Table UV-12. A) Allele and B) Genotype frequencies and population estimates for D antigen (n =_ Dominance B Genotype Phenotypic Trait Genotype Frequencies A Alleles р q D d Total = Allele Frequencies Calculations REQUIRED: Step A1: Step A2: 2) sol eqdong sidiano p² eint not agdonag adlezóg orti el terW rile otti ens fantW DD 2pq| Dd q² dd esideups17 08A 8 s (6) eart) elidirixe haril auool ailenepono aermeteve cuota toota OSA SOT no astells sont ens event soussa auleits seit) 10 anolisupe gradnisW-ybish ont seu Obre bos orit al JartW Sied olgoneria thenimoboo or al WT SIGU Total = Bw Population Estimates This bigyjonertą, ovisesos srt 2) 1GW 8 Silent Tales oigovoria oldizzoq to Telisy ezen estamites nuilstugog sdt bris esloroupant oqioneg bna olelle arti ele urd wora bre nobelagog JSCE IN prisupont erre Et-VU alds BFF
Table UV-12. A) Allele and B) Genotype frequencies and population estimates for D antigen (n =_ Dominance B Genotype Phenotypic Trait Genotype Frequencies A Alleles р q D d Total = Allele Frequencies Calculations REQUIRED: Step A1: Step A2: 2) sol eqdong sidiano p² eint not agdonag adlezóg orti el terW rile otti ens fantW DD 2pq| Dd q² dd esideups17 08A 8 s (6) eart) elidirixe haril auool ailenepono aermeteve cuota toota OSA SOT no astells sont ens event soussa auleits seit) 10 anolisupe gradnisW-ybish ont seu Obre bos orit al JartW Sied olgoneria thenimoboo or al WT SIGU Total = Bw Population Estimates This bigyjonertą, ovisesos srt 2) 1GW 8 Silent Tales oigovoria oldizzoq to Telisy ezen estamites nuilstugog sdt bris esloroupant oqioneg bna olelle arti ele urd wora bre nobelagog JSCE IN prisupont erre Et-VU alds BFF
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Chapter1: The Human Body: An Orientation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: The correct sequence of levels forming the structural hierarchy is A. (a) organ, organ system,...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
100%
Please help fill in table UV-12, A and B
Then the calculations

Transcribed Image Text:**Unit V: Immune & Lymphatic Systems: Population Genetics Lab 12**
**5.** Calculate the allele and genotype frequencies for D antigen (Rh factor) and the population estimates for D antigen provided below.
**6.** Fill in Table UV-12 with the frequencies and the calculations using the Hardy-Weinberg Equations 1 and 2.
---
**Calculations Required:**
**Step A1:**
- **Table UV-12. A) Allele and B) Genotype frequencies and estimates of the population possessing the antigen (D = __).**
| A | Alleles | | | | B | Genotype Frequencies | | Population Estimates |
|---|---------------|---|-----------|---|---|------------------------|---------------|----------------------|
| | Dominance | p | | D | | | | |
| | Recessive | q | | d | | | | |
| | Total = | | | | | Total = | | |
**Step A2:**
**Explanation of Diagrams:**
The table consists of two parts:
- Part A: This section focuses on the alleles, categorizing them into dominance (p) for the D antigen and recessive (q) for the d antigen, ultimately summing them as `Total =`.
- Part B: This section arranges the genotype frequencies, which include p^2 (homozygous dominant), 2pq (heterozygous), and q^2 (homozygous recessive).
These tables are intended to help calculate the allele and genotype frequencies using the Hardy-Weinberg principle.
This lab is designed to estimate the genetic variation in a population based on these calculations.

Transcribed Image Text:**Part 5: Calculating Frequencies**
**Over several semesters, a population of ISU students from the Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory typed their blood. In lab today, we will use their results to predict the allele and genotype frequencies in the Biol 3302L population.**
1. Divide into 12 separate groups with one to two people per group. Write your group’s number on the top of page UV:17.
2. Your instructor will project the data.
1. Determine the total number of students that typed their blood.
2. Fill in Table UV:11 with the number of students expressing the different phenotypic traits.
**A. Rh (Antigen) Frequencies**
- Remember the Rh Blood Group System is a genetic locus that exhibits two alleles: dominant and recessive. The phenotypic expression is represented by the presence (Rh+) or absence (Rh-) of the antigen on the surface of red blood cells. There are two possible alleles for the Rh factor: a dominant allele (D), which encodes for the presence of the antigen, and a recessive allele (d), which does not encode for the antigen.
3. What are the possible genotypes for the dominant Rh trait: _____________?
4. What are the possible genotypes for the recessive Rh trait: _____________?
**Table UV:11**
| Rh Phenotype | Number of Students |
|--------------|--------------------|
| Rh+ | 250 |
| Rh- | 72 |
| ABO Phenotype | Number of Students |
|---------------|--------------------|
| O | 115 |
| AB | 32 |
| A | 126 |
| B | 49 |
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Could you help fill in tables UV-13 to find the allele and genotype frequencies using the Hardy- Weinberg equations
Thank you
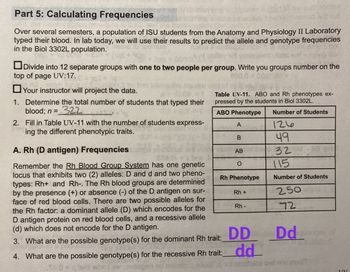
Transcribed Image Text:Part 5: Calculating Frequencies
Siltied
Over several semesters, a population of ISU students from the Anatomy and Physiology II Laboratory
typed their blood. In lab today, we will use their results to predict the allele and genotype frequencies
in the Biol 3302L population.
Divide into 12 separate groups with one to two people per group. Write you groups number on the
top of page UV:17.
Your instructor will project the data.
1. Determine the total number of students that typed their
blood; n = 322
2. Fill in Table UV-11 with the number of students express-
ing the different phenotypic traits.
A. Rh (D antigen) Frequencies
Remember the Rh Blood Group System has one genetic
locus that exhibits two (2) alleles: D and d and two pheno-
types: Rh+ and Rh-. The Rh blood groups are determined
by the presence (+) or absence (-) of the D antigen on sur-
face of red blood cells. There are two possible alleles for
the Rh factor: a dominant allele (D) which encodes for the
D antigen protein on red blood cells, and a recessive allele
(d) which does not encode for the D antigen.
Table UV-11. ABO and Rh phenotypes ex-
pressed by the students in Biol 3302L.
ABO Phenotype
A
B
elu AB
O
Rh Phenotype
Rh +
hbs
Rh-
DD
3. What are the possible genotype(s) for the dominant Rh trait:_
4. What are the possible genotype(s) for the recessive Rh trait: dd
Number of Students
ما12
49
32
115
Number of Students
250
72
Dd
UN
tulbs owt ens ens
LIV
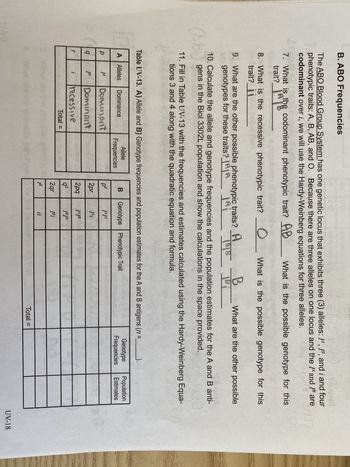
Transcribed Image Text:= (
B. ABO Frequencies
Age12
The ABO Blood Group System has one genetic locus that exhibits three (3) alleles: IA, IB, and i and four
phenotypic traits: A, B, AB, and O. Because there are three alleles on one locus and the and I are
codominant over i, we will use the Hardy-Weinberg equations for three alleles.
What is the possible genotype for this
TI-VO
7. What is the codominant phenotypic trait? AB
trait?
Lathe
O
8. What is the recessive phenotypic trait?
trait?_¡¡02
What is the possible genotype for this
9. What are the other possible phenotypic traits? A
B
genotypes for these traits? AA jAi 1818 |Bi
SA get?
10. Calculate the allele and genotype frequencies and the population estimates for the A and B anti-
(bb) gens in the Biol 3302L population and show the calculations in the space provided.
3
11. Fill in Table UV-13 with the frequencies and estimates calculated using the Hardy-Weinberg Equa-
tions 3 and 4 along with the quadratic equation and formula.
Table UV-13. A) Allele and B) Genotype frequencies and population estimates for the A and B antigens (n =
A Alleles Dominance
р
q
r
JA
[B
Dominant
Dominant
i recessive
Total =
Allele
Frequencies
What are the other possible
B Genotype Phenotypic Trait
p²
2pr
2pq
q²
2qr
p2²
JAJA
I^i
JAJB
IBIB
[Bi
ii
Total =
Genotype Population
Frequencies Estimates
UV-18
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780134580999
Author:
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:
PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781259398629
Author:
McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:
Mcgraw Hill Education,

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780134580999
Author:
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:
PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781259398629
Author:
McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:
Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780815344322
Author:
Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:
W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781260159363
Author:
Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9781260231700
Author:
Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:
McGraw Hill Education