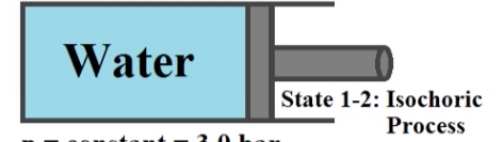
2 kg of water vapor in a piston-cylinder assembly expands at a constant pressure of 300 kPa (3.0 Bar) from a saturated vapor state to a volume of 2.064 m³. a. Determine the initial temperature, in °C b. Determine the final temperature, in °C c. Determine the work for the process, in kJ. Water p = constant = 3.0 bar V22.064 m³ m = 2 kg State 1-2: Isochoric Process
2 kg of water vapor in a piston-cylinder assembly expands at a constant pressure of 300 kPa (3.0 Bar) from a saturated vapor state to a volume of 2.064 m³. a. Determine the initial temperature, in °C b. Determine the final temperature, in °C c. Determine the work for the process, in kJ. Water p = constant = 3.0 bar V22.064 m³ m = 2 kg State 1-2: Isochoric Process
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:**Transcription for Educational Website**
---
**Problem Statement:**
A 2 kg mass of water vapor in a piston-cylinder assembly expands at a constant pressure of 300 kPa (3.0 Bar) from a saturated vapor state to a volume of 2.064 m³.
Tasks:
a. Determine the initial temperature, in °C.
b. Determine the final temperature, in °C.
c. Determine the work for the process, in kJ.
---
**Diagram Explanation:**
The image includes a schematic representation of the piston-cylinder system. In the diagram:
- The piston is shown as a movable boundary on the right side, enabling work to be done during expansion or compression.
- Within the cylinder, the substance is labeled as "Water," indicating the fluid inside.
- The diagram specifies the process between States 1 and 2 as an "Isochoric Process," which typically implies a constant volume; however, the problem states expansion at constant pressure. This may indicate a misunderstanding in the diagram labeling since the problem clearly outlines a constant pressure process.
Details highlighted in the diagram:
- **Pressure (p):** Constant at 3.0 bar
- **Final Volume (V₂):** 2.064 m³
- **Mass (m):** 2 kg
These parameters are essential for solving the problem as they help in calculating the required thermodynamic properties.
---
Expert Solution
Step 1: Given
The mass of water vapor is .
The pressure is .
The final volume is .
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 13 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY