
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Reagents used are to be suggested in each part.
Concept introduction:
The reaction which occurs in between two esters or one ester and another carbonyl compound, and forms a carbon–carbon bond, in the presence of a strong base, leading to the formation of a β-keto ester or a β-diketone is known as Claisen condensation.
The removal of carbon dioxide from a carbonyl compound is termed as a decarboxylation reaction.
Sodium borohydride
Hydrogen bromide
Answer to Problem 1PP
Solution:
(a)
Sodium ethoxide
(b)
An acid
(c)
Heat
(d)
Sodium borohydride
(e)
Hydrogen bromide
(f)
Base
Explanation of Solution
The first step is similar to a crossed Claisen condensation. The reagent used in this reaction is sodium ethoxide. The molecular formula of sodium ethoxide is
The reaction shown is as follows:
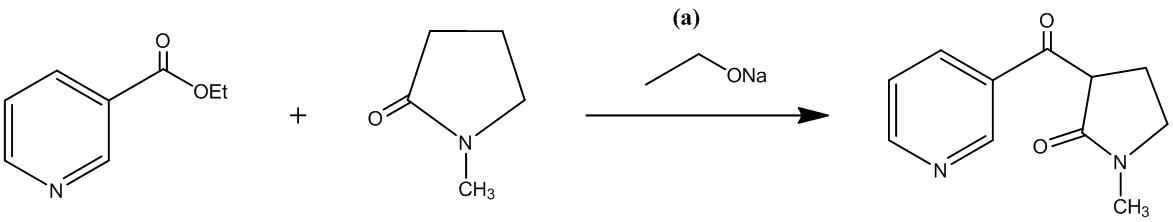
The second step involves the hydrolysis of an amide that is lactamide, which can be carried out with either an acid or a base. In the given reaction the desired product is formed by using an acid.
The reaction is shown as follows:
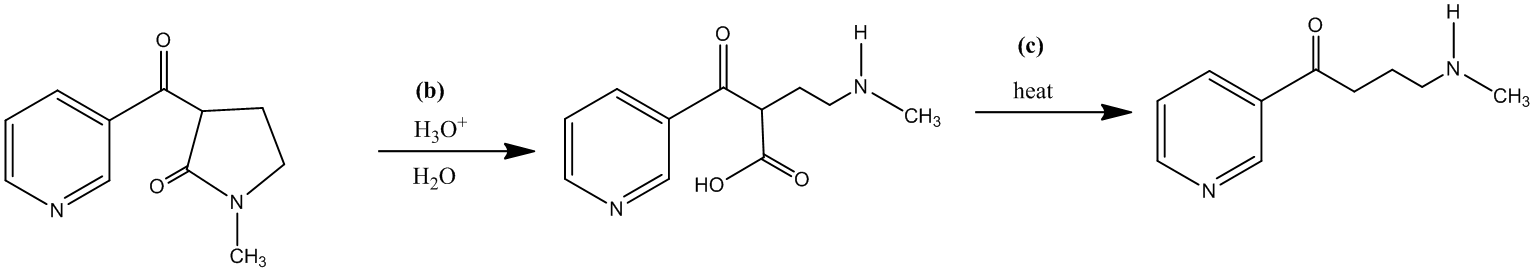
The third step is the decarboxylation of a β-keto acid, which is formed by the acidic hydrolysis of an amide. It requires only the application of heat to get the desired product. The reaction takes place along with the second step.
