An aqueous solution of calcium hydroxide is standardized by titration with a 0.138 M solution of hydrobromic acid. If 17.3 mL of base are required to neutralize 11.5 mL of the acid, what is the molarity of the calcium hydroxide solution? M calcium hydroxide
An aqueous solution of calcium hydroxide is standardized by titration with a 0.138 M solution of hydrobromic acid. If 17.3 mL of base are required to neutralize 11.5 mL of the acid, what is the molarity of the calcium hydroxide solution? M calcium hydroxide
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Chapter4: Stoichiometry Of Chemical Reactions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 91E: A sample of solid calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2, is allowed to stand in water until a saturated...
Related questions
Question
32
![**Titration of Hydrochloric Acid with Calcium Hydroxide**
An aqueous solution of **hydrochloric acid** is standardized by titration with a **0.116 M** solution of **calcium hydroxide**.
If **20.7 mL** of base is required to neutralize **22.9 mL** of the acid, what is the molarity of the hydrochloric acid solution?
[___] M hydrochloric acid
**Explanation for Students:**
In this experiment, you need to determine the molarity of hydrochloric acid by titration method using a known concentration of calcium hydroxide as the titrant. Note the volumes of the acid and base, as well as the molarity of the base provided.
**Key Concepts:**
- **Titration** is an analytical technique where a solution of known concentration (titrant) is used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution (analyte).
- **Molarity (M)** is a measure of the concentration of a solute in a solution, in terms of amount of substance in a given volume.
- The reaction between hydrochloric acid (HCl) and calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂) is a neutralization reaction, typically producing water and a salt. Use stoichiometry to find the molarity of hydrochloric acid.
This exercise helps demonstrate practical applications of neutralization and molarity calculations in chemistry.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F7bc30bfd-54a4-45be-8be6-a7bac17a47af%2F8aefce57-7fa3-4c81-a6ac-e051d3d401d5%2Faafrwld_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Titration of Hydrochloric Acid with Calcium Hydroxide**
An aqueous solution of **hydrochloric acid** is standardized by titration with a **0.116 M** solution of **calcium hydroxide**.
If **20.7 mL** of base is required to neutralize **22.9 mL** of the acid, what is the molarity of the hydrochloric acid solution?
[___] M hydrochloric acid
**Explanation for Students:**
In this experiment, you need to determine the molarity of hydrochloric acid by titration method using a known concentration of calcium hydroxide as the titrant. Note the volumes of the acid and base, as well as the molarity of the base provided.
**Key Concepts:**
- **Titration** is an analytical technique where a solution of known concentration (titrant) is used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution (analyte).
- **Molarity (M)** is a measure of the concentration of a solute in a solution, in terms of amount of substance in a given volume.
- The reaction between hydrochloric acid (HCl) and calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂) is a neutralization reaction, typically producing water and a salt. Use stoichiometry to find the molarity of hydrochloric acid.
This exercise helps demonstrate practical applications of neutralization and molarity calculations in chemistry.
![An aqueous solution of **calcium hydroxide** is standardized by titration with a **0.138 M** solution of **hydrobromic acid**.
If **17.3 mL** of base are required to neutralize **11.5 mL** of the acid, what is the molarity of the **calcium hydroxide** solution?
[Input box] M calcium hydroxide](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F7bc30bfd-54a4-45be-8be6-a7bac17a47af%2F8aefce57-7fa3-4c81-a6ac-e051d3d401d5%2Fbttxy6h_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:An aqueous solution of **calcium hydroxide** is standardized by titration with a **0.138 M** solution of **hydrobromic acid**.
If **17.3 mL** of base are required to neutralize **11.5 mL** of the acid, what is the molarity of the **calcium hydroxide** solution?
[Input box] M calcium hydroxide
Expert Solution
Step 1
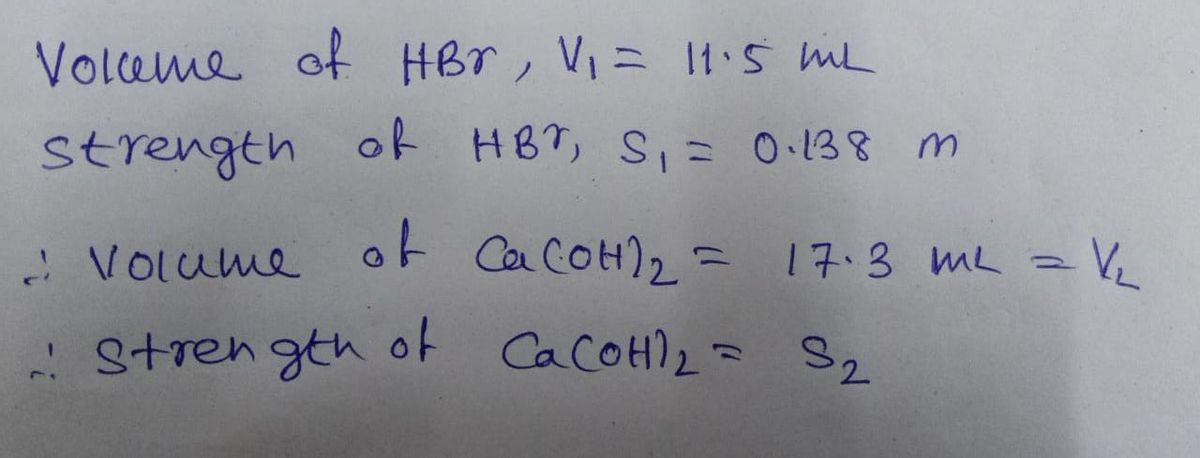
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079250
Author:
Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning