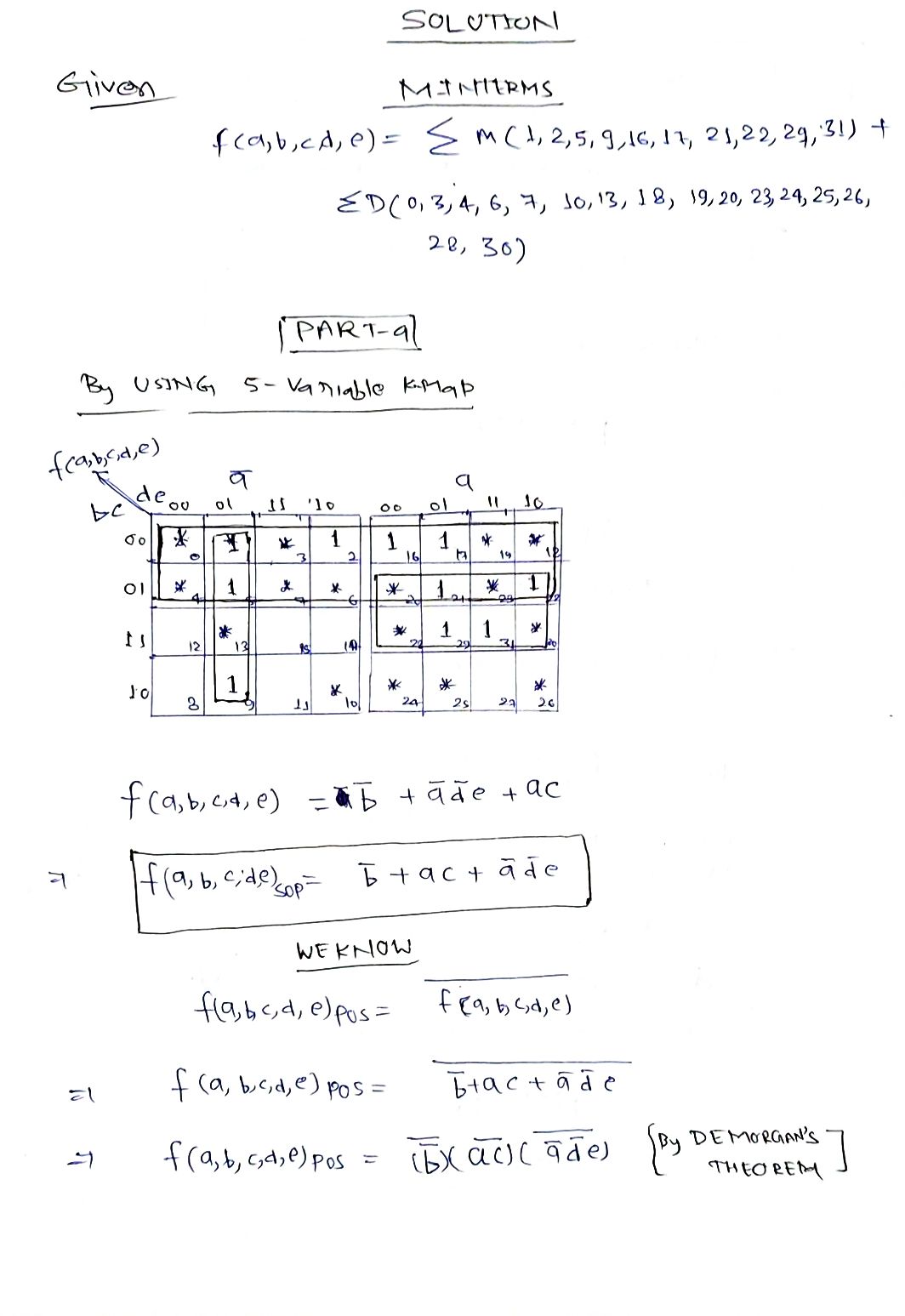
f(a, b, c, d, e) = m(1, 2, 5, 9, 16, 17, 21, 22, 29, 31) + D(0,3, 4, 6, 7, 10, 13, 18, 19, 20, 23, 24, 25, 26, 28, 30) (1) In this function, the minterm elements are m(1, 2,...) these are the truth table entries for which the function has logic value 1. The elements D(0, 3,...) indicate the don't care terms (for which the logic value of f is not important; you can assume the entry to be a 0 or a 1, as convenient. • Use a 5-variable Karnaugh maps to find a minimized SOP and POS expressions for function f in Equation (1). Draw an AND, OR, NOT gate circuit for your expression. Use only 2-input AND and OR gates. If your design requires gates with more than two inputs, change your design to use only 2-input gates. Map your design to chips: 7404 (NOT), 7408 (AND) and 7432 (OR).
f(a, b, c, d, e) = m(1, 2, 5, 9, 16, 17, 21, 22, 29, 31) + D(0,3, 4, 6, 7, 10, 13, 18, 19, 20, 23, 24, 25, 26, 28, 30) (1) In this function, the minterm elements are m(1, 2,...) these are the truth table entries for which the function has logic value 1. The elements D(0, 3,...) indicate the don't care terms (for which the logic value of f is not important; you can assume the entry to be a 0 or a 1, as convenient. • Use a 5-variable Karnaugh maps to find a minimized SOP and POS expressions for function f in Equation (1). Draw an AND, OR, NOT gate circuit for your expression. Use only 2-input AND and OR gates. If your design requires gates with more than two inputs, change your design to use only 2-input gates. Map your design to chips: 7404 (NOT), 7408 (AND) and 7432 (OR).
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:Robert L. Boylestad
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P: Visit your local library (at school or home) and describe the extent to which it provides literature...
Related questions
Question
please answer all parts to this question
![**Transcription and Explanation**
---
### Function Definition and Terms
The function \( f(a, b, c, d, e) \) is defined as:
\[
f(a, b, c, d, e) = \sum m(1, 2, 5, 9, 16, 17, 21, 22, 29, 31) + \sum D(0, 3, 4, 6, 7, 10, 13, 18, 19, 20, 23, 24, 25, 26, 28, 30)
\]
- **Minterm Elements**: \( m(1, 2, \ldots) \) are the truth table entries for which the function has logic value 1.
- **Don't Care Conditions**: \( D(0, 3, \ldots) \) indicate entries for which the logic value of \( f \) is not important. These can be assumed to be 0 or 1 as convenient.
### Instructional Tasks
- **Karnaugh Maps**:
- Use a 5-variable Karnaugh map to find minimized Sum of Products (SOP) and Product of Sums (POS) expressions for the function \( f \).
- **Circuit Design**:
- Design an AND, OR, NOT gate circuit for your expression. Use only 2-input AND and OR gates. If your design requires gates with more than two inputs, modify your design to use only 2-input gates.
- **Chip Mapping**:
- Map your circuit design to the following chips:
- **7404**: NOT gate
- **7408**: AND gate
- **7432**: OR gate
### Graphs or Diagrams
There are no specific graphs or diagrams included in the image, but there is a reference to using Karnaugh maps for simplifying logic expressions, which involves a grid used to visually simplify Boolean expressions by minimizing logic terms through grouping minterms and don't care conditions.
---
This transcription is designed to aid understanding on the specific steps needed to simplify and implement the given logic function using specific digital logic tools and methods.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F9ea0e50e-bc61-40aa-a108-fd1d63d4d69b%2Fbf102afe-5338-4e05-9ec2-8ca8df696b3e%2F9zusitj_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Transcription and Explanation**
---
### Function Definition and Terms
The function \( f(a, b, c, d, e) \) is defined as:
\[
f(a, b, c, d, e) = \sum m(1, 2, 5, 9, 16, 17, 21, 22, 29, 31) + \sum D(0, 3, 4, 6, 7, 10, 13, 18, 19, 20, 23, 24, 25, 26, 28, 30)
\]
- **Minterm Elements**: \( m(1, 2, \ldots) \) are the truth table entries for which the function has logic value 1.
- **Don't Care Conditions**: \( D(0, 3, \ldots) \) indicate entries for which the logic value of \( f \) is not important. These can be assumed to be 0 or 1 as convenient.
### Instructional Tasks
- **Karnaugh Maps**:
- Use a 5-variable Karnaugh map to find minimized Sum of Products (SOP) and Product of Sums (POS) expressions for the function \( f \).
- **Circuit Design**:
- Design an AND, OR, NOT gate circuit for your expression. Use only 2-input AND and OR gates. If your design requires gates with more than two inputs, modify your design to use only 2-input gates.
- **Chip Mapping**:
- Map your circuit design to the following chips:
- **7404**: NOT gate
- **7408**: AND gate
- **7432**: OR gate
### Graphs or Diagrams
There are no specific graphs or diagrams included in the image, but there is a reference to using Karnaugh maps for simplifying logic expressions, which involves a grid used to visually simplify Boolean expressions by minimizing logic terms through grouping minterms and don't care conditions.
---
This transcription is designed to aid understanding on the specific steps needed to simplify and implement the given logic function using specific digital logic tools and methods.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028229
Author:
Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134746968
Author:
James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028151
Author:
Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:
Mcgraw-hill Education,