
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
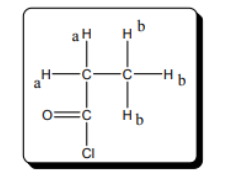
The number of chemically distinct protons in the given molecule should be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
NMR stands for nuclear magnetic resonance. A given compound contains different types of H-signals due to the presence of different magnetic environment within a molecule.
The number of signals obtained by the proton can be determined by spitting rule (n + 1), where n represents the number of the adjacent protons.
Answer to Problem 1CTQ
The number of chemically distinct proton in given molecule is 2.
Explanation of Solution
The protons present in the same environment are known as chemically equivalent protons. The number of chemically equivalent protons present in a molecule tells the number of peak obtained in the spectra for given molecule. The NMR spectra of the given molecule is represented as follows:
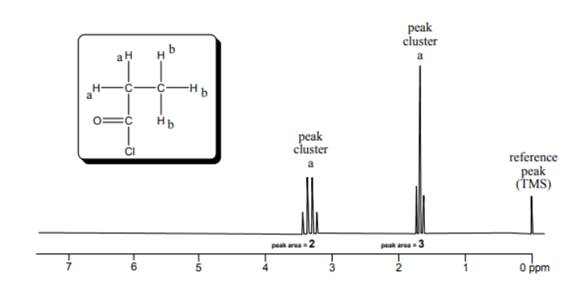
The triplet in the spectra represents that it has two neighbouring protons which means the triplet is representing protons a. on the other hand, the quartet means it has three neighbouring protons thus, representing the methyl group. As the number of peaks in the spectra is 2, that means two different chemically equivalent protons are present in the given molecule.
Thus, there are two chemically distinct protons in the model .
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter L4 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
- Given a system with an anodic overpotential, the variation of η as a function of current density- at low fields is linear.- at higher fields, it follows Tafel's law.Calculate the range of current densities for which the overpotential has the same value when calculated for both cases (the maximum relative difference will be 5%, compared to the behavior for higher fields).arrow_forwardUsing reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) = 2NH3 (g) AGº = -34. KJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 8.06 atm of nitrogen (N2) and 2.58 atm of ammonia (NH3) at 106. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: rise Under these conditions, will the pressure of N2 tend to rise or fall? ☐ x10 fall Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding H₂? In other words, if you said the pressure of N2 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding H2? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding H₂? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of H₂ needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. yes no ☐ atm Х ด ? olo 18 Ararrow_forwardFour liters of an aqueous solution containing 6.98 mg of acetic acid were prepared. At 25°C, the measured conductivity was 5.89x10-3 mS cm-1. Calculate the degree of dissociation of the acid and its ionization constant.Molecular weights: O (15.999), C (12.011), H (1.008).Limiting molar ionic conductivities (λ+0 and λ-0) of Ac-(aq) and H+(aq): 40.9 and 349.8 S cm-2 mol-1.arrow_forward
- Determine the change in Gibbs energy, entropy, and enthalpy at 25°C for the battery from which the data in the table were obtained.T (°C) 15 20 25 30 35Eo (mV) 227.13 224.38 221.87 219.37 216.59Data: n = 1, F = 96485 C mol–1arrow_forwardIndicate the correct options.1. The units of the transport number are Siemens per mole.2. The Siemens and the ohm are not equivalent.3. The Van't Hoff factor is dimensionless.4. Molar conductivity does not depend on the electrolyte concentration.arrow_forwardIdeally nonpolarizable electrodes can1. participate as reducers in reactions.2. be formed only with hydrogen.3. participate as oxidizers in reactions.4. form open and closed electrochemical systems.arrow_forward
- Indicate the options for an electrified interface:1. Temperature has no influence on it.2. Not all theories that describe it include a well-defined electrical double layer.3. Under favorable conditions, its differential capacitance can be determined with the help of experimental measurements.4. A component with high electronic conductivity is involved in its formation.arrow_forwardTo describe the structure of the interface, there are theories or models that can be distinguished by:1. calculation of the charge density.2. distribution of ions in the solution.3. experimentally measured potential difference.4. external Helmoltz plane.arrow_forwardIndicate the correct options when referring to Luther's equation:1. It is not always easy to compare its results with experimental results.2. It depends on the number of electrons exchanged in the species involved.3. Its foundation is thermodynamic.4. The values calculated with it do not depend on temperature.arrow_forward
- Indicate which of the unit options correspond to a measurement of current density.1. A s m-22. mC s-1 m-23. Ω m-24. V J-1 m-2arrow_forwardIndicate the options that are true when referring to electrode membranes:1. The Donnan potential, in general, does not always intervene in membranes.2. There are several ways to classify the same membrane.3. Any membrane can be used to determine the pH of a solution.4. Only one solution and one membrane are needed to determine the pH of that solution.arrow_forwardCalculate the maximum volume of carbon dioxide gasarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
