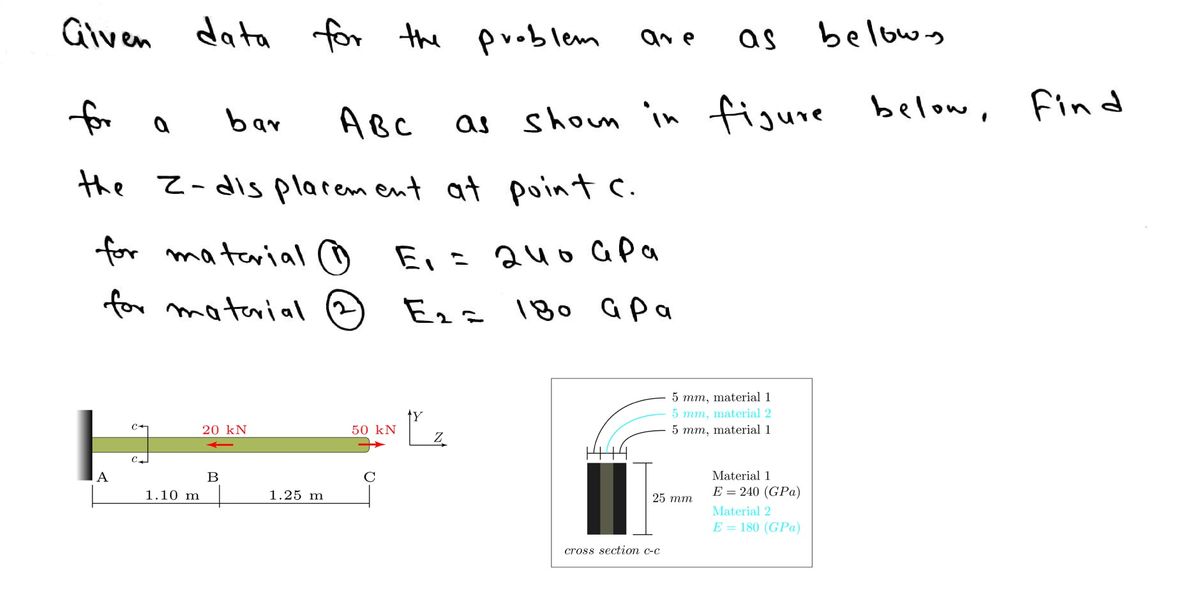
Bar A-B-C is made from a fully bonded composite of two materials as shown in the cross section below. Find the Z displacement at point C.
Bar A-B-C is made from a fully bonded composite of two materials as shown in the cross section below. Find the Z displacement at point C.
Materials Science And Engineering Properties
1st Edition
ISBN:9781111988609
Author:Charles Gilmore
Publisher:Charles Gilmore
Chapter6: Introduction To Mechanical Properties
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 12CQ
Related questions
Question
![**Problem Statement:**
Bar A-B-C is made from a fully bonded composite of two materials as shown in the cross section below. Find the Z displacement at point C.
**Description of the Diagram:**
1. **Bar Configuration:**
- The bar is composed of points A, B, and C.
- It is subject to two forces:
- \(20 \, \text{kN}\) acting leftward between points A and B.
- \(50 \, \text{kN}\) acting rightward at point C.
- Distances:
- \(AB = 1.10 \, \text{m}\)
- \(BC = 1.25 \, \text{m}\)
2. **Cross Section c-c:**
- The cross section is a composite made of two materials.
- Layers:
- Top layer: \(5 \, \text{mm}\), material 1
- Middle layer: \(5 \, \text{mm}\), material 2
- Bottom layer: \(5 \, \text{mm}\), material 1
- Total thickness: \(25 \, \text{mm}\)
3. **Material Properties:**
- Material 1:
- Young's Modulus, \(E = 240 \, \text{GPa}\)
- Material 2:
- Young's Modulus, \(E = 180 \, \text{GPa}\)
**Goal:**
Calculate the Z displacement (\(u_z\)) at point C.
\[
u_z = \underline{\ \qquad \ } \text{ mm (at C)}
\]](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fe8988a1a-5625-4af8-94a1-38513bb2393c%2Fe0e160ba-7087-4974-a0d4-33a4a037fe85%2Fp8z2lep_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem Statement:**
Bar A-B-C is made from a fully bonded composite of two materials as shown in the cross section below. Find the Z displacement at point C.
**Description of the Diagram:**
1. **Bar Configuration:**
- The bar is composed of points A, B, and C.
- It is subject to two forces:
- \(20 \, \text{kN}\) acting leftward between points A and B.
- \(50 \, \text{kN}\) acting rightward at point C.
- Distances:
- \(AB = 1.10 \, \text{m}\)
- \(BC = 1.25 \, \text{m}\)
2. **Cross Section c-c:**
- The cross section is a composite made of two materials.
- Layers:
- Top layer: \(5 \, \text{mm}\), material 1
- Middle layer: \(5 \, \text{mm}\), material 2
- Bottom layer: \(5 \, \text{mm}\), material 1
- Total thickness: \(25 \, \text{mm}\)
3. **Material Properties:**
- Material 1:
- Young's Modulus, \(E = 240 \, \text{GPa}\)
- Material 2:
- Young's Modulus, \(E = 180 \, \text{GPa}\)
**Goal:**
Calculate the Z displacement (\(u_z\)) at point C.
\[
u_z = \underline{\ \qquad \ } \text{ mm (at C)}
\]
Expert Solution
Step 1: given data
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Materials Science And Engineering Properties
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781111988609
Author:
Charles Gilmore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337094740
Author:
Segui, William T.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Materials Science And Engineering Properties
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781111988609
Author:
Charles Gilmore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337094740
Author:
Segui, William T.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305084766
Author:
Saeed Moaveni
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305086272
Author:
William P. Spence, Eva Kultermann
Publisher:
Cengage Learning