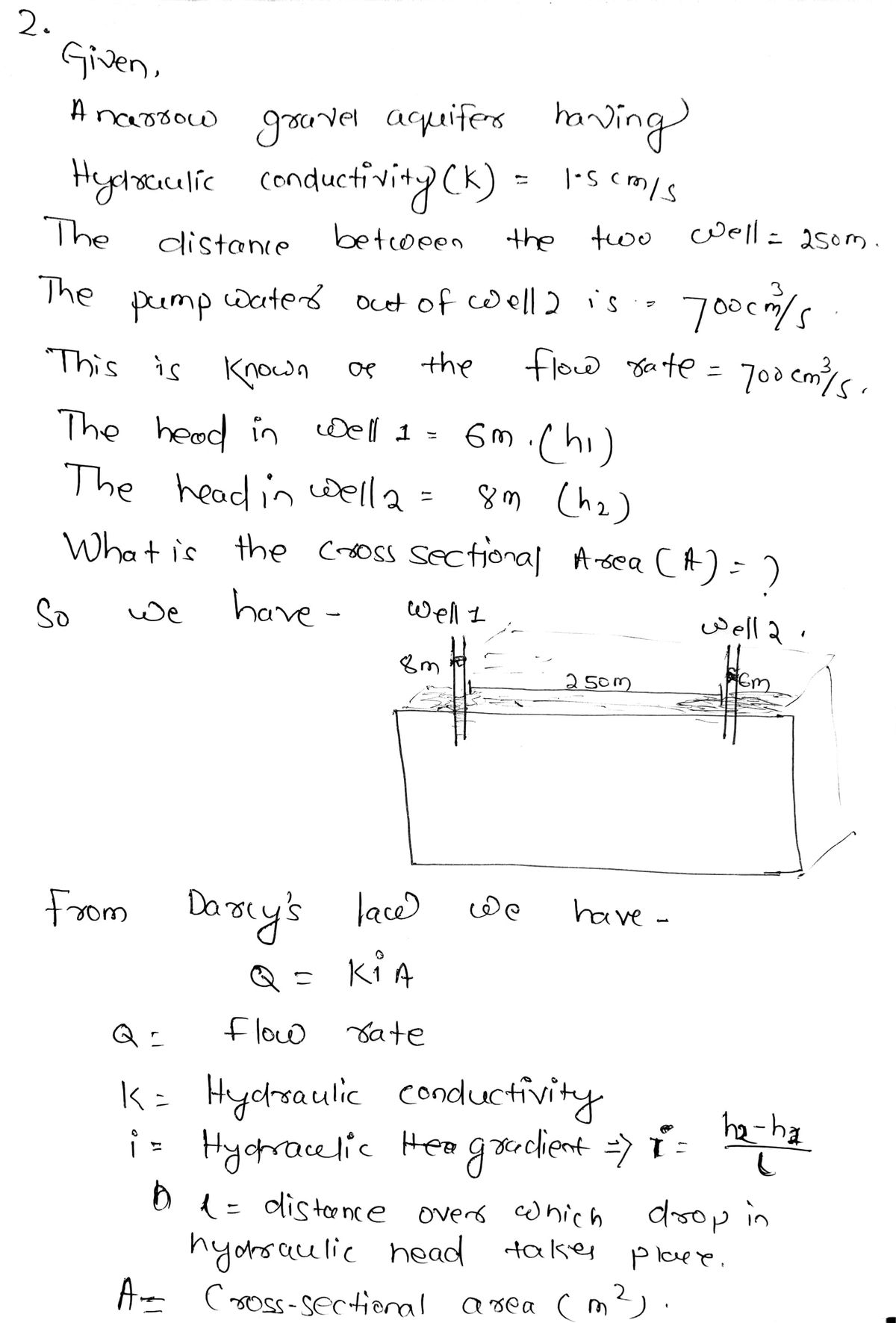
2. A long and narrow gravel aquifer is present below a floodplain, as illustrated in the figure below. From excavations into the aquifer at nearby locations, you know the gravel has a hydraulic conductivity of 1.5 cm/s. You install a well at the end of the aquifer (Well 2), and another 250 m away (Well 1), and then pump water out of Well 2 at a rate of 700 cm³/s. For this steady pumping rate, the head in that well is 6 m, while the head in Well 1 is 8 m. What is the cross-sectional area of the aquifer to the nearest m²?
2. A long and narrow gravel aquifer is present below a floodplain, as illustrated in the figure below. From excavations into the aquifer at nearby locations, you know the gravel has a hydraulic conductivity of 1.5 cm/s. You install a well at the end of the aquifer (Well 2), and another 250 m away (Well 1), and then pump water out of Well 2 at a rate of 700 cm³/s. For this steady pumping rate, the head in that well is 6 m, while the head in Well 1 is 8 m. What is the cross-sectional area of the aquifer to the nearest m²?
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
9th Edition
ISBN:9780134746241
Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Chapter1: The Study Of Minerals
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1LR
Related questions
Question
#2

Transcribed Image Text:1. In well A, you measure a water table elevation of 82 m above sea level. In well B, which
is 120 m away from well A, you measure a water table elevation of 76 m above sea level.
What is the average magnitude of the hydraulic gradient between well A and well B to the
nearest hundredth?
2. A long and narrow gravel aquifer is present below a floodplain, as illustrated in the
figure below. From excavations into the aquifer at nearby locations, you know the gravel
has a hydraulic conductivity of 1.5 cm/s. You install a well at the end of the aquifer (Well
2), and another 250 m away (Well 1), and then pump water out of Well 2 at a rate of 700
cm³/s. For this steady pumping rate, the head in that well is 6 m, while the head in Well 1
is 8 m. What is the cross-sectional area of the aquifer to the nearest m²?
Expert Solution
Step 1 Answer for 2

Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Applications and Investigations in Earth Science …
Earth Science
ISBN:
9780134746241
Author:
Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:
PEARSON

Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:
9780134041360
Author:
Greg Carbone
Publisher:
PEARSON

Environmental Science
Earth Science
ISBN:
9781260153125
Author:
William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Applications and Investigations in Earth Science …
Earth Science
ISBN:
9780134746241
Author:
Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:
PEARSON

Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:
9780134041360
Author:
Greg Carbone
Publisher:
PEARSON

Environmental Science
Earth Science
ISBN:
9781260153125
Author:
William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Earth Science (15th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:
9780134543536
Author:
Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:
PEARSON

Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)
Earth Science
ISBN:
9781337569613
Author:
G. Tyler Miller, Scott Spoolman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physical Geology
Earth Science
ISBN:
9781259916823
Author:
Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, Lisa
Publisher:
Mcgraw-hill Education,