**Title: Elucidating Products and Mechanisms in Diels-Alder Reactions** **Introduction:** In the study of organic chemistry, the Diels-Alder reaction stands out as a powerful method for forming cyclic compounds. This pericyclic reaction involves a conjugated diene and a dienophile, typically producing a six-membered ring. Below, we explore a series of reactions designed to synthesize various products using different dienophiles. Each reaction will require proposing a mechanism for product formation, particularly focusing on reactions where alkyne dienophiles are employed. **Reactions:** 1. **Reaction A:** - **Reactants:** A diene and a methoxy-substituted dienophile. - **Analysis:** Consider the electronic effects of the methoxy groups on the dienophile and how they influence the reaction pathway. 2. **Reaction B:** - **Reactants:** A diene and a maleic acid derivative. - **Analysis:** Examine the influence of carboxylic acid groups on the reactivity of the dienophile. 3. **Reaction C:** - **Reactants:** A diene and an acrylate ester. - **Analysis:** Look into the carbonyl group’s role in activating the dienophile for cycloaddition. 4. **Reaction D:** - **Reactants:** A diene and a diacetylene derivative. - **Analysis:** Explore the reactivity of the alkyne dienophile, considering the presence of multiple carbonyl groups. 5. **Reaction E:** - **Reactants:** A diene and a maleic anhydride. - **Analysis:** Understand the reactivity influence of the cyclic anhydride structure. 6. **Reaction F:** - **Reactants:** A diene and a dicyanoacetylene. - **Analysis:** Investigate the effects of the nitrile groups on the electron-withdrawing capability of the dienophile. 7. **Reaction G:** - **Reactants:** A diene and a cyclopentanone. - **Analysis:** Note the intramolecular cyclization facilitated by ketone groups. 8. **Reaction H:** - **Reactants:** A diene and a propiolate derivative. - **Analysis:** Consider how the terminal alkyne and ester functional group influence the reaction. 9. **Reaction I:** - **Reactants
**Title: Elucidating Products and Mechanisms in Diels-Alder Reactions** **Introduction:** In the study of organic chemistry, the Diels-Alder reaction stands out as a powerful method for forming cyclic compounds. This pericyclic reaction involves a conjugated diene and a dienophile, typically producing a six-membered ring. Below, we explore a series of reactions designed to synthesize various products using different dienophiles. Each reaction will require proposing a mechanism for product formation, particularly focusing on reactions where alkyne dienophiles are employed. **Reactions:** 1. **Reaction A:** - **Reactants:** A diene and a methoxy-substituted dienophile. - **Analysis:** Consider the electronic effects of the methoxy groups on the dienophile and how they influence the reaction pathway. 2. **Reaction B:** - **Reactants:** A diene and a maleic acid derivative. - **Analysis:** Examine the influence of carboxylic acid groups on the reactivity of the dienophile. 3. **Reaction C:** - **Reactants:** A diene and an acrylate ester. - **Analysis:** Look into the carbonyl group’s role in activating the dienophile for cycloaddition. 