Find the number of different kinds proton and carbon signals in the following compound. Write the spin multiplicity of each proton in these compounds?
Find the number of different kinds proton and carbon signals in the following compound. Write the spin multiplicity of each proton in these compounds?
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
Find the number of different kinds proton and carbon signals in the following compound.
Write the spin multiplicity of each proton in these compounds?

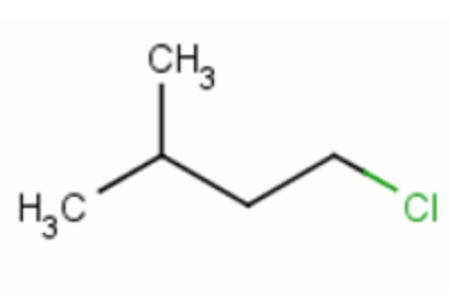
Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts the structural formula of an organic compound called 2-chlorobutane.
**Structure Explanation:**
- The molecule consists of a four-carbon chain.
- The backbone of the molecule is a chain of carbon atoms, represented as follows:
- The first carbon (starting from the left) is bonded to three hydrogen atoms (CH₃–).
- The second carbon is bonded to a methyl group (CH₃) and a hydrogen (-CH-).
- The third carbon is bonded to two hydrogens (CH₂–).
- The fourth carbon is bonded to two hydrogens and a chlorine atom (Cl), represented at the end of the chain.
**Functional Group:**
- The chlorine atom is attached to the second carbon in the chain, making this an example of a haloalkane, specifically an alkyl chloride.
**Chemical Information:**
- This compound is named 2-chlorobutane because the chlorine atom is attached to the second carbon atom in the butane chain.
Expert Solution
Step 1
We are given the following molecule:
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY