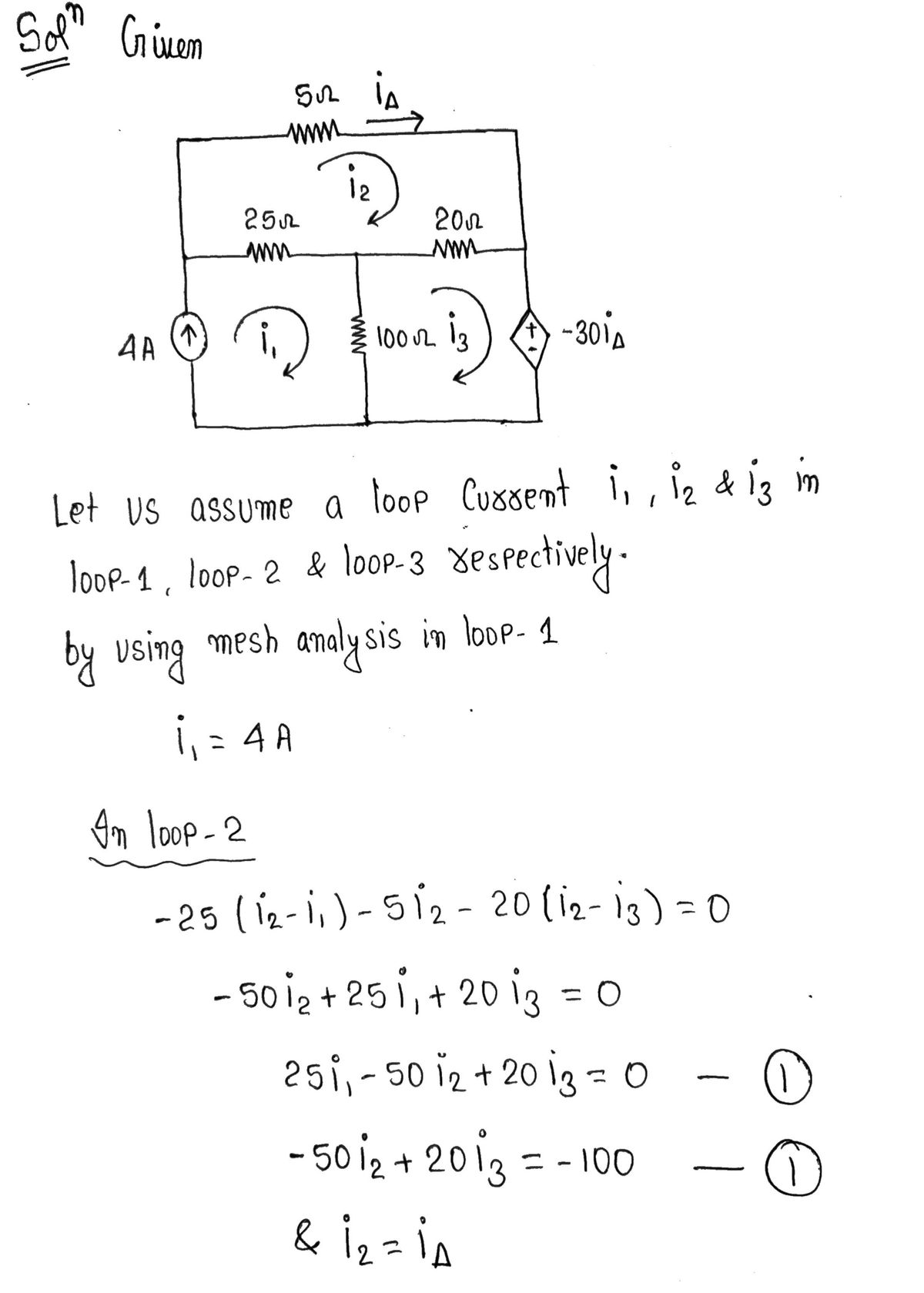
Consider the circuit in (Figure 1). Suppose that i = 4.0 A. Figure 25 Ω ww 502 is 2002 m 100 Ω 1 of 1 -30% Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ▾ View Available Hint(s) Hint 1. How to approach the problem Use the mesh-current method to determine the currents for all the circuit elements. Then, apply the power equation along with the passive sign convention to obtain the total power developed in the circuit. Hint 2. How to use the mesh-current method for a circuit with a dependent voltage source First of all, identify the meshes of the circuit, label the corresponding mesh currents, and determine the number of simultaneous equations needed to obtain these currents. Then, write a KVL equation for each mesh; if the circuit contains a dependent source, write a dependent source constraint equation that defines the controlling variable for the dependent source in terms of the mesh currents. Solve the obtained system of equations for unknown mesh currents. Once you know all the mesh currents, you can directly determine the branch currents for the circuit. Pdev = 1200 HÅ Review W Submit Previous Answers Request Answer ?
Consider the circuit in (Figure 1). Suppose that i = 4.0 A. Figure 25 Ω ww 502 is 2002 m 100 Ω 1 of 1 -30% Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ▾ View Available Hint(s) Hint 1. How to approach the problem Use the mesh-current method to determine the currents for all the circuit elements. Then, apply the power equation along with the passive sign convention to obtain the total power developed in the circuit. Hint 2. How to use the mesh-current method for a circuit with a dependent voltage source First of all, identify the meshes of the circuit, label the corresponding mesh currents, and determine the number of simultaneous equations needed to obtain these currents. Then, write a KVL equation for each mesh; if the circuit contains a dependent source, write a dependent source constraint equation that defines the controlling variable for the dependent source in terms of the mesh currents. Solve the obtained system of equations for unknown mesh currents. Once you know all the mesh currents, you can directly determine the branch currents for the circuit. Pdev = 1200 HÅ Review W Submit Previous Answers Request Answer ?
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:Robert L. Boylestad
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P: Visit your local library (at school or home) and describe the extent to which it provides literature...
Related questions
Question
Question asks for the total power developed in the circuit.

Transcribed Image Text:Consider the circuit in (Figure 1). Suppose that i = 4.0 A.
Figure
i
25 Ω
5Ω
20 Ω
100 Ω
1 of 1
-30iA
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
View Available Hint(s)
Hint 1. How to approach the problem
Use the mesh-current method to determine the currents for all the circuit elements. Then, apply the
power equation along with the passive sign convention to obtain the total power developed in the circuit.
Hint 2. How to use the mesh-current method for a circuit with a dependent voltage source
First of all, identify the meshes of the circuit, label the corresponding mesh currents, and determine the
number of simultaneous equations needed to obtain these currents. Then, write a KVL equation for each
mesh; if the circuit contains a dependent source, write a dependent source constraint equation that
defines the controlling variable for the dependent source in terms of the mesh currents.
Solve the obtained system of equations for unknown mesh currents. Once you know all the mesh
currents, you can directly determine the branch currents for the circuit.
Pdev =
Submit
1200
μÀ
Review
W
Previous Answers Request Answer
?
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133923605
Author:
Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:
PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337900348
Author:
Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780073373843
Author:
Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028229
Author:
Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134746968
Author:
James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9780078028151
Author:
Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:
Mcgraw-hill Education,