
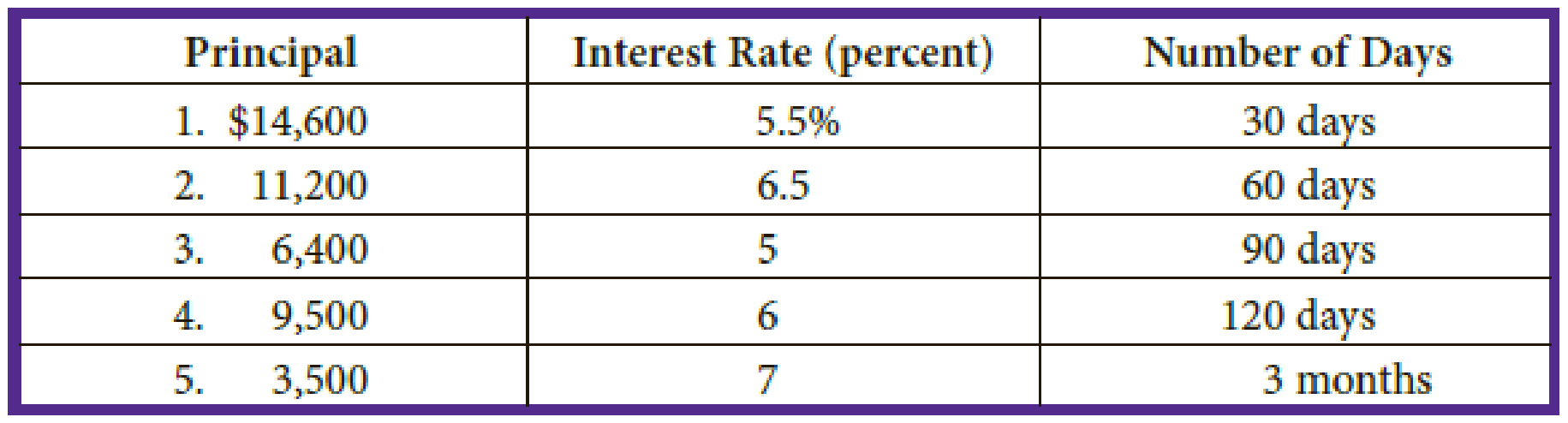
Part A: Calculate the interest on the following notes:
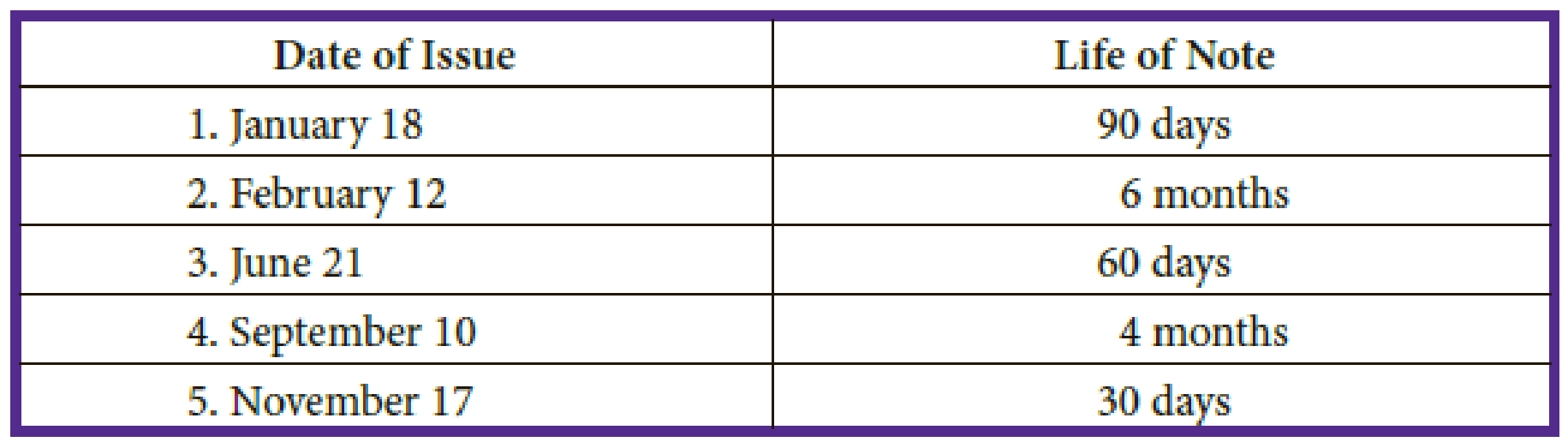
Part B: Determine the maturity dates on the following notes:
Check Figure
1. Interest, $66.92
A.
Compute the interest for the given notes.
Explanation of Solution
Interest: The money charged by the lender for using lender’s funds is referred to as interest. So, interest is an expense for the borrower and revenue for the lender. The interest is generally, computed as a percentage of the money borrowed.
Compute the interest for the given notes.
| Principal | × | Rate of Interest | × | Time of Note | = | Interest | |
| 1. | $14,600 | × | 5.5% | × | = | $66.92 | |
| 2. | 11,200 | × | 6.5% | × | = | 121.33 | |
| 3. | 6,400 | × | 5.0% | × | = | 80.00 | |
| 4. | 9,500 | × | 6.0% | × | = | 190.00 | |
| 5. | 3,500 | × | 7.0% | × | = | 61.25 | |
Table (1)
B.
Compute the maturity dates.
Explanation of Solution
Maturity date: The date on which the borrower should pay the principal amount of loan, or bond, is referred to as maturity date.
Compute the maturity date for the note issued on January 18 with the life of note for 90 days.
| Description | Count |
| Number of days left in January (From 18th to 31st) | 13 days |
| Number of days in February | 28 days |
| Number of days in March | 31 days |
| 72 days | |
| Number of days required in April to total 90 days (90 days–72 days) | 18 days |
| Total days of the term | 90 days |
Table (2)
Hence, the maturity date is 18th April.
Compute the maturity date for the note issued on February 12 with the life of note for 6 months.
| Description | Count |
| Number of months from February 12 to March 12 | 1 month |
| Number of months from March 12 to April 12 | 1 month |
| Number of months from April 12 to May 12 | 1 month |
| Number of months from May 12 to June 12 | 1 month |
| Number of months from June 12 to July 12 | 1 month |
| Number of months from July 12 to August 12 | 1 month |
| Total months of the term | 6 months |
Table (3)
Hence, the maturity date is 12th August.
Compute the maturity date for the note issued on June 21 with the life of note for 60 days.
| Description | Count |
| Number of days left in June (From 21st to 30th) | 9 days |
| Number of days in July | 31 days |
| 40 days | |
| Number of days required in August to total 60 days (60 days–40 days) | 20 days |
| Total days of the term | 60 days |
Table (4)
Hence, the maturity date is 20th August.
Compute the maturity date for the note issued on September 10 with the life of note for 4 months.
| Description | Count |
| Number of months from September 10 to October 10 | 1 month |
| Number of months from October 10to November 10 | 1 month |
| Number of months from November 10 to December 10 | 1 month |
| Number of months from December 10 to January 10 | 1 month |
| Total months of the term | 4 months |
Table (5)
Hence, the maturity date is 10th January.
Compute the maturity date for the note issued on November 17 with the life of note for 30 days.
| Description | Count |
| Number of days left in November (From 17th to 30th) | 13 days |
| Number of days required in December to total 30 days (30 days–13 days) | 17 days |
| Total days of the term | 30 days |
Table (6)
Hence, the maturity date is 17th December.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter D Solutions
EBK COLLEGE ACCOUNTING: A CAREER APPROA
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Fundamentals of Management (10th Edition)
Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains (12th Edition) (What's New in Operations Management)
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Principles of Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management (10th Edition)
Gitman: Principl Manageri Finance_15 (15th Edition) (What's New in Finance)
- provide correct answerarrow_forwardWrite down as many descriptions describing rock and roll that you can. From these descriptions can you come up with s denition of rock and roll? What performers do you recognize? What performers don’t you recognize? What can you say about musical inuence on these current rock musicians? Try to break these inuences into genres and relate them to the rock musicians. What does Mick Jagger say about country artists? What does pioneering mean? What kind of ensembles warrow_forwardRecently, Abercrombie & Fitch has been implementing a turnaround strategy since its sales had been falling for the past few years (11% decrease in 2014, 8% in 2015, and just 3% in 2016.) One part of Abercrombie's new strategy has been to abandon its logo-adorned merchandise, replacing it with a subtler look. Abercrombie wrote down $20.6 million of inventory, including logo-adorned merchandise, during the year ending January 30, 2016. Some of this inventory dated back to late 2013. The write-down was net of the amount it would be able to recover selling the inventory at a discount. The write-down is significant; Abercrombie's reported net income after this write-down was $35.6 million. Interestingly, Abercrombie excluded the inventory write-down from its non-GAAP income measures presented to investors; GAAP earnings were also included in the same report. Question: What impact would the write-down of inventory have had on Abercrombie's expenses, Gross margin, and Net income?arrow_forward
- Recently, Abercrombie & Fitch has been implementing a turnaround strategy since its sales had been falling for the past few years (11% decrease in 2014, 8% in 2015, and just 3% in 2016.) One part of Abercrombie's new strategy has been to abandon its logo-adorned merchandise, replacing it with a subtler look. Abercrombie wrote down $20.6 million of inventory, including logo-adorned merchandise, during the year ending January 30, 2016. Some of this inventory dated back to late 2013. The write-down was net of the amount it would be able to recover selling the inventory at a discount. The write-down is significant; Abercrombie's reported net income after this write-down was $35.6 million. Interestingly, Abercrombie excluded the inventory write-down from its non-GAAP income measures presented to investors; GAAP earnings were also included in the same report. Question: What impact would the write-down of inventory have had on Abercrombie's assets, Liabilities, and Equity?arrow_forwardNeed answer general Accountingarrow_forwardProvide correct answer of this question answer general Accountingarrow_forward
 College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College


