
Mechanics of Materials
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134321158
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9.3, Problem 9.4FP
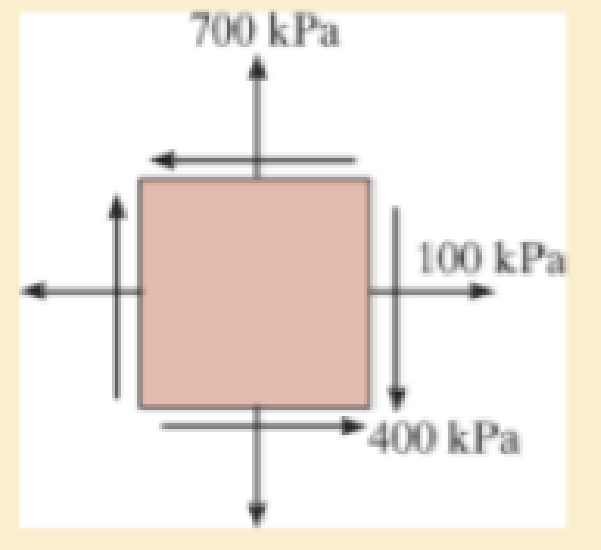
Determine the equivalent state of stress on an element at the same point that represents the maximum in-plane shear stress at the point.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Consider a double-fluid manometer attached to an air pipe shown below. If the specific gravity ofone fluid is 13.8, determine the specific gravity of the other fluid for the indicated absolutepressure of air. Take the atmospheric pressure to be 95 kPa
A race car enters the circular portion of a track that has a radius of 65 m. Disregard the 70 m in the picture. When the car enters the curve at point P, it is traveling with a speed of 120 km/h that is increasing at 5 m/s^2 . Three seconds later, determine the x and y components of velocity and acceleration of the car. I'm having trouble getting the correct y component of acceleration. all the other answers are correct. thank you!
Figure: 06_P041
Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, publishing a Prentice Hall
2. Determine the force that the jaws J of the metal cutters exert on the smooth cable C if 100-N
forces are applied to the handles. The jaws are pinned at E and A, and D and B. There is also
a pin at F.
400 mm
15°
20 mm
A
15°
15
D
B
30 mm² 80 mm
20 mm
400 mm
Figure: 06_P090
Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, publishing as Prentice Hall
15°
100 N
100 N
15°
Chapter 9 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials
Ch. 9.3 - In each case, the state of stress x, y, xy...Ch. 9.3 - Given the state of stress shown on the element,...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the normal stress and shear stress...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - Also, find the corresponding orientation of the...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the maximum principal stress at point B.Ch. 9.3 - Determine the principal stress at point C.Ch. 9.3 - Prove that the sum of the normal stresses x + y =...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the stress components acting on the...
Ch. 9.3 - Determine the stress components acting on the...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the normal stress and shear stress...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the normal stress and shear stress...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the stress components acting on the...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the stress components acting on the...Ch. 9.3 - Solve Prob.97 using the stress transformation...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the stress components acting on the...Ch. 9.3 - Solve Prob.99 using the stress transformation...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent slate of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the stress components acting on the...Ch. 9.3 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9.3 - The state of stress at a point is shown on the...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - A point on a thin plate is subjected to the two...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9.3 - The stress along two planes at a point is...Ch. 9.3 - The stress acting on two planes at a point is...Ch. 9.3 - The state of stress at a point in a member is...Ch. 9.3 - The grains of wood in the board make an angle of...Ch. 9.3 - The wood beam is subjected to a load of 12 kN. If...Ch. 9.3 - The internal loadings at a section of the beam are...Ch. 9.3 - Solve Prob.925 for point B. 925. The internal...Ch. 9.3 - Solve Prob.925 for point C. 925. The internal...Ch. 9.3 - It is subjected to a torque of 12 kip in. and a...Ch. 9.3 - The bell crank is pinned at A and supported by a...Ch. 9.3 - The beam has a rectangular cross section and is...Ch. 9.3 - A paper tube is formed by rolling a cardboard...Ch. 9.3 - Solve Prob.931 for the normal stress acting...Ch. 9.3 - The 2-in.-diameter drive shaft AB on the...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the principal stresses in the...Ch. 9.3 - The internal loadings at a cross section through...Ch. 9.3 - The internal loadings at a cross section through...Ch. 9.3 - The shaft has a diameter d and is subjected to the...Ch. 9.3 - The steel pipe has an inner diameter of 2.75 in....Ch. 9.3 - Solve Prob.938 for point B, w1ich is located on...Ch. 9.3 - The wide-flange beam is subjected to the 50-kN...Ch. 9.3 - Solve Pro b. 9-40 for point B located on the web...Ch. 9.3 - The box beam is subjected to the 26-kN force that...Ch. 9.3 - Solve Prob.942 for point B. 942. The box beam is...Ch. 9.4 - Use Mohrs circle to determine the normal stress...Ch. 9.4 - Also, find the corresponding orientation of the...Ch. 9.4 - Draw Mohrs circle and determine the principal...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the principal stresses at a point on the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the principal stresses at point A on the...Ch. 9.4 - Point A is just below the flange.Ch. 9.4 - Solve Prob.9-2 using Mohrs circle. 92. Determine...Ch. 9.4 - Solve Prob.93 using Mohrs circle. 93. Determine...Ch. 9.4 - Solve Prob.96 using Mohrs circle. 96. Determine...Ch. 9.4 - Solve Prob.911 using Mohrs circle. 911. Determine...Ch. 9.4 - Solve Prob.915 using Mohrs circle. 915. The state...Ch. 9.4 - Solve Prob.916 using Mohrs circle. 916. Determine...Ch. 9.4 - Mohrs circle for the state of stress is shown in...Ch. 9.4 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the equivalent state of stress if an...Ch. 9.4 - Draw Mohrs circle that describes each of the...Ch. 9.4 - Draw Mohrs circle trial describes each of the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9.4 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9.4 - Draw Mohrs circle that describes each of the...Ch. 9.4 - The grains of wood in the board make an angle of...Ch. 9.4 - The post is fixed supported at its base and a...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the principal stresses, the maximum...Ch. 9.4 - The thin-walled pipe has an inner diameter of 0.5...Ch. 9.4 - The frame supports the triangular distributed load...Ch. 9.4 - The frame supports the triangular distributed load...Ch. 9.4 - The rotor shaft of the helicopter is subjected to...Ch. 9.4 - The pedal crank for a bicycle has the cross...Ch. 9.4 - A spherical pressure vessel has an inner radius of...Ch. 9.4 - The cylindrical pressure vessel has an inner...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the normal and shear stresses at point D...Ch. 9.4 - Determine the principal stress at point D, Which...Ch. 9.4 - If the box wrench is subjected to the 50 lb force,...Ch. 9.4 - If the box wrench is subjected to the 50-lb force,...Ch. 9.4 - The post is fixed supported at its base and the...Ch. 9.5 - Draw the three Mohrs circles that describe each of...Ch. 9.5 - Draw the three Mohrs circles that describe the...Ch. 9.5 - Draw the three Mohrs circles that describe the...Ch. 9.5 - Determine the principal stresses and the absolute...Ch. 9.5 - Determine the principal stresses and the absolute...Ch. 9.5 - Determine the principal stresses and the absolute...Ch. 9.5 - Determine the principal stresses and the absolute...Ch. 9.5 - The solid shaft is subjected to a torque, bending...Ch. 9.5 - The frame is subjected to a horizontal force and...Ch. 9.5 - The bolt is fixed to its support at C. If a force...Ch. 9.5 - The bolt is fixed to its support at C. If a force...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9.1RPCh. 9 - The steel pipe has an inner diameter of 2.75 in....Ch. 9 - Determine the equivalent state of stress If an...Ch. 9 - The crane is used to support the 350-lb load....Ch. 9 - Determine the equivalent state of stress on an...Ch. 9 - The propeller shaft of the tugboat is subjected to...Ch. 9 - Determine the principal stresses in the box beam...Ch. 9 - Determine (a) the principal stresses and (b) the...Ch. 9 - Determine the stress components acting on the...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
A nozzle at A discharges water with an initial velocity of 36 ft/s at an angle with the horizontal. Determine ...
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Write a summary list of the problem-solving steps identified in the chapter, using your own words.
BASIC BIOMECHANICS
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
This optional Google account security feature sends you a message with a code that you must enter, in addition ...
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
How are relationships between tables expressed in a relational database?
Modern Database Management
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A telemetry system is used to quantify kinematic values of a ski jumper immediately before the jumper leaves the ramp. According to the system r=560 ft , r˙=−105 ft/s , r¨=−10 ft/s2 , θ=25° , θ˙=0.07 rad/s , θ¨=0.06 rad/s2 Determine the velocity of the skier immediately before leaving the jump. The velocity of the skier immediately before leaving the jump along with its direction is ? I have 112.08 ft/s but can't seem to get the direction correct. Determine the acceleration of the skier at this instant. At this instant, the acceleration of the skier along with its direction is ? acceleration is 22.8 ft/s^2 but need help with direction. Need help with velocity direction and acceleration direction please.arrow_forwardFor Problems 18-22 (Table 7-27), design a V-belt drive. Specify the belt size, the sheave sizes, the number of belts, the actual output speed, and the center distance.arrow_forwardonly 21arrow_forward
- only 41arrow_forwardNormal and tangential components-relate to x-y coordinates A race car enters the circular portion of a track that has a radius of 65 m. When the car enters the curve at point P, it is traveling with a speed of 120 km/h that is increasing at 5 m/s^2 . Three seconds later, determine the x and y components of velocity and acceleration of the car. I need help with finding the y component of the total acceleration. I had put -32 but its incorrect. but i keep getting figures around that numberarrow_forwardThe bracket BCD is hinged at C and attached to a control cable at B. Let F₁ = 275 N and F2 = 275 N. F1 B a=0.18 m C A 0.4 m -0.4 m- 0.24 m Determine the reaction at C. The reaction at C N Z F2 Darrow_forward
- Consider the angle bar shown in the given figure A W 240 mm B 80 mm Draw the free-body diagram needed to determine the reactions at A and B when a = 150 mm. This problem could also be approached as a 3-force body using method of Section 4.2B.arrow_forwardA telemetry system is used to quantify kinematic values of a ski jumper immediately before the jumper leaves the ramp. According to the system r=560 ft , r˙=−105 ft/s , r¨=−10 ft/s2 , θ=25° , θ˙=0.07 rad/s , θ¨=0.06 rad/s2 Determine the velocity of the skier immediately before leaving the jump. The velocity of the skier immediately before leaving the jump along with its direction is ? I have 112.08 ft/s but can't seem to get the direction correct. Determine the acceleration of the skier at this instant. At this instant, the acceleration of the skier along with its direction is ? acceleration is 22.8 ft/s^2 but need help with direction. Need help with velocity direction and acceleration direction please.arrow_forwardFor the stop bracket shown, locate the x coordinate of the center of gravity. Consider a = = 16.50 mm. 34 mm 62 mm 51 mm 10 mm 100 mm 88 mm 55 mm 45 mm The x coordinate of the center of gravity is mm.arrow_forward
- In the given figure, the bent rod ABEF is supported by bearings at C and D and by wire AH. The portion AB of the rod is 250 mm long, and the load W is 580 N. Assume that the bearing at D does not exert any axial thrust. H B A с 30° 250 mm D Z 50 mm 300 mm F 250 mm 50 mm W Draw the free-body diagram needed to determine the tension in wire AH and the reactions at C and D.arrow_forwardA 10-ft boom is acted upon by the 810-lb force as shown in the figure. D 6 ft 6 ft E B 7 ft C 6 ft x 4 ft W Draw the free-body diagram needed to determine the tension in each cable and the reaction at the ball-and-socket joint at A.arrow_forwardLocate the center of gravity of the sheet-metal form shown. Given: r = 26.40 mm . 50 mm 40 mm X 150 mm The center of gravity (✗) of the sheet-metal form is The center of gravity (Y) of the sheet-metal form is The center of gravity ( Z ) of the sheet-metal form is mm. mm. (Round the final answer to three decimal places.) mm.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Understanding Stress Transformation and Mohr's Circle; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_DH3546mSCM;License: Standard youtube license