A) g/L 3) How much heat is required to raise the temperature of 1.5 g of A) 12.55 kJ B) 6.27 kJ C) 25.1 kJ 4) Estimate the temperature where AG-0 for the following reaction: (Given: AH-155 kJ and AS-284.5 J/K) CAUTION: Beware of units.NH3(g) + HCl(g)-NH.CI(s) A) 685 K B) 545 k C) 467 K D) 634 K CH4 + CO₂
Thermochemistry
Thermochemistry can be considered as a branch of thermodynamics that deals with the connections between warmth, work, and various types of energy, formed because of different synthetic and actual cycles. Thermochemistry describes the energy changes that occur as a result of reactions or chemical changes in a substance.
Exergonic Reaction
The term exergonic is derived from the Greek word in which ‘ergon’ means work and exergonic means ‘work outside’. Exergonic reactions releases work energy. Exergonic reactions are different from exothermic reactions, the one that releases only heat energy during the course of the reaction. So, exothermic reaction is one type of exergonic reaction. Exergonic reaction releases work energy in different forms like heat, light or sound. For example, a glow stick releases light making that an exergonic reaction and not an exothermic reaction since no heat is released. Even endothermic reactions at very high temperature are exergonic.
![An
(molar mass of H-1, N-14g/mol), (R-0.0821 L.atm/K.mol), (The specific heat of water is 4.184J/g.°C)]
1) The volume of a sample of nitrogen N2 is 7 L at 38°C and 740 torr. What volume will it occupy at STP?
A) 7.78 L
B) 7.18 L
D)5.98 L
C) 6.90 L
2) What is the density of NH3 at 4 atm pressure and a temperature of 30°C?
A) 16.6 g/L
C) 3.36 g/L
B) 1.39 g/L
D) 2.73 g/L
3) How much heat is required to raise the temperature of 1.5 g of water from 25°C to 29°C?
A) 12.55 kJ
B) 6.27 kJ
C) 25.1 kJ
D) 40.5 kJ
4) Estimate the temperature where AG - 0 for the following reaction: (Given: AH = -155 kJ and
AS = -284.5 J/K) CAUTION: Beware of units.NH3(g) + HCl(g)-NH.CI(s)
A) 685 K
B) 545 K
C) 467 K
D) 634 K
5) Calculate AH° for the reaction:
(1) CO+Hz
(2)CO ) +H_O»
(3) CO(g) + 3H2(g) →
A) 33 kJ
6) Calculate AG for the reaction
CO(g)
CO2(g)
CO) + 1/2O2() -
A) 217.2 kJ
Which is the strongest
A) Dipole-dipole
2C+2H2O --->
C) + H₂O
H2(g) + CO2(g)
CH48) + H₂O(g)
B) 53 kJ
C(s) + 1/2O2(g)
C()+ O2(g)
CO2(g)
CH4(g) + CO2(g)
AH-140 kJ
AH 41kJ
ΔΗ°=-206kJ
C) -372 kJ
AG° = ??
AG = 454.4 kJ
AG = -237.2 kJ
C) 197.2 kJ
B)-265.8 kJ
D) 651.6 kJ
D) London
C) Ionic bonding
intermolecular force among a group of molecules of comparable molar mass?
B) Hydrogen bonding
7)
8) Which of the following pure substances exhibits hydrogen
A) HCI
B) H₂S
D) -116 kJ
C) NH3
bonding?
D) CH4
9) A solution was made by dissolving 3.15 g of a solute in
120.3 g of acetone. The solution boiled at
56.58° C. The boiling point of pure acetone is 55.95° C, and the Kb -1.71° C/m. What is the molecular
weight of the solute?
A) 140
B) 105
C) 12.7
D) 71.1
D) 9.34 kg
10) What mass of ethylene glycol (M.W. = 62.1 g/mol) antifreeze must be added to 12.0 liters of water to
C) 0.78 kg
produce a solution that freezes at -23.3 C degrees. Density of water is 1 g/ml and Kr= 1.86° C/m.
B) 3.41 g
A) 6.22 Kg](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fbfaea92a-9638-4015-ac2a-6c50f8cc86a5%2F42cc0a4d-ed7c-45c5-a8b5-67c803008463%2Fkrpg21_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
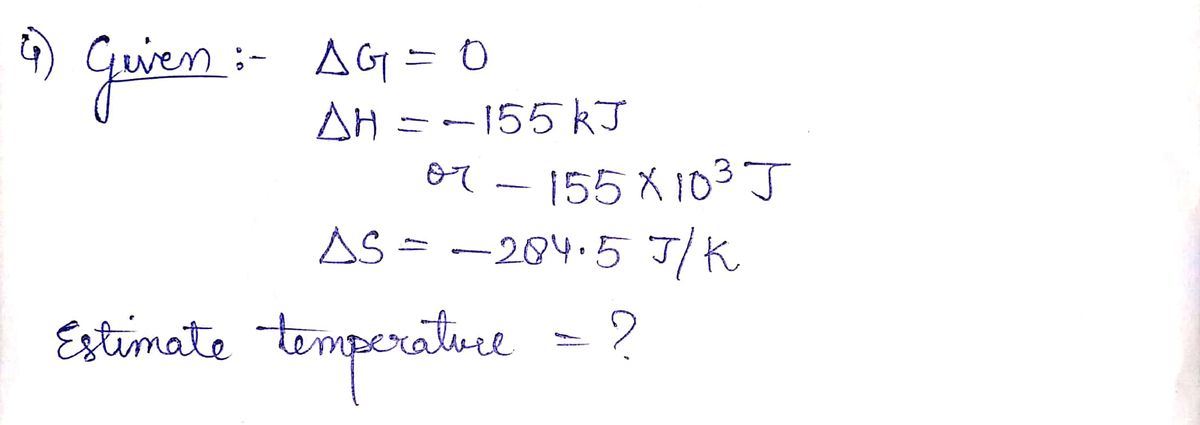
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









