
For Problems 7-21, please provide the following information.
(a) What is the level of significance? Stale the null and alternate hypotheses, (b) Check Requirements What sampling distribution will you use? Do you think the sample size is sufficiently large? Explain Compute the value of the sample test statistic and corresponding z value. (c) Find the P-value of the test statistic Sketch the sampling distribution and show the area corresponding to the P-value.
(d) Based on sour answers in parts (a) to (c), will you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis? Are the data statistic ally significant at level
(c) Interpret your conclusion in the context of the application.
Focus Problem: Benford's Law Please read the Focus Problem at the beginning of this chapter. Recall that Benford's Lam claims that numbers chosen from very large data files lend to have " 1“ as the first nonzero digit disproportionately often. In fact, research has shown that if you randomly draw a number from a very large data file, the
Now suppose you are an auditor for a very large corporation. The revenue report involves millions of numbers in a large computer file. Let us say you took a random sample of n = 215numerical entries from the file, and r = 46 of the entries had a first nonzero digit of 1. Let p represent the population proportion of all numbers in the corporate file that have a first nonzero digit of 1.
Test the claim that p is less than 0.301 Use
If p is in fact less than 0.301, would it make you suspect that there are not enough numbers in the data file with leading Is? Could this indicate that the books have been “cooked" by “pumping up" or inflating the numbers? Comment from the view point of a stockholder. Comment from the perspective of the Federal Bureau of Investigation as ii looks for money laundering in the form of false profits.
iii. Comment on the following statement “If we reject the null hypothesis at level of significance
(i)
(a)
The level of significance, null and alternative hypothesis.
Answer to Problem 7P
Solution: The level of significance is
Explanation of Solution
The level of significance is defined as the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true, it is denoted by
Null hypothesis
Alternative hypothesis
(b)
To find: The sampling distribution that should be used and compute the z value of the sample test statistic.
Answer to Problem 7P
Solution: The sampling distribution
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The
The standardized sample test statistic for
(c)
To find: The P-value of the test statistic and sketch the sampling distribution showing the area corresponding to the P-value.
Answer to Problem 7P
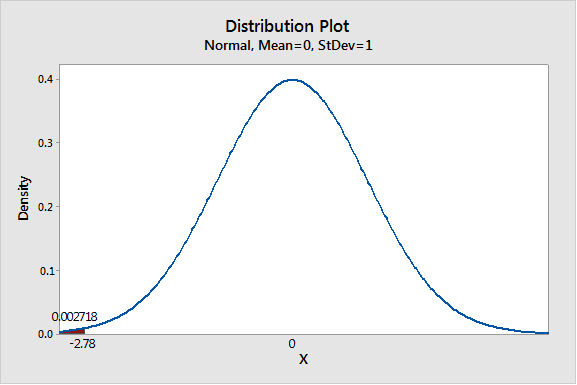
Solution: The P-value of the test statistic is 0.0027.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
We have z = -2.78
Using Table 3 from the Appendix to find the specified area:
Thus P- value is 0.0027.
Graph:
To draw the required graphs using the Minitab, follow the below instructions:
Step 1: Go to the Minitab software.
Step 2: Go to Graph > Probability distribution plot > View probability.
Step 3: Select ‘Normal’ and enter Mean 0 and Standard deviation 1.
Step 4: Click on the Shaded area > X value.
Step 5: Enter X-value as -2.78 and select ‘Left tail’.
Step 6: Click on OK.
The obtained distribution graph is:
(d)
Whether we reject or fail to reject the null hypothesisand whether the data is statistically significant for a level of significance of 0.01.
Answer to Problem 7P
Solution: The P-value
Explanation of Solution
The P-value of 0.0027 is less than the level of significance (
(e)
The interpretation for the conclusion.
Answer to Problem 7P
Solution: There is enough evidence to conclude that population proportion of numbers with leading “1” in the revenue file is less than the probability 0.301 predicted by Benford’s law.
Explanation of Solution
The P-value of 0.0027 is less than the level of significance (
(ii)
To explain: Whether it is suspect that there are not enough numbers in the data file with leading 1's.
Answer to Problem 7P
Solution: Yes. The revenue data file seems to include more numbers with higher first nonzero digits than Benford's law predicts.
Explanation of Solution
There are not enough numbers in the data file with leading 1's than Benford's law predicts. So, we cannot say that it is an indication of the books have been “cooked” by “pumping up” or inflating the numbers. From the viewpoint of a stockholder and the Federal Bureau of Investigation as it looks for money laundering, it may be true or false profit because there are not enough numbers in the data file with leading 1’s.
(iii)
To explain: Whether it recommends further investigation before accusing the company of fraud.
Answer to Problem 7P
Solution: Our data lead us to reject the null hypothesis, more investigation is merited.
Explanation of Solution
Since, we reject the null hypothesis
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK UNDERSTANDING BASIC STATISTICS
- The table available below shows the costs per mile (in cents) for a sample of automobiles. At a = 0.05, can you conclude that at least one mean cost per mile is different from the others? Click on the icon to view the data table. Let Hss, HMS, HLS, Hsuv and Hмy represent the mean costs per mile for small sedans, medium sedans, large sedans, SUV 4WDs, and minivans respectively. What are the hypotheses for this test? OA. Ho: Not all the means are equal. Ha Hss HMS HLS HSUV HMV B. Ho Hss HMS HLS HSUV = μMV Ha: Hss *HMS *HLS*HSUV * HMV C. Ho Hss HMS HLS HSUV =μMV = = H: Not all the means are equal. D. Ho Hss HMS HLS HSUV HMV Ha Hss HMS HLS =HSUV = HMVarrow_forwardQuestion: A company launches two different marketing campaigns to promote the same product in two different regions. After one month, the company collects the sales data (in units sold) from both regions to compare the effectiveness of the campaigns. The company wants to determine whether there is a significant difference in the mean sales between the two regions. Perform a two sample T-test You can provide your answer by inserting a text box and the answer must include: Null hypothesis, Alternative hypothesis, Show answer (output table/summary table), and Conclusion based on the P value. (2 points = 0.5 x 4 Answers) Each of these is worth 0.5 points. However, showing the calculation is must. If calculation is missing, the whole answer won't get any credit.arrow_forwardBinomial Prob. Question: A new teaching method claims to improve student engagement. A survey reveals that 60% of students find this method engaging. If 15 students are randomly selected, what is the probability that: a) Exactly 9 students find the method engaging?b) At least 7 students find the method engaging? (2 points = 1 x 2 answers) Provide answers in the yellow cellsarrow_forward
- In a survey of 2273 adults, 739 say they believe in UFOS. Construct a 95% confidence interval for the population proportion of adults who believe in UFOs. A 95% confidence interval for the population proportion is ( ☐, ☐ ). (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardFind the minimum sample size n needed to estimate μ for the given values of c, σ, and E. C=0.98, σ 6.7, and E = 2 Assume that a preliminary sample has at least 30 members. n = (Round up to the nearest whole number.)arrow_forwardIn a survey of 2193 adults in a recent year, 1233 say they have made a New Year's resolution. Construct 90% and 95% confidence intervals for the population proportion. Interpret the results and compare the widths of the confidence intervals. The 90% confidence interval for the population proportion p is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) J.D) .arrow_forward
- Let p be the population proportion for the following condition. Find the point estimates for p and q. In a survey of 1143 adults from country A, 317 said that they were not confident that the food they eat in country A is safe. The point estimate for p, p, is (Round to three decimal places as needed.) ...arrow_forward(c) Because logistic regression predicts probabilities of outcomes, observations used to build a logistic regression model need not be independent. A. false: all observations must be independent B. true C. false: only observations with the same outcome need to be independent I ANSWERED: A. false: all observations must be independent. (This was marked wrong but I have no idea why. Isn't this a basic assumption of logistic regression)arrow_forwardBusiness discussarrow_forward
- Spam filters are built on principles similar to those used in logistic regression. We fit a probability that each message is spam or not spam. We have several variables for each email. Here are a few: to_multiple=1 if there are multiple recipients, winner=1 if the word 'winner' appears in the subject line, format=1 if the email is poorly formatted, re_subj=1 if "re" appears in the subject line. A logistic model was fit to a dataset with the following output: Estimate SE Z Pr(>|Z|) (Intercept) -0.8161 0.086 -9.4895 0 to_multiple -2.5651 0.3052 -8.4047 0 winner 1.5801 0.3156 5.0067 0 format -0.1528 0.1136 -1.3451 0.1786 re_subj -2.8401 0.363 -7.824 0 (a) Write down the model using the coefficients from the model fit.log_odds(spam) = -0.8161 + -2.5651 + to_multiple + 1.5801 winner + -0.1528 format + -2.8401 re_subj(b) Suppose we have an observation where to_multiple=0, winner=1, format=0, and re_subj=0. What is the predicted probability that this message is spam?…arrow_forwardConsider an event X comprised of three outcomes whose probabilities are 9/18, 1/18,and 6/18. Compute the probability of the complement of the event. Question content area bottom Part 1 A.1/2 B.2/18 C.16/18 D.16/3arrow_forwardJohn and Mike were offered mints. What is the probability that at least John or Mike would respond favorably? (Hint: Use the classical definition.) Question content area bottom Part 1 A.1/2 B.3/4 C.1/8 D.3/8arrow_forward
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill

