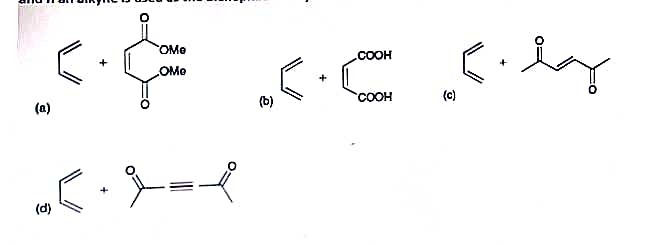
**Title: Understanding Reaction Mechanisms and Product Formation** **Objective:** Identify the products for the following reactions and propose a mechanism explaining their formation. In reactions (d), (f), and (h), an alkyne is used as the dienophile. Explore the potential products. **Reactions:** 1. **Reaction (a):** - **Reactants:** A diene and a cyclic anhydride with methoxy groups (OMe) on each side. - **Mechanism:** Diels-Alder reaction, involving the formation of a new cyclic compound through [4+2] cycloaddition. 2. **Reaction (b):** - **Reactants:** A diene and a maleic acid compound. - **Mechanism:** Anticipate an addition reaction yielding a product with carboxylic acid groups. 3. **Reaction (c):** - **Reactants:** A diene and a compound with two ketone groups and conjugated double bonds. - **Mechanism:** Likely involves conjugate addition, influencing stereo- and regioselectivity. 4. **Reaction (d):** - **Reactants:** A diene and a diketone featuring an internal alkyne. - **Mechanism:** Potential for a [4+2] cycloaddition, forming a new ring structure. 5. **Reaction (e):** - **Reactants:** A diene and an unsaturated dicarboxylic anhydride. - **Mechanism:** Expect the formation of a cyclic compound, potentially through a pericyclic reaction. 6. **Reaction (f):** - **Reactants:** A diene and a cyclic anhydride. - **Mechanism:** Diels-Alder reaction resulting in the creation of a bicyclic compound. 7. **Reaction (g):** - **Reactants:** A diene and a cyclic ketone. - **Mechanism:** Predicted formation of a new ketone product through addition. 8. **Reaction (h):** - **Reactants:** A diene combined with a nitrile-substituted alkyne. - **Mechanism:** Anticipate an addition reaction, considering alkyne electronic effects. 9. **Reaction (i):** - **Reactants:** A diene and a cyclohexanone derivative with an alpha, beta-unsaturated carbonyl
**Title: Understanding Reaction Mechanisms and Product Formation** **Objective:** Identify the products for the following reactions and propose a mechanism explaining their formation. In reactions (d), (f), and (h), an alkyne is used as the dienophile. Explore the potential products. **Reactions:** 1. **Reaction (a):** - **Reactants:** A diene and a cyclic anhydride with methoxy groups (OMe) on each side. - **Mechanism:** Diels-Alder reaction, involving the formation of a new cyclic compound through [4+2] cycloaddition. 2. **Reaction (b):** - **Reactants:** A diene and a maleic acid compound. - **Mechanism:** Anticipate an addition reaction yielding a product with carboxylic acid groups. 3. **Reaction (c):** - **Reactants:** A diene and a compound with two ketone groups and conjugated double bonds. - **Mechanism:** Likely involves conjugate addition, influencing stereo- and regioselectivity. 4. **Reaction (d):** - **Reactants:** A diene and a diketone featuring an internal alkyne. - **Mechanism:** Potential for a [4+2] cycloaddition, forming a new ring structure. 5. **Reaction (e):** - **Reactants:** A diene and an unsaturated dicarboxylic anhydride. - **Mechanism:** Expect the formation of a cyclic compound, potentially through a pericyclic reaction. 6. **Reaction (f):** - **Reactants:** A diene and a cyclic anhydride. - **Mechanism:** Diels-Alder reaction resulting in the creation of a bicyclic compound. 7. **Reaction (g):** - **Reactants:** A diene and a cyclic ketone. - **Mechanism:** Predicted formation of a new ketone product through addition. 8. **Reaction (h):** - **Reactants:** A diene combined with a nitrile-substituted alkyne. - **Mechanism:** Anticipate an addition reaction, considering alkyne electronic effects. 9. **Reaction (i):** - **Reactants:** A diene and a cyclohexanone derivative with an alpha, beta-unsaturated carbonyl
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
![**Title: Understanding Reaction Mechanisms and Product Formation**
**Objective:**
Identify the products for the following reactions and propose a mechanism explaining their formation. In reactions (d), (f), and (h), an alkyne is used as the dienophile. Explore the potential products.
**Reactions:**
1. **Reaction (a):**
- **Reactants:** A diene and a cyclic anhydride with methoxy groups (OMe) on each side.
- **Mechanism:** Diels-Alder reaction, involving the formation of a new cyclic compound through [4+2] cycloaddition.
2. **Reaction (b):**
- **Reactants:** A diene and a maleic acid compound.
- **Mechanism:** Anticipate an addition reaction yielding a product with carboxylic acid groups.
3. **Reaction (c):**
- **Reactants:** A diene and a compound with two ketone groups and conjugated double bonds.
- **Mechanism:** Likely involves conjugate addition, influencing stereo- and regioselectivity.
4. **Reaction (d):**
- **Reactants:** A diene and a diketone featuring an internal alkyne.
- **Mechanism:** Potential for a [4+2] cycloaddition, forming a new ring structure.
5. **Reaction (e):**
- **Reactants:** A diene and an unsaturated dicarboxylic anhydride.
- **Mechanism:** Expect the formation of a cyclic compound, potentially through a pericyclic reaction.
6. **Reaction (f):**
- **Reactants:** A diene and a cyclic anhydride.
- **Mechanism:** Diels-Alder reaction resulting in the creation of a bicyclic compound.
7. **Reaction (g):**
- **Reactants:** A diene and a cyclic ketone.
- **Mechanism:** Predicted formation of a new ketone product through addition.
8. **Reaction (h):**
- **Reactants:** A diene combined with a nitrile-substituted alkyne.
- **Mechanism:** Anticipate an addition reaction, considering alkyne electronic effects.
9. **Reaction (i):**
- **Reactants:** A diene and a cyclohexanone derivative with an alpha, beta-unsaturated carbonyl](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F637a8243-98d2-45ca-8dd1-4e9d7d0f97ca%2F43715018-a88b-40de-92bc-af56a883d412%2F8njowla.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Title: Understanding Reaction Mechanisms and Product Formation**
**Objective:**
Identify the products for the following reactions and propose a mechanism explaining their formation. In reactions (d), (f), and (h), an alkyne is used as the dienophile. Explore the potential products.
**Reactions:**
1. **Reaction (a):**
- **Reactants:** A diene and a cyclic anhydride with methoxy groups (OMe) on each side.
- **Mechanism:** Diels-Alder reaction, involving the formation of a new cyclic compound through [4+2] cycloaddition.
2. **Reaction (b):**
- **Reactants:** A diene and a maleic acid compound.
- **Mechanism:** Anticipate an addition reaction yielding a product with carboxylic acid groups.
3. **Reaction (c):**
- **Reactants:** A diene and a compound with two ketone groups and conjugated double bonds.
- **Mechanism:** Likely involves conjugate addition, influencing stereo- and regioselectivity.
4. **Reaction (d):**
- **Reactants:** A diene and a diketone featuring an internal alkyne.
- **Mechanism:** Potential for a [4+2] cycloaddition, forming a new ring structure.
5. **Reaction (e):**
- **Reactants:** A diene and an unsaturated dicarboxylic anhydride.
- **Mechanism:** Expect the formation of a cyclic compound, potentially through a pericyclic reaction.
6. **Reaction (f):**
- **Reactants:** A diene and a cyclic anhydride.
- **Mechanism:** Diels-Alder reaction resulting in the creation of a bicyclic compound.
7. **Reaction (g):**
- **Reactants:** A diene and a cyclic ketone.
- **Mechanism:** Predicted formation of a new ketone product through addition.
8. **Reaction (h):**
- **Reactants:** A diene combined with a nitrile-substituted alkyne.
- **Mechanism:** Anticipate an addition reaction, considering alkyne electronic effects.
9. **Reaction (i):**
- **Reactants:** A diene and a cyclohexanone derivative with an alpha, beta-unsaturated carbonyl
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY