1H 10 2H 2h 3H An IR spectrum, a 13C NMR spectrum, and a ¹H NMR spectrum were obtained for an unknown structure. Draw the structure of this compound. ppm
1H 10 2H 2h 3H An IR spectrum, a 13C NMR spectrum, and a ¹H NMR spectrum were obtained for an unknown structure. Draw the structure of this compound. ppm
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:**Transcription for Educational Website**
**Title**: Analyzing NMR Spectroscopy Data
**Description**: In this exercise, an IR spectrum, a \(^{13}C\) NMR spectrum, and a \(^{1}H\) NMR spectrum were obtained for an unknown structure. The task is to draw the structure of this compound based on the given data.
**Graph Explanation**:
The image displays a \(^{1}H\) NMR spectrum with specific peaks at different chemical shifts. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
- **Peaks and Chemical Shifts**:
- A singlet at approximately 11 ppm corresponding to 1H, indicating the presence of a deshielded proton, possibly an acidic proton.
- Peaks at around 7–8 ppm, each representing 2H, typically associated with aromatic protons.
- A significant singlet at approximately 4 ppm corresponding to 3H, suggesting a -CH3 group possibly adjacent to an electronegative atom or group.
- **X-axis (ppm)**: Parts per million, representing the chemical shift.
- **Y-axis**: Intensity of the signal (not labeled but standard for such spectra).
These insights will assist in deducing the possible structure of the compound based on its spectral data.

Transcribed Image Text:**Infrared Spectrum Analysis:**
**Graph 1 - Infrared (IR) Spectrum:**
- **X-axis:** Wavenumber (cm⁻¹) ranging from 4000 to 500 cm⁻¹.
- **Y-axis:** Absorbance or transmittance (not labeled, typically shown in IR spectra).
- **Description:** The IR spectrum displays several sharp peaks at various wavenumbers, indicating different molecular vibrations. High-intensity peaks appear around 3300, 2100, 1600, and 600 cm⁻¹, corresponding to specific functional groups or structural characteristics within the molecule being analyzed.
**Graph 2 - Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectrum:**
- **X-axis:** Chemical shift (ppm) ranging from -10 to 180 ppm.
- **Y-axis:** Intensity (not labeled, generally implies signal amplitude).
- **Description:** The NMR spectrum features multiple peaks that represent different environments of nuclei (typically hydrogen or carbon) within the compound. Notable peaks are observed at approximately 170, 150, and 70 ppm, providing insight into the chemical structure and composition of the sample.
These spectra are used in chemistry to determine the structural properties and molecular identity of substances, helping in research, quality control, and material verification.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Hello, this answer came back as incorrect, please help
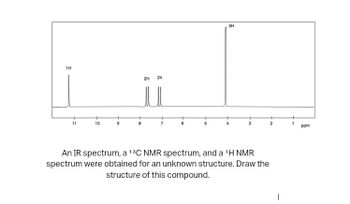
Transcribed Image Text:1H
11
10
2H
2h
5
3H
3
An IR spectrum, a 13C NMR spectrum, and a ¹H NMR
spectrum were obtained for an unknown structure. Draw the
structure of this compound.
2
1
ppm
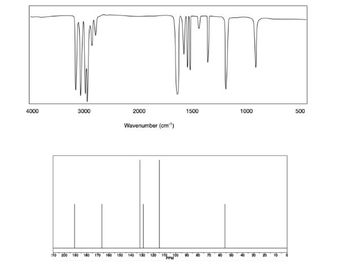
Transcribed Image Text:4000
3000
to 200
2000
150
Hill
MT
Wavenumber (cm¹)
140
1500
1000
500
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY