
Interpretation:
Mass spectra of
Concept introduction:
The ionization process causes the loss of a single electron from a closed-shell, uncharged molecule, so the molecular ion must have an unpaired electron, making it a free radical. More specifically, it also carries a positive charge, so the molecular ion is a radical cation, and
Answer to Problem G.1P
The structures for
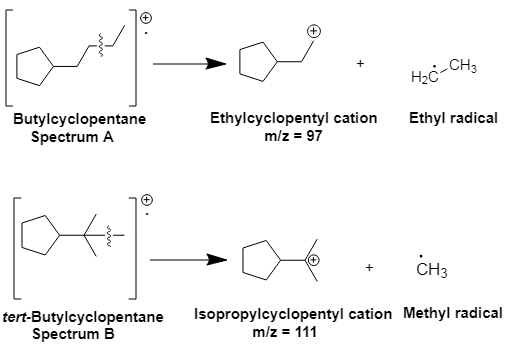
Explanation of Solution
The peak in Spectrum A at m/z =
Spectrum A is for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter G Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- 1. Provide a step-by-step mechanism for formation of ALL STEREOISOMERS in the following reaction. Na HCO3 (Sodium bicarbonate, baking soda) is not soluble in CH2Cl2. The powder is a weak base used to neutralize strong acid (pKa < 0) produced by the reaction. Redraw the product to show the configuration(s) that form at C-2 and C-4. Br2 OH CH2Cl2 Na* HCO3 Br HO OH + Na Br +arrow_forward2. Specify the solvent and reagent(s) required to carry out each of the following FGI. If two reagent sets must be used for the FGI, specify the solvent and reagent(s) for each reagent set. If a reaction cannot be carried out with reagents (sets) class, write NP (not possible) in the solvent box for reagent set #1. Use the letter abbreviation for each solvent; use a number abbreviation for reagent(s). Solvents: CH2Cl2 (A); H₂O (B); Reagents: HBr (1); R₂BH (6); H2SO4 (2); CH3OH (C); Br₂ (3); CH3CO₂H (D) NaHCO3 (4); Hg(OAc)2 (5); H₂O2/HO (7); NaBH4 (8) Reagent Set #1 Reagent Set #2 FGI + enant OH Solvent Reagent(s) Solvent Reagent(s)arrow_forwardGermanium (Ge) is a semiconductor with a bandgap of 2.2 eV. How could you dope Ge to make it a p-type semiconductor with a larger bandgap? Group of answer choices It is impossible to dope Ge and have this result in a larger bandgap. Dope the Ge with silicon (Si) Dope the Ge with gallium (Ga) Dope the Ge with phosphorus (P)arrow_forward
- Which of the following semiconductors would you choose to have photons with the longest possible wavelengths be able to promote electrons to the semiconductor's conduction band? Group of answer choices Si Ge InSb CdSarrow_forwardWhich of the following metals is the only one with all of its bands completely full? Group of answer choices K Na Ca Alarrow_forward2. Specify the solvent and reagent(s) required to carry out each of the following FGI. If two reagent sets must be used for the FGI, specify the solvent and reagent(s) for each reagent set. If a reaction cannot be carried out with reagents (sets) class, write NP (not possible) in the solvent box for reagent set #1. Use the letter abbreviation for each solvent; use a number abbreviation for reagent(s). Solvents: CH2Cl2 (A); Reagents: H₂O (B); CH3CO₂H (D) NaHCO3 (4); Hg(OAc)2 (5); HBr (1); R₂BH (6); H2SO4 (2); CH3OH (C); Br₂ (3); H₂O₂ / HO- (7); NaBH4 (8) Reagent Set #1 Reagent Set #2 FGI OH - α-α Br + enant Solvent Reagent(s) Solvent Reagent(s)arrow_forward
- Based on concepts from Lecture 3-5, which of the following ionic compounds should be most soluble in water? Group of answer choices MgO BeO CaO BaOarrow_forwardFrom an energy standpoint, which two process - in the correct order - are involved in the dissolving of an ionic compound crystal? Group of answer choices Water coordination to the ions followed by sublimation into the gas phase Sublimation of the crystal into gas-phase ions followed by water coordination to the ions Ion dissociation from the crystal followed by water coordination to the ions Water coordination to the ions followed by ion dissociation from the crystalarrow_forwardFor which Group 2 metal (M), is this process the most exothermic? M2+(g) + O2−(g) + CO2(g) → MO(s) + CO2(g) Group of answer choices M = Sr M = Mg M = Ca M = Baarrow_forward
- 2. Specify the solvent and reagent(s) required to carry out each of the following FGI. If two reagent sets must be used for the FGI, specify the solvent and reagent(s) for each reagent set. If a reaction cannot be carried out with reagents (sets) class, write NP (not possible) in the solvent box for reagent set #1. Use the letter abbreviation for each solvent; use a number abbreviation for reagent(s). Solvents: CH2Cl2 (A); H₂O (B); Reagents: HBr (1); H2SO4 (2); CH3OH (C); Br₂ (3); CH3CO₂H (D) NaHCO3 (4); Hg(OAc)2 (5); R₂BH (6); H₂O₂ / HO- (7); NaBH4 (8) Reagent Set #1 Reagent Set #2 FGI Solvent Reagent(s) Solvent Reagent(s) HO OHarrow_forwardFor which of the following ionic compounds would you expect the smallest difference between its theoretical and experimental lattice enthalpies? (You may assume these all have the same unit cell structure.) Electronegativities: Ca (1.0), Fe (1.8), Mg (1.2), O (3.5), S (2.5), Zn (1.6) Group of answer choices ZnO MgS CaO FeSarrow_forwardIn the Born-Haber cycle for KCl crystal formation, what enthalpy component must be divided by two? Group of answer choices KCl(s) enthalpy of formation Ionization energy for K(g) K(s) sublimation enthalpy Cl2 bond dissociation enthalpyarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





