A simple random sample of size n = 40 is drawn from a population. The sample mean is found to be 108.6, and the sample standard deviation is found to be 19.6. Is the population mean greater than 100 at the x = 0.01 level of significance? Determine the null and alternative hypotheses. Ho: μ = 100 H₁: μ> 100 tatatinti
A simple random sample of size n = 40 is drawn from a population. The sample mean is found to be 108.6, and the sample standard deviation is found to be 19.6. Is the population mean greater than 100 at the x = 0.01 level of significance? Determine the null and alternative hypotheses. Ho: μ = 100 H₁: μ> 100 tatatinti
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
![**Problem Statement:**
A simple random sample of size \( n = 40 \) is drawn from a population. The sample mean is found to be 108.6, and the sample standard deviation is found to be 19.6. Is the population mean greater than 100 at the \( \alpha = 0.01 \) level of significance?
**Steps to solve the problem:**
1. **Determine the null and alternative hypotheses.**
- Null Hypothesis \( (H_0) \): \( \mu = 100 \)
- Alternative Hypothesis \( (H_1) \): \( \mu > 100 \)
2. **Compute the test statistic.**
\[
t_0 = 2.78 \text{ (Round to two decimal places as needed.)}
\]
3. **Determine the P-value.**
\[
\text{The P-value is } 0.004. \text{ (Round to three decimal places as needed.)}
\]
4. **Test Results:**
- Reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis and explain why:
- Reject the null hypothesis because the P-value is less than the level of significance.
- Conclusion at \( \alpha = 0.01 \) level of significance:
- At the \( \alpha = 0.01 \) level of significance, the population mean is greater than 100.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fac3be618-b645-4bd8-855b-808ff3fc18d4%2Ff66a48ca-028b-4b56-950f-e14ac82ef5cc%2Fmtadypa_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem Statement:**
A simple random sample of size \( n = 40 \) is drawn from a population. The sample mean is found to be 108.6, and the sample standard deviation is found to be 19.6. Is the population mean greater than 100 at the \( \alpha = 0.01 \) level of significance?
**Steps to solve the problem:**
1. **Determine the null and alternative hypotheses.**
- Null Hypothesis \( (H_0) \): \( \mu = 100 \)
- Alternative Hypothesis \( (H_1) \): \( \mu > 100 \)
2. **Compute the test statistic.**
\[
t_0 = 2.78 \text{ (Round to two decimal places as needed.)}
\]
3. **Determine the P-value.**
\[
\text{The P-value is } 0.004. \text{ (Round to three decimal places as needed.)}
\]
4. **Test Results:**
- Reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis and explain why:
- Reject the null hypothesis because the P-value is less than the level of significance.
- Conclusion at \( \alpha = 0.01 \) level of significance:
- At the \( \alpha = 0.01 \) level of significance, the population mean is greater than 100.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
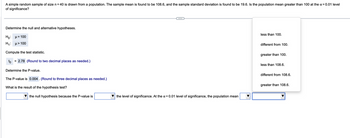
Transcribed Image Text:A simple random sample of size n = 40 is drawn from a population. The sample mean is found to be 108.6, and the sample standard deviation is found to be 19.6. Is the population mean greater than 100 at the α = 0.01 level
of significance?
Determine the null and alternative hypotheses.
Ho: μ = 100
H₁: μ> 100
Compute the test statistic.
to = 2.78 (Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Determine the P-value.
The P-value is 0.004. (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
What is the result of the hypothesis test?
the null hypothesis because the P-value is
the level of significance. At the α = 0.01 level of significance, the population mean
less than 100.
different from 100.
greater than 100.
less than 108.6.
different from 108.6.
greater than 108.6.
Solution
Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman