Consider a voltaic cell constructed using the following two reductions:
Fe+3 +3e- -->Fe E°red = -0.036 V
Pb+2 +2e- -->Pb E°red = -0.13 V
What will be the equilibrium constant when the cell reaction reaches equilibrium at 25oC?
5.80 x 104
38.7
3.37 x 109
8.69 x 107
When there if flow of electrons from one half cell to the another due to which some potential difference gets created when this process takes place that gives the potential of cell called as E cell.
The reduction half reactions are as shown:
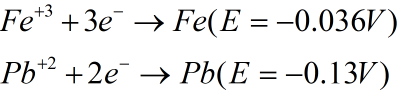
Since reduction potential of Fe is higher than Pb thus Fe will get reduced and Pb will get oxidized.
Thus the oxidation potential of Pb will be +0.13 V
The formula to calculate the standard reduction potential is
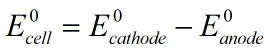
The electrode potential of cathode is -0.036 V and that of anode is +0.13 V
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 5 images