4. **Reaction D:** - **Reactants:** A diene and a diacetylene derivative. - **Analysis:** Explore the reactivity of the alkyne dienophile, considering the presence of multiple carbonyl groups. 5. **Reaction E:** - **Reactants:** A diene and a maleic anhydride. - **Analysis:** Understand the reactivity influence of the cyclic anhydride structure. 6. **Reaction F:** - **Reactants:** A diene and a dicyanoacetylene. - **Analysis:** Investigate the effects of the nitrile groups on the electron-withdrawing capability of the dienophile. 7. **Reaction G:** - **Reactants:** A diene and a cyclopentanone. - **Analysis:** Note the intramolecular cyclization facilitated by ketone groups. 8. **Reaction H:** - **Reactants:** A diene and a propiolate derivative. - **Analysis:** Consider how the terminal alkyne and ester functional group influence the reaction. 9. **Reaction I:** - **Reactants
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
Can you answer the question and explain it? With the mechanism
Only a and b

Transcribed Image Text:**Title: Elucidating Products and Mechanisms in Diels-Alder Reactions**
**Introduction:**
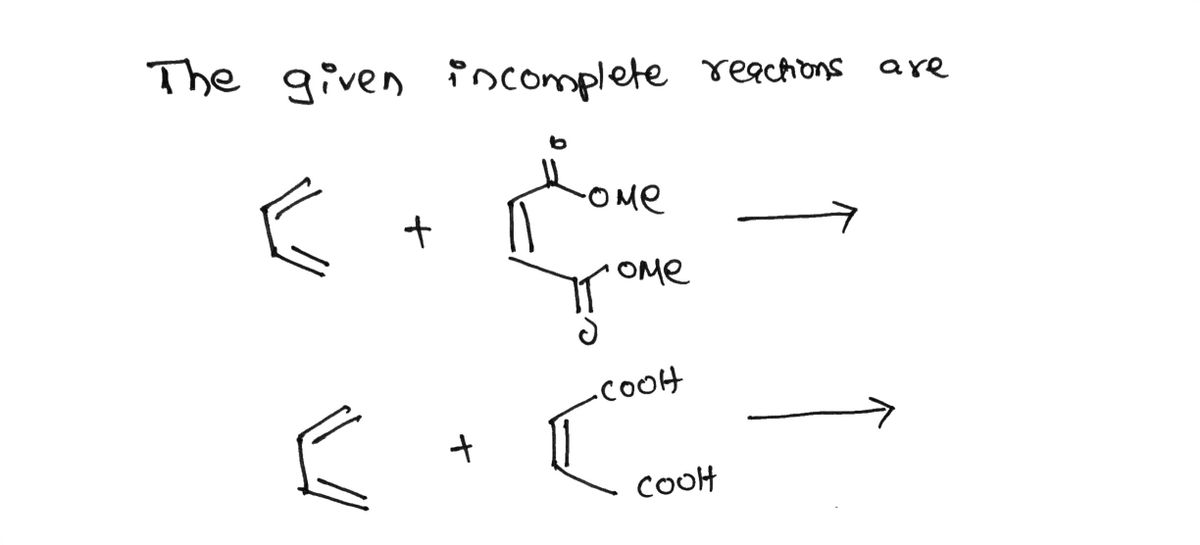
In the study of organic chemistry, the Diels-Alder reaction stands out as a powerful method for forming cyclic compounds. This pericyclic reaction involves a conjugated diene and a dienophile, typically producing a six-membered ring. Below, we explore a series of reactions designed to synthesize various products using different dienophiles. Each reaction will require proposing a mechanism for product formation, particularly focusing on reactions where alkyne dienophiles are employed.
**Reactions:**
1. **Reaction A:**
- **Reactants:** A diene and a methoxy-substituted dienophile.
- **Analysis:** Consider the electronic effects of the methoxy groups on the dienophile and how they influence the reaction pathway.
2. **Reaction B:**
- **Reactants:** A diene and a maleic acid derivative.
- **Analysis:** Examine the influence of carboxylic acid groups on the reactivity of the dienophile.
3. **Reaction C:**
- **Reactants:** A diene and an acrylate ester.
- **Analysis:** Look into the carbonyl group’s role in activating the dienophile for cycloaddition.
4. **Reaction D:**
- **Reactants:** A diene and a diacetylene derivative.
- **Analysis:** Explore the reactivity of the alkyne dienophile, considering the presence of multiple carbonyl groups.
5. **Reaction E:**
- **Reactants:** A diene and a maleic anhydride.
- **Analysis:** Understand the reactivity influence of the cyclic anhydride structure.
6. **Reaction F:**
- **Reactants:** A diene and a dicyanoacetylene.
- **Analysis:** Investigate the effects of the nitrile groups on the electron-withdrawing capability of the dienophile.
7. **Reaction G:**
- **Reactants:** A diene and a cyclopentanone.
- **Analysis:** Note the intramolecular cyclization facilitated by ketone groups.
8. **Reaction H:**
- **Reactants:** A diene and a propiolate derivative.
- **Analysis:** Consider how the terminal alkyne and ester functional group influence the reaction.
9. **Reaction I:**
- **Reactants
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY