
Concept explainers
Draw a suitable tree and use general loop analysis to find i10 in the circuit of (a) Fig. A1.13a by writing just one equation with i10 as the variable; (b) Fig. A1.13b by writing just two equations with i10 and i3 as the variables.
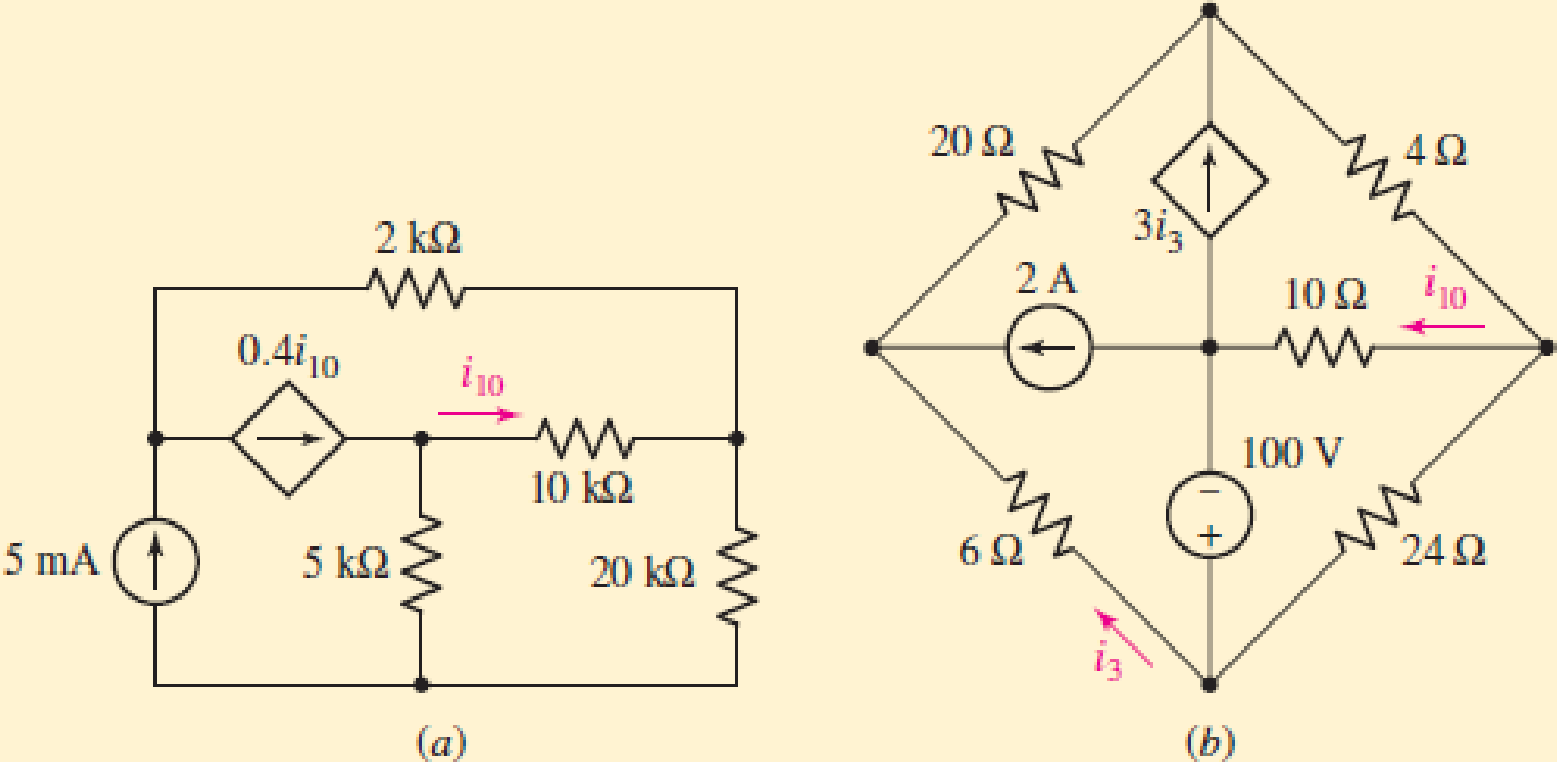
(a)
The value of the current
Answer to Problem 2P
The value of the current
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The given diagram is shown in Figure 1.
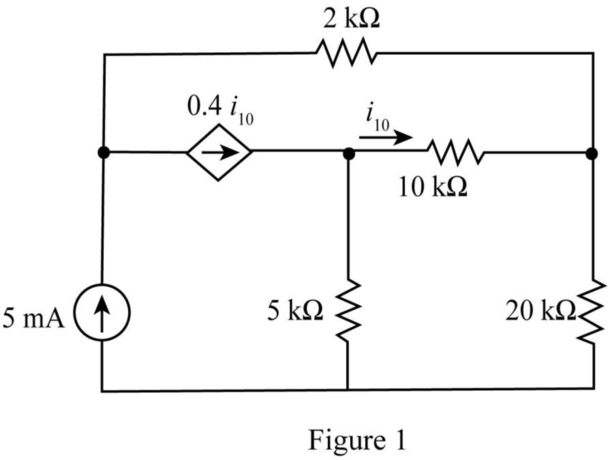
Calculation:
Draw the tree diagram of the given network.
The required diagram is shown in Figure 2.
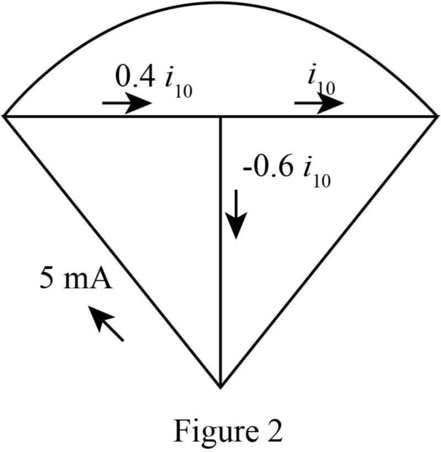
The current
The modified diagram is shown in Figure 3.
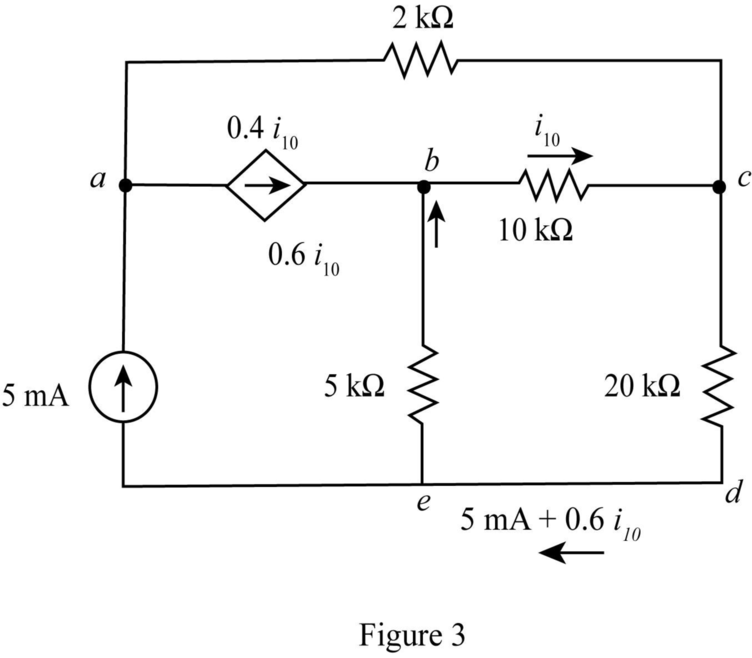
The conversion from
The conversion from
The conversion from
The conversion from
The conversion from
The conversion from
Write the KVL for the loop
The conversion from
The conversion from
Hence, the current
Conclusion:
Therefore, the value of the current
(b)
The value of the current
Answer to Problem 2P
The value of the current
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The given diagram is shown in Figure 4.
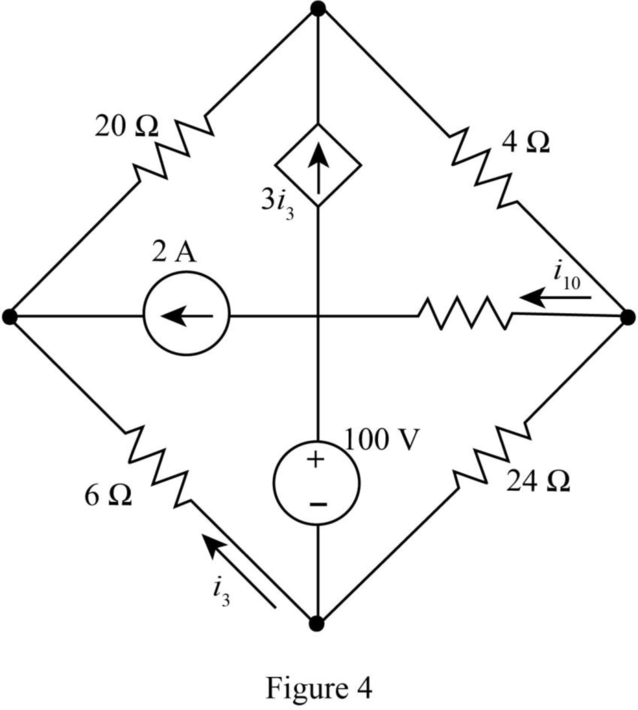
Calculation:
Draw tree diagram for the given network.
The required diagram is shown in Figure 5.
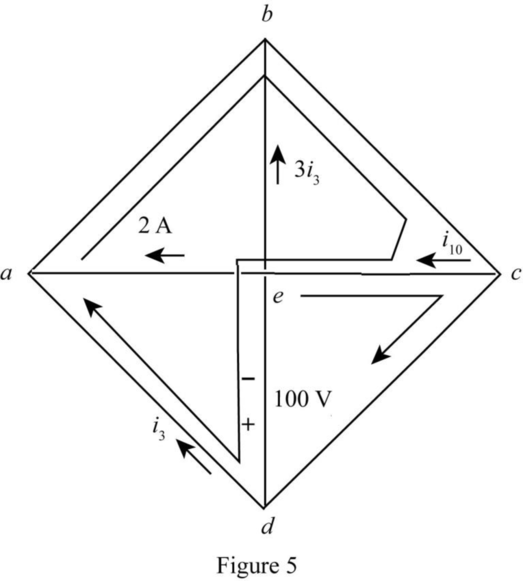
Write the KVL for the loop
Write the KVL for the loop
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the value of the current
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter A1 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
BASIC BIOMECHANICS
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Modern Database Management
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
- Note: You might want to do the last question first because the last question asks you to write some python code to calculate the zeros and poles. You could use that code here to help you (except the first problem which you should be able to do by inspection alone) Find the poles and zeros for each of the following transfer functions 1. S+3 H(s) = 8 5 2. H(s): = s238 +1 s2 +48 +3 3. s(s+4) H(s) s3+2s23s 4. 82-586 H(s) = - 8382-68 5. H(s): = s2 +48 +3 s45836s2 - 6arrow_forwardWrite python program to plot the zeros and poles if a user provides the coefficients for the numerator and denominator of the transfer function. Since the zeros and poles can be complex, this plot is essentially and argand diagram, where the x axis is the real component and the y axis the imaginary component of a given zero or pole. Create a method called plot-poles zeros(num, den) which takes two lists containing the coefficients. Here is an example and the resulting plot. num [1, 3, 7] # yields zeros at -1.5 +/- 2.17945j den = [1, 4, 5, 3] # yields poles at -2.46557, -0.7672143 +/- 0.7925519j plot_poles_zeros(num, den) Imaginary Page 2 Pole-Zero Plot 3 Zeros × Poles 2 1 -2 1 * Real When you write your code you are only allowed to use the packages numpy and matplotlib. Make sure you label the axes, provide a legend and give a title to your plot (See the example plot). Hint: numpy has a method called roots. When given a list of numbers corresponding to the coefficients of a polynomial,…arrow_forwarda) [10] Compute the zeros and poles for the following transfer function: $2 +5s+6 H(s): s2 +3s+2 b) [10] Factor both polynomials in the numerator and denominator. What does this tell you about one of the poles and zeros you found in a)?arrow_forward
- Pls show neat and whole solutionarrow_forward2. Find the steady-state current i(t) in the circuit shown below when Vs(t) = 100cos(500t -30) volts. Express your answer in cosine form i.e., i(t) Im cos (oot+). (20 pts) LLE) 10052 Vs (E) 40uF 0.3 Harrow_forward1. Determine the thevenin equivalent circuit (i.e., Vth, Zth) from the terminals a-b in the circuit shown below. (15 pts) j512 1052 1020arrow_forward
- Need schematic diagram for this computerized don't use guidelines answer okk will dislikearrow_forwardthe question with its answer but i still dont see how the expansion and the calculation done. please show detailed steps.arrow_forwardQ6) Find the current density J for the magnetic field intensity vectors: (a) H = x²yax + y²zay - 2xzaz pzap + p³a + 3pz²a (b) H = sin cos (c) H = a,arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