The forth step is the reduction of the ketone, obtained in third step, into a secondary alcohol. There are many reducing agents, which can reduce a ketone into an alcohol, for instance, sodium borohydride. The molecular formula for the same is
The reaction shown is as follows:
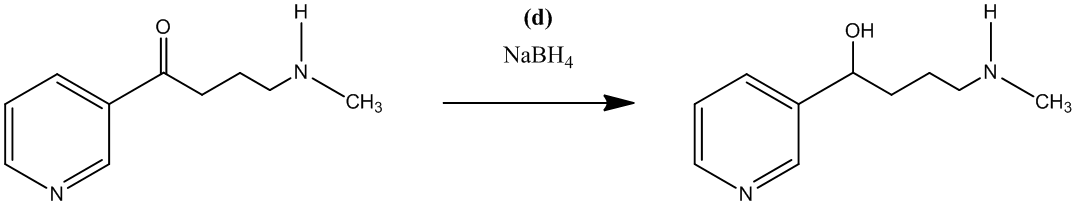
The fifth step is the conversion of the secondary alcohol, obtained in forth step, to an alkyl bromide by using hydrogen bromide. This reagent also gives a hydrobromide salt of the aliphatic
The reaction shown is as follows:
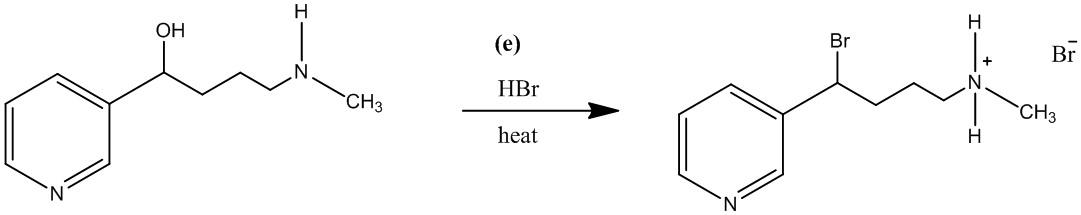
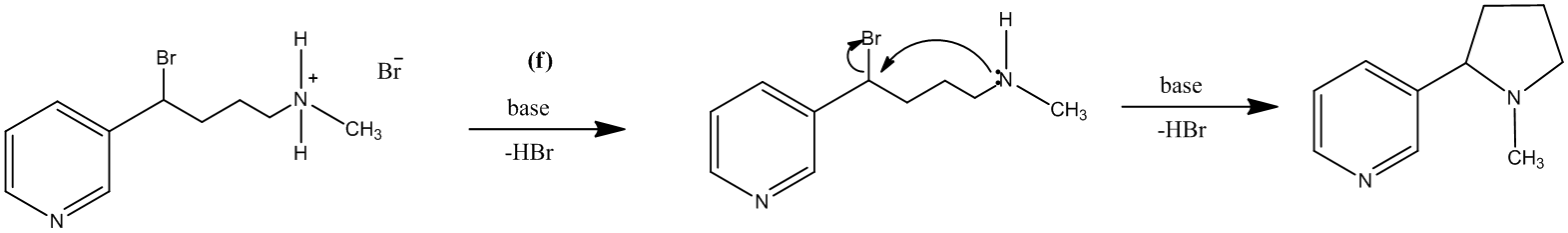
The treatment of the salt with base will lead to the formation of the secondary amine. It will further act as a nucleophile and attack the carbon atom bearing the bromine. This reaction leads to the formation of a five-membered ring and (±) nicotine.
The reaction is shown as follows:
The reagents that could be used for each part are suggested as:
(a): Sodium ethoxide
(b): An acid
(c): Heat
(d): Sodium borohydride
(e): Hydrogen bromide
(f): Base
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter H Solutions
ORGANIC CHEM. VOL.1+2-W/WILEYPLUS
- Find the pH of a 0.120 M solution of HNO2. Find the pH ignoring activity effects (i.e., the normal way). Find the pH in a solution of 0.050 M NaCl, including activityarrow_forwardPlease help me answer these three questions. Required info should be in data table.arrow_forwardDraw the major organic substitution product or products for (2R,3S)-2-bromo-3-methylpentane reacting with the given nucleophile. Clearly drawn the stereochemistry, including a wedged bond, a dashed bond and two in-plane bonds at each stereogenic center. Omit any byproducts. Bri CH3CH2O- (conc.) Draw the major organic product or products.arrow_forward
- Tartaric acid (C4H6O6) is a diprotic weak acid. A sample of 875 mg tartaric acid are dissolved in 100 mL water and titrated with 0.994 M NaOH. How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the first equivalence point? How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the second equivalence point?arrow_forwardIncluding activity, calculate the solubility of Pb(IO3)2 in a matrix of 0.020 M Mg(NO3)2.arrow_forwardIncluding activity coefficients, find [Hg22+] in saturated Hg2Br2 in 0.00100 M KBr.arrow_forward
- Including activity, calculate the pH of a 0.010 M HCl solution with an ionic strength of 0.10 M.arrow_forwardCan I please get the graph 1: Concentration vs. Density?arrow_forwardOrder the following series of compounds from highest to lowest reactivity to electrophilic aromatic substitution, explaining your answer: 2-nitrophenol, p-Toluidine, N-(4-methylphenyl)acetamide, 4-methylbenzonitrile, 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile.arrow_forward
- Ordene la siguiente serie de compuestos de mayor a menor reactividad a la sustitución aromática electrofílica, explicando su respuesta: ácido bencenosulfónico, fluorobenceno, etilbenceno, clorobenceno, terc-butilbenceno, acetofenona.arrow_forwardCan I please get all final concentrations please!arrow_forwardState the detailed mechanism of the reaction of benzene with isopropanol in sulfuric acid.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
