
Concept explainers
a)
To determine: The decision table for the decision.
Introduction: Decision table is formats or visual representations were data is expressed arranged, determined and calculated to make a effective decision making. A decision table is a tabular representation that is used to analyze decision alternatives and states of nature.
b.
To determine: Maximax decision
Introduction:
Maximax is the decision making method which come decision making under uncertainty. This method finds an alternative that maximizes the maximum outcome of each alternative or we can say that calculating the maximum outcome within every alternatives.
c.
To determine: The minimax decision.
Introduction
Maximin is the decision making method which makes decision making under uncertainty. This method will find an alternative that maximizes the minimum outcome of every alternative or we can say that calculating the minimum outcome within the each alternative.
d.
To determine: Equally likely decision
Introduction
Equally likely is the decision method which come decision making under uncertainty. Under this condition, equal probability is assigned under each uncertainty state of nature.
e.
To draw: Decision tree. Assume each outcome is equally likely, and find the highest EMV.
Introduction:
Decision tree is graphical representation of decision making process which has state of nature, alternative, payoffs and their probabilities of outcomes.
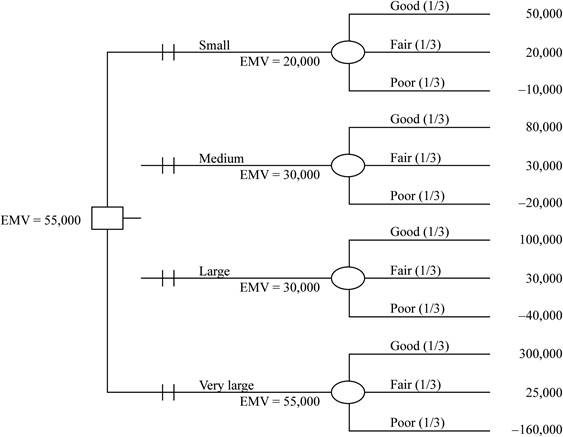
EMV: It is expected value or payout that has different possible state of nature, each with their associated possibilities.
Formula:
Here probabilities are equal likely in each case. So probabilities of the be 1/3= 0.3333
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter A Solutions
Mylab Operations Management With Pearson Etext -- Access Card -- For Operations Management: Sustainability And Supply Chain Management (13th Edition)
- SECTION B: TOPIC STRUCTURE CAPSTONE PROJECT TOPIC SUBMISSION TEMPLATE SECTION A: STUDENT DETAILS Student number Title (Mr/Miss/Ms/Mrs) Surname First name/s Title of research Date and year of registration Work Home Contact details Cell Region Date submitted Email 1.1 Title Insert title of the research. Choose a title that captures the essence of your proposed project. 1.2 Background to the Problem This section will be used to create the readers' interest. It can include a specific description of the topic that is to be investigated. A brief preview of the topic and the foundation of the problem should also be given. The researcher can achieve this through building up a detailed background of circumstances that lead to the problem being examined. Therefore, the background helps the reader understand the specific problem addressed by the researcher. This section should not include the background/history of the organisation. The background to the problem should not be more than ½ a page.…arrow_forwardDoes Nike Corporation's emphasis on lean operations help the Vietnamese workforce that still earns $150.00 minimum wage a month since 2014?arrow_forwardInformation Security Innovation within a Contemporary Business Environment All organisations using computers need to consider the security of information they keep. Many organisations utilise Websites for their core business functions and this results in monetary transactions being carried out on the Websites.arrow_forward
- Please help with a complete research report on the topic below: "Information Security Innovation within a Contemporary Business Environment " The format of the report should follow this below.arrow_forward7. Wireless Infrastructure in the Cloud Wireless devices have changed the way organisations and their customers interact. Wireless enabled devices have driven the mindset that wireless networks must be ubiquitous, fast, and constantly available. These are demands that have traditionally put organisations and their user communities in direct conflict with their IT departments, as constructing and maintaining wireless infrastructures are typically time-consuming, complex, and costly endeavours.arrow_forwardIM.54 A growing online retailer sells thousands of items yet has has one specialty product category with just 30 items. They want to classify these thirty items according to the annual dollar volume (revenue) generated by each item. The table below lists each item number, Annual Sales (in units), and Price per unit: Item # Annual Sales Price 1 221 $25.85 2 446 $14.15 3 8,940 $168.19 4 2,965 $15.99 5 1,322 $29.37 6 2,575 $12.77 7 767 $28.43 8 5,803 $163.01 9 2,673 $20.51 10 642 $14.71 11 4,168 $54.53 12 1,881 $22.55 13 2,417 $29.63 14 5,207 $36.41 15 1,381 $20.55 16 9,635 $173.69 17 17,406 $27.07 18 1,573 $25.99 19 6,471 $64.99 20 6,047 $29.83 21 433 $20.89 22 2,279 $53.59 23 15,532 $106.91 24 1,585 $4.09 25 5,376 $65.23 26 2,965 $37.93 27 2,048 $28.51 28 1,174 $22.99 29 381 $5.57 30 2,930 $3.43 Which item in the table above has the highest annual dollar volume? In the answer field below, write the ITEM # that…arrow_forward
- IM.84 An outdoor equipment manufacturer sells a rugged water bottle to complement its product line. They sell this item to a variety of sporting goods stores and other retailers. The manufacturer offers quantity discounts per the following discount schedule: Option Plan Quantity Price A 1 - 2,199 $5.00 B 2,200 - 3,699 $4.55 C 3,700+ $3.90 A large big-box retailer expects to sell 9,200 units this year. This retailer estimates that it incurs an internal administrative cost of $235 each time it places an order with the manufacturer. Holding cost for the retailer is $60 per case per year. (There are 52 units or water bottles per case.)Based on this information, and not taking into account any quantity discount offers, what is the calculated EOQ (in units)? (Display your answer to the nearest whole number.) Based on this information, sort each quantity discount plan from left to right by dragging the MOST preferred option plan to the left, and the LEAST preferred option…arrow_forwardPlease provide detailed solutions to the following problems/exercises (4 problems/exercises x 9 points each): 1) View the video ON Unveils ‘Lightspray’ Technology (4.55 mins, Ctrl+Click in the link), and The Secret of Lightspray (8.27 mins, Ctrl+Click in the link), answer the following questions: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wjmeaC-wlZs a) What is new about the design of ON’s shoes? b) How will ON’s new manufacturing technique affect location planning for footwear firms? c) How does ON focus on it sustainability strategy? Note: As a rough guideline, please try to keep the written submission to one or two paragraphs for each of the questions. 2) Unimed Hospital currently processes patient admissions through three admitting clerks who are set up to work in series, with respective reliabilities of 0.96, 0.95, and 0.90 (see figure below). a) Find the reliability of the current admission process. Due to rising patient complaints, the hospital administrator, Chimeg…arrow_forward3) A startup firm, Pocket International, has come up with a tiny programmable computer, NerdCom Mini Air, that sells for $49.99. The firm estimates that the programmable computers have an expected life that is exponential, with a mean of 24 months. The firm wants to estimate the probability that the NerdCom Mini Air will have a life that ends: a) after the initial 24 months of service. b) before the 24 months of service is completed. c) not before 48 months of service. Note: You could work out the problem by hand or use excel; in chapter 4S, section 4S.2 of the Stevenson text, reliability (finding the probability of functioning for a specified length of time) is covered with examples; chapters 4 & 4S Stevenson lecture power point slides 33 to 38 (chapters 4 & 4S lecture: 32.30 mins to 38.56 mins) cover reliability over time with examples.arrow_forward
- Discuss how training and development programs can be best presented to ultimately change the behavior of employees, often without their knowledge or awareness.arrow_forwardDoctor Earrow_forwardConsidering contemporary challenges in business, analyze a real-world case where a company successfully navigated a major shift in its marketing strategy to adapt to changing market dynamics. Discussion Question and Prompt: Identify the key factors that contributed to the success of their marketing strategy in the face of contemporary issues. How can businesses draw insights from this case to inform their own marketing strategies amid current business challenges?arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub



