
Concept explainers
Compute
Dungan Corporation is evaluating a proposal to purchase a new drill press to replace a less efficient machine presently in use. The cost of the new equipment at time 0, including delivery and installation, is $200,000. If it is purchased, Dungan will incur costs of $5,000 to remove the present equipment and revamp its facilities. This $5,000 is tax deductible at time 0.
Depreciation for tax purposes will be allowed as follows: year 1, $40,000; year 2, $70,000; and in each of years 3 through 5, $30,000 per year. The existing equipment has a book and tax value of $100,000 and a remaining useful life of 10 years. However, the existing equipment can be sold for only $40,000 and is being
Management has provided you with the following comparative
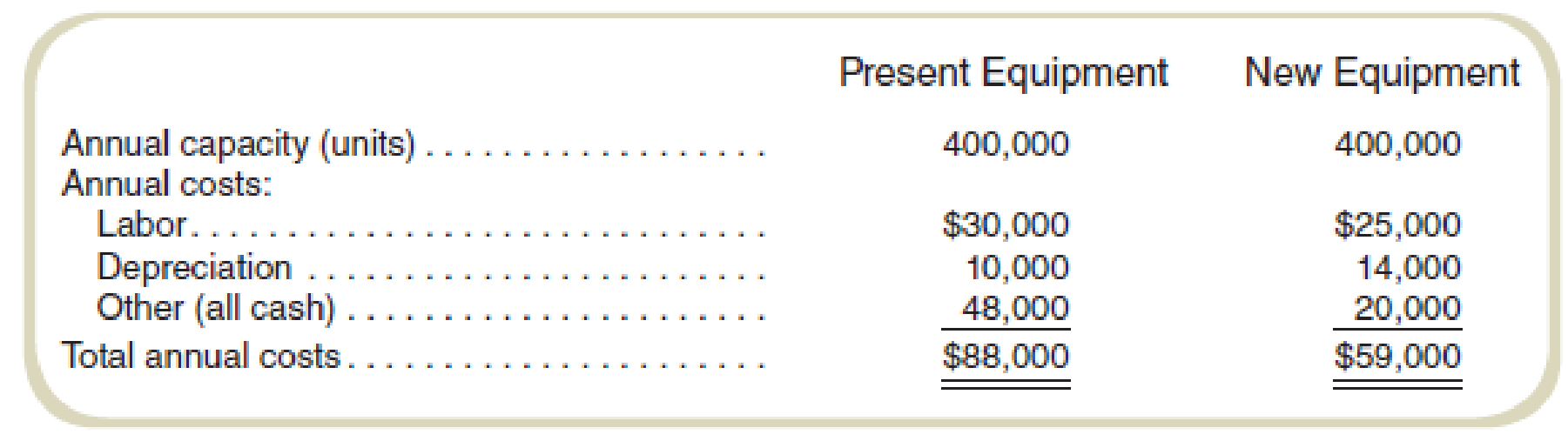
The existing equipment is expected to have a salvage value equal to its removal costs at the end of 10 years. The new equipment is expected to have a salvage value of $60,000 at the end of 10 years, which will be taxable, and no removal costs. No changes in
Required
- a. Calculate the removal costs of the existing equipment net of tax effects.
- b. Compute the depreciation tax shield.
- c. Compute the forgone tax benefits of the old equipment.
- d. Calculate the
cash inflow , net of taxes, from the sale of the new equipment in year 10. - e. Calculate the tax benefit arising from the loss on the old equipment.
- f. Compute the annual differential
cash flows arising from the investment in years 1 through 10. - g. Compute the net present value of the project.
a.
Compute the removal costs of the existing equipment net of tax effects.
Explanation of Solution
Net of tax:
Net of tax is the resultant amount that determines the final amount of the accounting period for the tax savings. The net of tax is determined by taking gross figures in the account.
Compute the equipment removal net of tax effects:
Thus, the value of equipment removal net of tax effects is $3,000.
b.
Compute the depreciation tax shield.
Explanation of Solution
Depreciation:
Depreciation is the method of calculating the value of the assets for the current accounting period. The value of any capital asset cannot be accounted for the total cost it has incurred in the period that it has been bought in. The value of the asset is distributed over different accounting periods according to the utility of the asset.
Compute the depreciation tax shield:
| Year | Depreciation | Tax shield | PV factor | Present value |
| 1 | $40,000 | $16,000 | 0.862 | $13,792 |
| 2 | $70,000 | $28,000 | 0.743 | $20,804 |
| 3 | $30,000 | $12,000 | 0.641 | $7,692 |
| 4 | $30,000 | $12,000 | 0.552 | $6,624 |
| 5 | $30,000 | $12,000 | 0.476 | $5,712 |
| Total | $200,000 | $80,000 | $54,624 |
Table: (1)
Thus, the PV of the depreciation schedule is $54,624.
c.
Compute the foregone tax benefits of the old equipment.
Explanation of Solution
Tax shield:
Tax shield refers to a reduction in taxable income. The reduction in taxable income is achieved by claiming the allowable deductions.
Compute the foregone tax benefits of the old equipment:
Thus, the value of foregone tax benefits is $4,000.
d.
Compute the cash inflow, net of taxes, from the sale of the new equipment in year 10.
Explanation of Solution
Gain:
Gain is the resultant value of the difference between revenue earned on sale and the cost of the same.
Compute gain from salvage of new equipment:
Thus, the value of gain from salvage of new equipment is $36,000.
e.
Compute the tax benefit arising from the loss on the old equipment.
Explanation of Solution
Tax shield:
Tax shield refers to a reduction in taxable income. The reduction in taxable income is achieved by claiming the allowable deductions.
Compute the tax benefit arising from a loss on old equipment:
Thus, the value of the tax benefit is $24,000.
f.
Compute the annual differential cash flows arising from the investment in years 1 through 10.
Explanation of Solution
Differential cash flow:
Differential cash flow is the difference between several options of businesses’ cash flows.
Compute the differential cash flows:
Thus, the value of differential cash flows is $19,800.
g.
Compute the net present value of the project.
Explanation of Solution
Net present value (NPV):
Net present value (NPV) is a type of intrinsic valuation analysis. NPV is the sum total of all the future cash flows (inflows/outflows) that will occur over the lifetime of a project discounted to the present.
| Year | |||||||||||
| Particulars | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Investment flows: | |||||||||||
| Equipment cost | ($200,000) | ||||||||||
| Removal | ($3,000) | ||||||||||
| Salvage of old equipment | $40,000 | ||||||||||
| Tax benefit-sale of old equipment | $24,000 | ||||||||||
| Periodic operating flows | $19,800 | $19,800 | $19,800 | $19,800 | $19,800 | $19,800 | $19,800 | $19,800 | $19,800 | $19,800 | |
| Tax shield from depreciation: | |||||||||||
| Year 1 | $16,000 | ||||||||||
| Year 2 | $28,000 | ||||||||||
| Year 3-5 | $12,000 | $12,000 | $12,000 | ||||||||
| Old equipment (forgone) | ($4,000) | ($4,000) | ($4,000) | ($4,000) | ($4,000) | ($4,000) | ($4,000) | ($4,000) | ($4,000) | ($4,000) | |
| Disinvestment: | |||||||||||
| Proceeds of disposal | $60,000 | ||||||||||
| Tax on gain | ($24,000) | ||||||||||
| Total cash flows | ($139,000) | $31,800 | $43,800 | $27,800 | $27,800 | $27,800 | $15,800 | $15,800 | $15,800 | $15,800 | $51,800 |
| PV factor | $1.000 | $0.862 | $0.743 | $0.641 | $0.552 | $0.476 | $0.410 | $0.354 | $0.305 | $0.263 | $0.227 |
|
Present value | ($139,000) | $27,412 | $32,543 | $17,820 | $15,346 | $13,233 | $6,478 | $5,593 | $4,819 | $4,155 | $11,759 |
| Net present value | $157 | ||||||||||
Table: (1)
Thus, the NPV of the project is $157.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter A Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF...(LL)-W/ACCESS>CUSTOM<
- I don't need ai answer accounting questionsarrow_forwardFraud Triangle The three elements of the fraud triangle are motive, opportunity, and rationalization. Individuals are motivated to commit fraud when these three elements come together: (1) some kind of perceived pressure, (2) some perceived opportunity, and (3) some way to rationalize the fraud as not being inconsistent with one's values. Please respond to the following in a discussion post: When looking at the evidence of fraud, describe the Who, What, Where, When, How, that contribute to the elements of the triangle of fraud action: the act, concealment, and conversion and its role in antifraud and forensic accounting investigations. Be sure to respond to at least one of your classmates' posts.arrow_forwardGeneral accountingarrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning

