
Comprehensive Part a. Reproduced in the following table are the first three lines from the 2% columns of each of several tables of mathematical values. For each of the following items, select from among these fragmentary tables the one from which the amount required can be obtained most directly (assuming that the complete table was available in each instance):
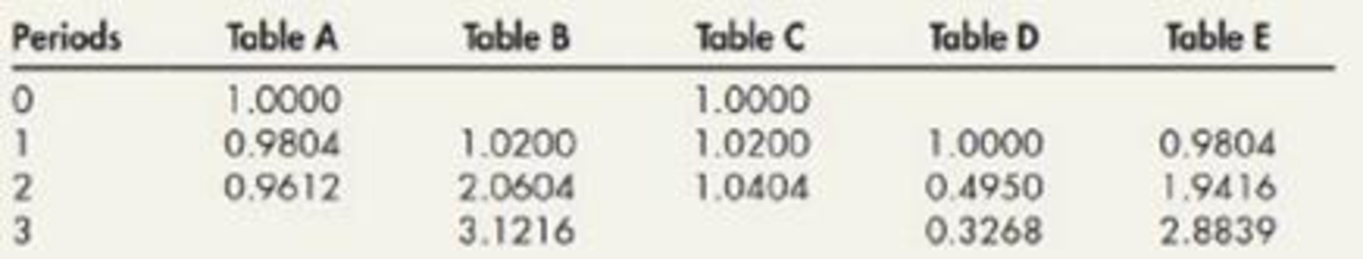
- 1. The amount to which a single sum would accumulate at compound interest by the end of a specified period (interest compounded annually)
- 2. The amount that must be deposited at the beginning of each of a specific number of years to provide for the accumulation, at annually compounded interest, of $1.02
- 3. The amount that must be deposited in a fund that will earn interest at a specified rate, compounded annually, in order to make possible the withdrawal of certain equal sums annually over a specified period starting 1 year from date of deposit
- 4. The amount of interest that will accumulate on a single deposit by the end of a specified period (interest compounded semiannually)
- 5. The amount that if paid now would settle a debt of larger amount due at a specified future date Part b. The following tables of values at 10% interest may be used as needed to answer the questions in this part of the problem.
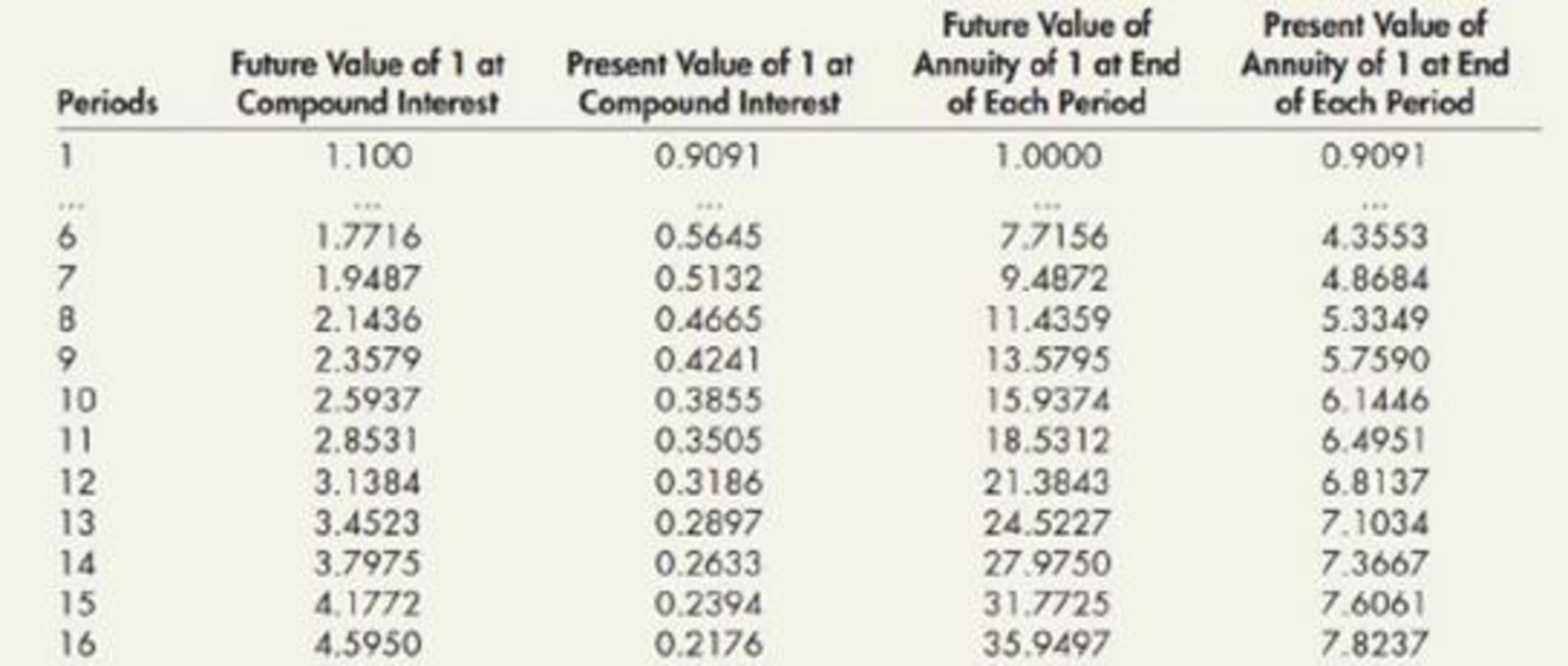
- 1. Your client will make annual payments of $2,500 into a fund at the dose of each year. She has asked you how many $2,500 annual payments will be required to bring the fund to $22,500 assuming that the fund earns interest at 10% compounded annually. Compute the total number of full payments of $2,500 required and the amount of the final payment if it does not require the entire $2,500. Carefully label all computations supporting your answer.
- 2. Your client wishes to provide for the payment of an obligation of $200,000 due on July 1,2026. He plans to deposit $20,000 in a special fund each July 1 for 7 years starting July 1, 2020. He wishes to make an initial deposit on July 1, 2019, of an amount that, with its accumulated interest, will bring the fund up to $200,000 at the maturity of the obligation. He expects that the fund will earn interest at the rate of 10% compounded annually. Compute the amount to be deposited July 1, 2019. Carefully label all computations supporting your answer.
a.
Determine the table from which amount required can be obtained most directly from the table for each of the given situations.
Explanation of Solution
Situation 1:
Accumulated amount from an investment of a single sum (present value) at a specified interest at the end of the specific period can be determined using the Amount from Table C (future value of $1).
Situation 2:
Whenever there is an equal cash flow occurs an annuity must be referred. Here deposit made at the beginning of the each period to accumulate a known amount of future value. To determine the required amount of deposit Table D’s amount can be used.
Situation 3:
To withdraw an equal amount of money annually at the end of each time period, a deposit must be made at present. Hence, the deposit amount can be determined by using Table E (it shows the present value of an ordinary annuity of $1)
Situation 4:
Table C must be used to determine the future value of a single sum at a compounded interest by the end of a certain future period.
Situation 5:
When a large amount due has to be settled at a specified future date, it can be discounted at a specified interest rate for the given time period and the balance amount can be paid at present date. Hence, Table A should be used to know the amount has to be paid at present date.
b. 1.
Determine the number of full $2,500 payment is required and determine the amount of required final payment.
Answer to Problem 10P
Client has to pay $2,500 each for first 6 years, and the amount of last payment will be $1,282.07
Explanation of Solution
Now, determine how many deposits of $2,500 have to be made by the client at the end of each year to accumulate $22,500.
While looking at 10% column in the future value of an ordinary annuity of $1 table (at the end of the time value money module), it is observed that the factor of 9.000000 is available between 6th and 7th cash flow. Here, it is necessary to consider only less number of cash flow that is 6, thereby the client can pay $2,500 each for 6 years, and as 7th payment the client can pay an amount of fund (less than $2,500) require to accumulate $25,500.
Hence, the client has to pay $2,500 each for 6 years.
Determine the amount of final payment (7th payment).
To determine the amount of the final payment, first calculate the future value of an annuity due of 6 payments of $2,500 at 10%.
Note:
Future value of ordinary annuity of $1: n = 7, i =10% is taken from the table value (Table 2 at the end of the time value money module). There is no separate table provided in this module for future value of annuity due. Thus, factor of annuity due is calculated with the help of ordinary annuity table.
Now, determine the amount of final payment.
Hence, the amount of last payment will be $1,282.07.
b. 2.
Determine the amount to be deposited on July 1, 2019.
Answer to Problem 10P
An amount of $5,263.25 required to be deposited as an initial payment on July 1, 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the deficiency at the end of 7 years.
Note:
Future value of ordinary annuity of $1: n = 7, i =10% is taken from the table value (Table 2 at the end of the time value money module).
Determine the amount of required initial deposit.
Hence, an amount of $5,263.25 required to be deposited as an initial payment on July 1, 2019.
Note:
Present value of $1: n = 7, i =10% is taken from the table value (Table 3 at the end of the time value money module).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter M Solutions
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College

