in Earth's atmosphere could be collected into a sphere of diameter 1,999 km at a pressure of 1.00 atm. What is the mass (in kg) of the air in Earth's atmosphere? (Assume the density of air used in this calculation was 1.225 kg/m³.) kg (d) If all 7 billion humans on Earth inhaled simultaneously, what percentage of the atmosphere would be inhaled during this process? (Assume the air temperature is 25.0°C everywhere on Earth.) %Please help meThe gas law for an ideal gas at absolute temperature T (in kelvins), pressure P (in atmospheres), and volume V (in liters) is PV = nRT, where n is the number of moles of the gas and R = 0.0821 is the gas constant. Suppose that, at a certain instant, P = 9.0 atm and is increasing at a rate of 0.15 atm/min and V = 13 L and is decreasing at a rate of 0.17 L/min. Find the rate of change of T with respect to time at that instant if n = 10 mol. (Round your answer to four decimal places.) dT=0.512 dt X K/min
- A sealed 19 m3 tank is filled with 7,011 moles of ideal oxygen gas (diatomic) at an initial temperature of 292 K The gas is heated to a final temperature of 490 K. The atomic mass of oxygen is 16.0 g/mol. The final pressure of the gas, in MPa, is closest to: answer round to 4 sig.fign = 3.9 moles of an ideal gas are pumped into a chamber of volume V = 0.135 m3 Part (a) The initial pressure of the gas is 1 atm. What is the initial temperature (in K) of the gas? Part (b) The pressure of the gas is increased to 10 atm. Now what is the temperature (in K) of the gasIf gas pressure (absolute value) for an ideal gas is held constant, the relationship between gas temperature and volume is direct inverse of the form y = mx + c O parabolic
- n = 3.9 moles of an ideal gas are pumped into a chamber of volume V = 0.135 m3 50% Part (a) The initial pressure of the gas is 1 atm. What is the initial temperature (in K) of the gas? T = 421.76T = 421.8 ✔ Correct! 50% Part (b) The pressure of the gas is increased to 10 atm. Now what is the temperature (in K) of the gas?The gas law for an ideal gas at absolute temperature T (in kelvins), pressure P (in atmospheres), and volume V (in liters) is PV = nRT, where n is the number of moles of the gas and R = 0.0821 is the gas constant. Suppose that, at a certain instant, P = 7.0 atm and is increasing at a rate of 0.15 atm/min and V = 13 and is decreasing at a rate of 0.17 L/min. Find the rate of change of T with respect to time (in K/min) at that instant if n = 10 mol.(Round your answer to four decimal places.)Problem 3. The viral coefficients of a gas at 20 °C and 11.5 bar are B = -138 cm³ mol¹ and C=7222 cmº mol². Calculate the V (molar volume) Z (compressibility factor) of the gas. Use the equation below (R = 83.14 cm³ bar mol-¹ K-¹). PV 2 = ² = (1 + = + =) Z RT
- When the gas is in state 1, its temperature is T1. Find the temperature in T3 of the gas when it is in state 3. (Keep in mind that this is an ideal gas.) Express T3 in terms of T1.0.52 mol of argon gas is admitted to an evacuated 3.00 liter (3.00 × 10-3 m3) container at 20.0°C. The gas then undergoes an isobaric process to a temperature of 260°C. What is the final pressure of the gas, in atm? Your answer needs to have 3 significant figures, including the negative sign in your answer if needed. Do not include the positive sign if the answer is positive. No unit is needed in your answer, it is already given in the question statement.