
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name for the given trivial name is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols consist of an alkyl group attached to a hydroxyl group,
In a tertiary alcohol, the
IUPAC name for the given structure is determined by first identifying the longest continuous carbon chain or the largest ring containing the
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name for the given trivial name is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols consist of an alkyl group attached to a hydroxyl group,
In a tertiary alcohol, the
iso is a trivial name for the alkyl group, and its structure is
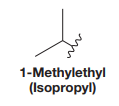
IUPAC name for the given structure is determined by first identifying the longest continuous carbon chain or the largest ring containing the functional group. The chain is then numbered so that to assign the lowest possible locator numbers to the carbon atoms that contain the functional group. The suffix is replaced by ol while writing the name.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name for the given trivial name is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols consist of an alkyl group attached to a hydroxyl group,
In a tertiary alcohol, the
IUPAC name for the given structure is determined by first identifying the longest continuous carbon chain or the largest ring containing the functional group. The chain is then numbered so as to assign the lowest possible locator numbers to the carbon atoms that contain the functional group. The suffix is replaced by ol while writing the name.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name for the given trivial name is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols consist of an alkyl group attached to a hydroxyl group,
In a tertiary alcohol, the
IUPAC name for the given structure is determined by first identifying the longest continuous carbon chain or the largest ring containing the functional group. The chain is then numbered so as to assign the lowest possible locator numbers to the carbon atoms that contain the functional group. The suffix is replaced by ol while writing the name.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter E Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY PRINCIPLES & MECHANISM
- if the answer is no reaction than state that and please hand draw!arrow_forward"I have written solutions in text form, but I need experts to rewrite them in handwriting from A to Z, exactly as I have written, without any changes."arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Please correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardreciprocal lattices rotates along with the real space lattices of the crystal. true or false?arrow_forwardDeducing the reactants of a Diels-Alder reaction vn the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? Δ O If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. • If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Product can't be made in one step. Explanation Checkarrow_forward
- Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: Δ ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Larrow_forward> Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? Δ • If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accesarrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: O O + A ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. eserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center >arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning



