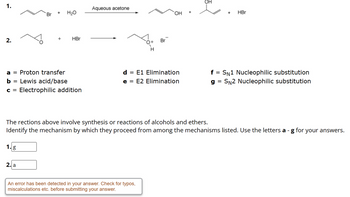
2. Br + + H₂O HBr a Proton transfer b = Lewis acid/base c = Electrophilic addition Aqueous acetone OH d = E1 Elimination e = E2 Elimination HBr f = SN1 Nucleophilic substitution g= SN2 Nucleophilic substitution
Ionic Equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium and ionic equilibrium are two major concepts in chemistry. Ionic equilibrium deals with the equilibrium involved in an ionization process while chemical equilibrium deals with the equilibrium during a chemical change. Ionic equilibrium is established between the ions and unionized species in a system. Understanding the concept of ionic equilibrium is very important to answer the questions related to certain chemical reactions in chemistry.
Arrhenius Acid
Arrhenius acid act as a good electrolyte as it dissociates to its respective ions in the aqueous solutions. Keeping it similar to the general acid properties, Arrhenius acid also neutralizes bases and turns litmus paper into red.
Bronsted Lowry Base In Inorganic Chemistry
Bronsted-Lowry base in inorganic chemistry is any chemical substance that can accept a proton from the other chemical substance it is reacting with.
![**Reaction Mechanisms in Alcohols and Ethers**
This section involves understanding the mechanisms through which certain reactions involving alcohols and ethers proceed. Below are two reactions, followed by a list of possible mechanisms. Your task is to identify the mechanism used in each reaction by choosing from the options provided.
**Reaction 1:**
A compound with a bromine group reacts with water in the presence of aqueous acetone to form an alcohol and HBr.
**Reaction 2:**
An epoxide reacts with HBr to form a bromohydrin intermediate.
**Mechanism Options:**
- **a = Proton transfer**
- **b = Lewis acid/base**
- **c = Electrophilic addition**
- **d = E1 Elimination**
- **e = E2 Elimination**
- **f = S<sub>N</sub>1 Nucleophilic substitution**
- **g = S<sub>N</sub>2 Nucleophilic substitution**
**Instructions:**
Match each reaction with the appropriate mechanism:
1. Reaction 1: [ ]
2. Reaction 2: [ ]
These reactions illustrate fundamental processes in organic chemistry, emphasizing the transformation of functional groups and the approach of different nucleophiles and electrophiles.
**Note:** Understanding these mechanisms is essential for predicting reaction outcomes and for the synthesis of complex molecules in organic chemistry.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F4f7442e5-ed1a-4154-ba5d-4813abad6cff%2F30441039-14c8-4a41-9a36-88d0bb0140cb%2F0qpif15_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Given are organic reactions.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Previous solution is incorrect, please help with correct solution, thank you