A researcher wanted to examine whether type of dog food (freeze dried meat vs generic brand kibble) would affect dogs' attention span. The researcher hypothesized that dogs who ate freeze dried meat would not have the same attention span as those who ate generic kibble. The researcher used a single sample of 13 dogs, that took part in both treatment conditions. The mean was 7.0 and the SS for the difference in attention spans was 144. Alpha was set at the 0.05 level. Calculate the appropriate
A researcher wanted to examine whether type of dog food (freeze dried meat vs generic brand kibble) would affect dogs' attention span. The researcher hypothesized that dogs who ate freeze dried meat would not have the same attention span as those who ate generic kibble. The researcher used a single sample of 13 dogs, that took part in both treatment conditions. The mean was 7.0 and the SS for the difference in attention spans was 144. Alpha was set at the 0.05 level.
Calculate the appropriate t to the nearest thousandths and include the +/- value in front of the t. For example, -5.369.
What is the corresponding critical t?
What decision can you make about the null hypothesis?
Was there a treatment effect?

Solution
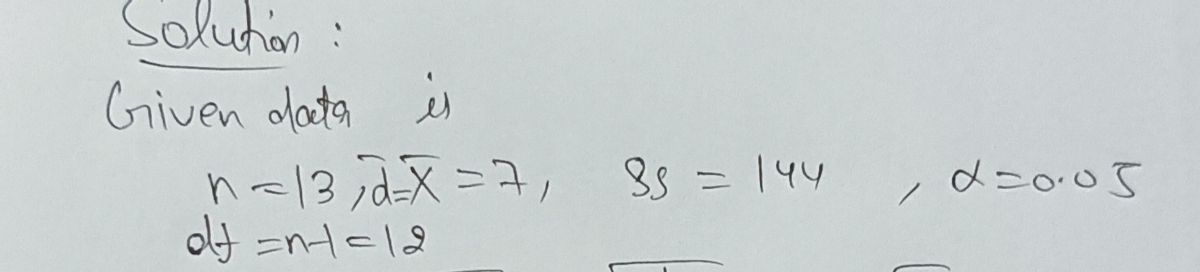
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









