Derive the change in the entropy due to pressure increase from p; to pf at constant T of a gas that obeys the following equation of state: nRT V-nb Compare the obtained expression to that of an ideal gas. P=
Derive the change in the entropy due to pressure increase from p; to pf at constant T of a gas that obeys the following equation of state: nRT V-nb Compare the obtained expression to that of an ideal gas. P=
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Derive the change in the entropy due to pressure increase from p; to p; at constant T
of a gas that obeys the following equation of state:
nRT
p= V-nb
Compare the obtained expression to that of an ideal gas.
Expert Solution
Step 1: Entropy change
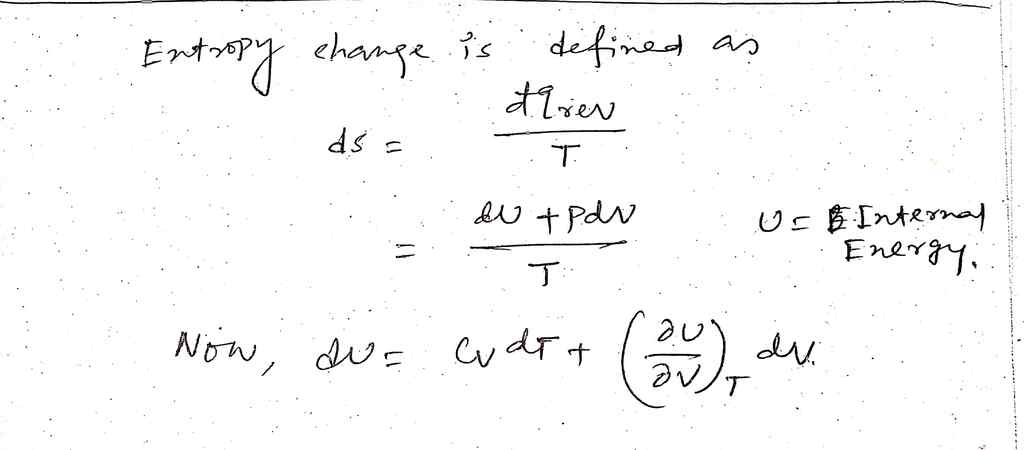

Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images
