Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question

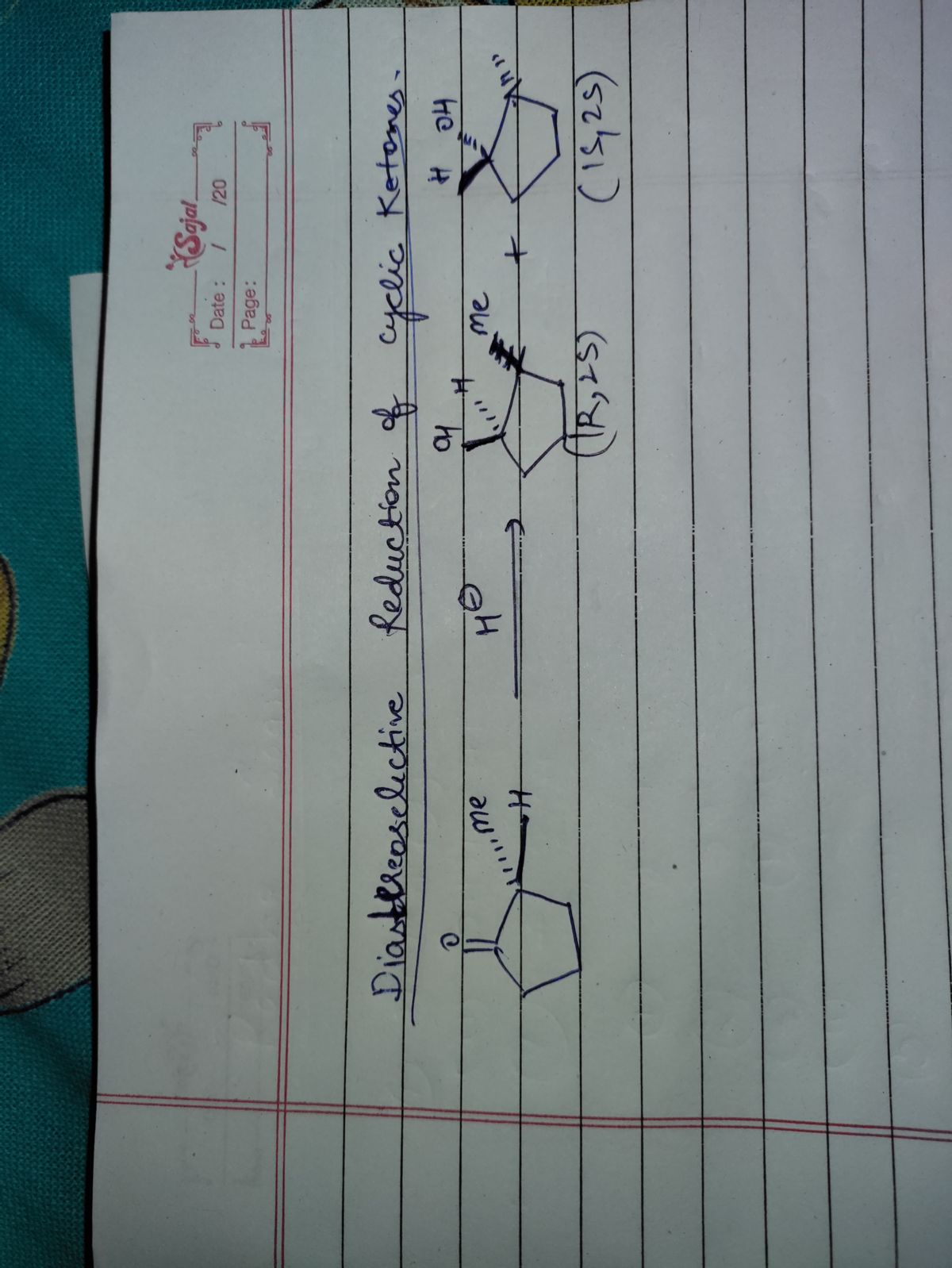
Transcribed Image Text:**Reaction Analysis**
**The reaction below will generate...**
A diagram features a six-membered carbon ring with an oxygen double-bonded (a ketone group). It undergoes the following reaction:
1. **Reagents:**
- LiAlH₄/ether
- Dilute H⁺/H₂O
**Reaction Options:**
- ○ a single diastereomer
- ○ a pair of diastereomers
- ○ a pair of enantiomers
- ○ a pair of constitutional isomers
**Explanation:**
The diagram depicts a ketone undergoing a reduction reaction. The LiAlH₄ is a strong reducing agent that will typically convert ketones to secondary alcohols. The following aqueous acidic workup (dil. H⁺/H₂O) facilitates the protonation of the alkoxide intermediate to form the alcohol. The outcome may produce different stereochemical results (e.g., diastereomers or enantiomers) based on the positions around the chiral center created in the reaction. Consider the stereochemistry at the site of reduction to determine the correct option.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY