A counselor predicts that an alpha blocker medication will influence social anxiety. In patients diagnosed with social anxiety, the average score is 36 on the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI). The counselor has 22 outside patients take the recommended dosage of the medication. After 35 days, the counselor tested the outside patients on STAI and obtained an average of 45 and a standard deviation of 12. What can be concluded with α = 0.05? A) critical value = test statistic = B) Compute CI C)Compute the corresponding effect size(s) and indicate magnitude(s). d= r2 =
A counselor predicts that an alpha blocker medication will influence social anxiety. In patients diagnosed with social anxiety, the average score is 36 on the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI). The counselor has 22 outside patients take the recommended dosage of the medication. After 35 days, the counselor tested the outside patients on STAI and obtained an average of 45 and a standard deviation of 12. What can be concluded with α = 0.05?
A)
critical value =
test statistic =
B) Compute CI
C)Compute the corresponding effect size(s) and indicate magnitude(s).
d=
r2 =
Null hypothesis:
µ=36.
Alternative hypothesis:
µ≠36.
This is a two tailed test.
Here, the sample mean, x-bar is 45.
Population mean, µ is 36.
Sample standard deviation, s = 12.
Sample size, n is 22.
Hence, the degrees of freedom is 21.
Given that the level of significance is 0.05.
Since the population standard deviation is unknown, the appropriate test is one sample t-test.
a).
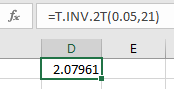
Critical value:
The critical value of t-distribution at 21 degrees of freedom and 0.05 level of significance can be obtained using the excel formula “=T.INV.2T(0.05,21)”.
The test statistic value can be obtained as follows:
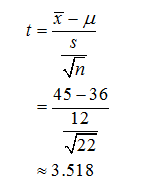
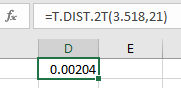
Computation of P-value:
The P-value of t-distribution at 21 degrees of freedom can be obtained using the excel formula “=T.DIST.2T(3.518,21)”.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 6 images









