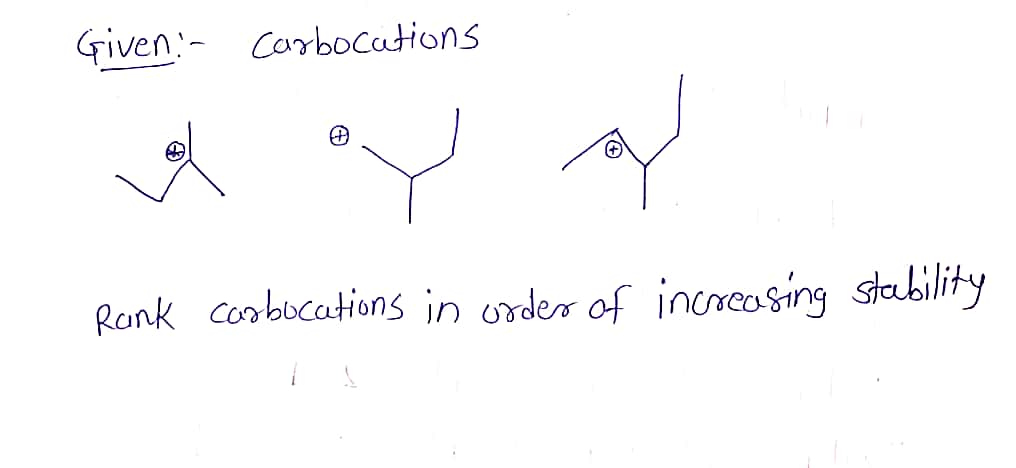
9. (a)Rank each of the carbocations below in the order of increasing stability (most stable =1) and explain the logic underlying your ranking.
Reactive Intermediates
In chemistry, reactive intermediates are termed as short-lived, highly reactive atoms with high energy. They rapidly transform into stable particles during a chemical reaction. In specific cases, by means of matrix isolation and at low-temperature reactive intermediates can be isolated.
Hydride Shift
A hydride shift is a rearrangement of a hydrogen atom in a carbocation that occurs to make the molecule more stable. In organic chemistry, rearrangement of the carbocation is very easily seen. This rearrangement can be because of the movement of a carbocation to attain stability in the compound. Such structural reorganization movement is called a shift within molecules. After the shifting of carbocation over the different carbon then they form structural isomers of the previous existing molecule.
Vinylic Carbocation
A carbocation where the positive charge is on the alkene carbon is known as the vinyl carbocation or vinyl cation. The empirical formula for vinyl cation is C2H3+. In the vinyl carbocation, the positive charge is on the carbon atom with the double bond therefore it is sp hybridized. It is known to be a part of various reactions, for example, electrophilic addition of alkynes and solvolysis as well. It plays the role of a reactive intermediate in these reactions.
Cycloheptatrienyl Cation
It is an aromatic carbocation having a general formula, [C7 H7]+. It is also known as the aromatic tropylium ion. Its name is derived from the molecule tropine, which is a seven membered carbon atom ring. Cycloheptatriene or tropylidene was first synthesized from tropine.
Stability of Vinyl Carbocation
Carbocations are positively charged carbon atoms. It is also known as a carbonium ion.

Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









