
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Reagents used are to be suggested in each part.
Concept introduction:
The reaction which occurs in between two esters or one ester and another carbonyl compound, and forms a carbon–carbon bond, in the presence of a strong base, leading to the formation of a β-keto ester or a β-diketone is known as Claisen condensation.
The removal of carbon dioxide from a carbonyl compound is termed as a decarboxylation reaction.
Sodium borohydride
Hydrogen bromide
Answer to Problem 1PP
Solution:
(a)
Sodium ethoxide
(b)
An acid
(c)
Heat
(d)
Sodium borohydride
(e)
Hydrogen bromide
(f)
Base
Explanation of Solution
The first step is similar to a crossed Claisen condensation. The reagent used in this reaction is sodium ethoxide. The molecular formula of sodium ethoxide is
The reaction shown is as follows:
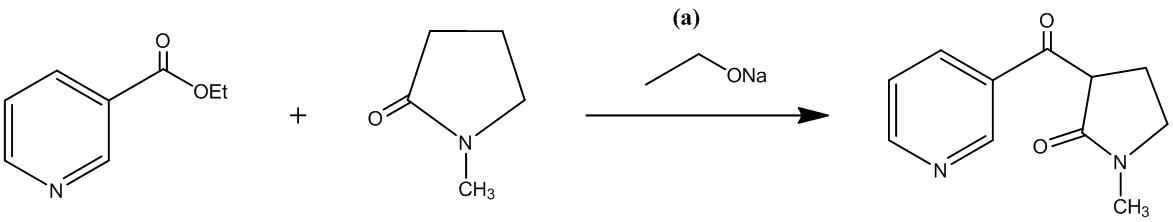
The second step involves the hydrolysis of an amide that is lactamide, which can be carried out with either an acid or a base. In the given reaction the desired product is formed by using an acid.
The reaction is shown as follows:
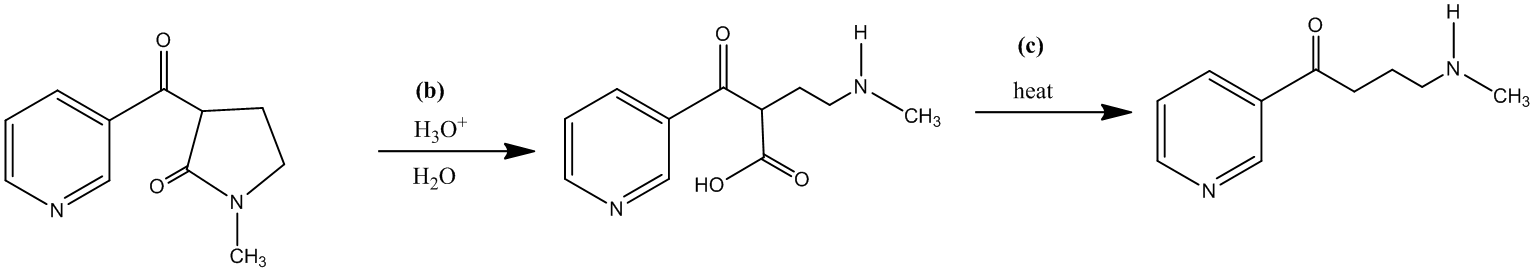
The third step is the decarboxylation of a β-keto acid, which is formed by the acidic hydrolysis of an amide. It requires only the application of heat to get the desired product. The reaction takes place along with the second step.
The forth step is the reduction of the ketone, obtained in third step, into a secondary alcohol. There are many reducing agents, which can reduce a ketone into an alcohol, for instance, sodium borohydride. The molecular formula for the same is
The reaction shown is as follows:
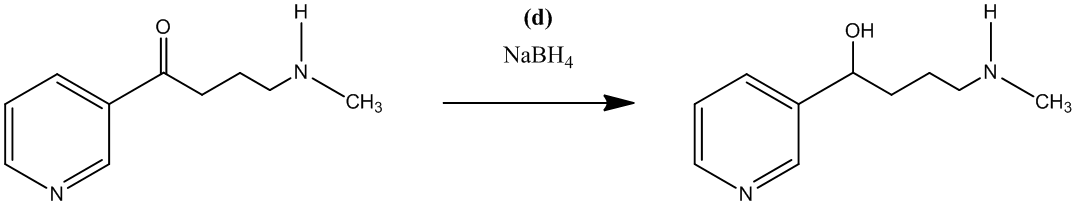
The fifth step is the conversion of the secondary alcohol, obtained in forth step, to an alkyl bromide by using hydrogen bromide. This reagent also gives a hydrobromide salt of the aliphatic
The reaction shown is as follows:
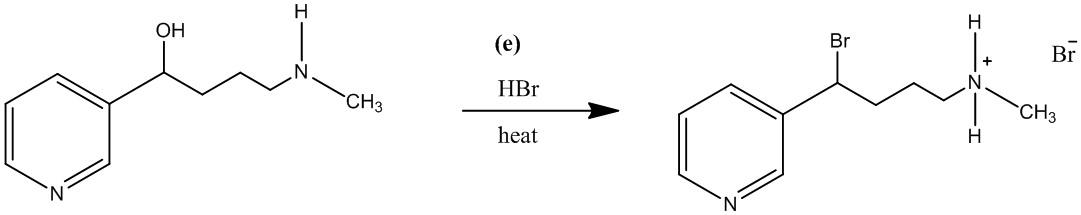
The treatment of the salt with base will lead to the formation of the secondary amine. It will further act as a nucleophile and attack the carbon atom bearing the bromine. This reaction leads to the formation of a five-membered ring and (±) nicotine.
The reaction is shown as follows:
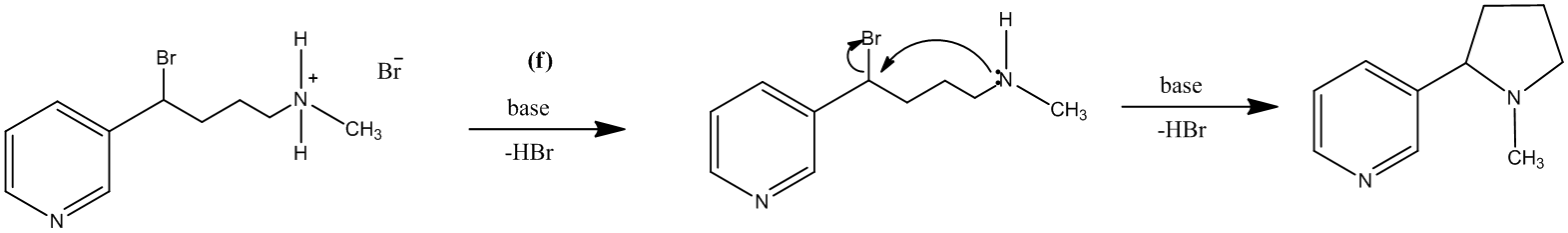
The reagents that could be used for each part are suggested as:
(a): Sodium ethoxide
(b): An acid
(c): Heat
(d): Sodium borohydride
(e): Hydrogen bromide
(f): Base
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter H Solutions
Organic Chemistry, 12e Study Guide/Student Solutions Manual
- Help me solve this problem.arrow_forwardDraw a mechanism for the following synthetic transformation including reagents and any isolable intermediates throughout the process. Please clearly indicate bond cleavage/formation using curly arrows. MeO2Carrow_forwardCHEM 310 Quiz 8 Organic Chemistry II Due: Tuesday, April 25th, at 11:59 pm. This quiz is open textbook / open notes - but you must work alone. You cannot use the internet or the solutions manual for the book. Scan in your work and record an explanation of your mechanism. You may record this any way that you like. One way would be to start an individual Zoom meeting, start recording, "share your screen" and then talk through the problem. This will be converted to an .mp4 file that you can upload into Canvas using the "record/upload media" feature. Pyridine, benzoic acid and benzene are dissolved in ethyl acetate. Design and provide a plan / flow chart for separating and isolating each of these components. Pyridine and benzene are liquids at room temperature. Benzoic acid is a solid. You have ethyl acetate, 2M NaOH, 2M HCI and anhydrous MgSO4 available, as well as all the glassware and equipment that you used in the organic lab this year. Provide accurate acid/base reactions for any…arrow_forward
- Can anyone help me solve this step by step. Thank you in advaarrow_forwardPlease draw the mechanism for this Friedel-crafts acylation reaction using arrowsarrow_forwardDraw the Fischer projection of D-fructose. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Skip Part Check AP 14 tv SC F1 F2 80 F3 a F4 ! 2 # 3 CF F5 75 Ax MacBook Air 894 $ 5olo % Λ 6 > W F6 K F7 &arrow_forward
- Consider this step in a radical reaction: Y What type of step is this? Check all that apply. Draw the products of the step on the right-hand side of the drawing area below. If more than one set of products is possible, draw any set. Also, draw the mechanism arrows on the left-hand side of the drawing area to show how this happens. ionization propagation initialization passivation none of the abovearrow_forward22.16 The following groups are ortho-para directors. (a) -C=CH₂ H (d) -Br (b) -NH2 (c) -OCHS Draw a contributing structure for the resonance-stabilized cation formed during elec- trophilic aromatic substitution that shows the role of each group in stabilizing the intermediate by further delocalizing its positive charge. 22.17 Predict the major product or products from treatment of each compound with Cl₁/FeCl₂- OH (b) NO2 CHO 22.18 How do you account for the fact that phenyl acetate is less reactive toward electro- philic aromatic substitution than anisole? Phenyl acetate Anisole CH (d)arrow_forwardShow how to convert ethyl benzene to (a) 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid and (b) 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid.arrow_forward
- Help me solve this problem. Thank you in advance.arrow_forward22.7 Predict the monoalkylated products of the following reactions with benzene. (a) AlCl3 Ya (b) AlCl3 (c) H3PO4 (d) 22.8 Think-Pair-Share AICI3 The reaction below is a common electrophilic aromatic substitution. SO3 H₂SO4 SO₂H (a) Draw the reaction mechanism for this reaction using HSO,+ as the electrophile. (b) Sketch the reaction coordinate diagram, where the product is lower in energy than the starting reactant. (c) Which step in the reaction mechanism is highest in energy? Explain. (d) Which of the following reaction conditions could be used in an electrophilic aro- matic substitution with benzene to provide substituted phenyl derivatives? (i) AICI3 HNO3 H₂SO4 K2Cr2O7 (iii) H₂SO4 (iv) H₂PO₁arrow_forwardIs an acid-base reaction the only type of reaction that would cause leavening products to rise?arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
