
The exergy destruction associated with each process of the Brayton cycle and the exergy of the exhaust gases at the exit of the regenerator.
Answer to Problem 150P
The exergy destruction associated with process 1-2 for Brayton cycle is
The exergy destruction associated with process 3-4 for Brayton cycle is
The exergy destruction associated with regeneration process for Brayton cycle is
The exergy destruction associated with process 5-3 for Brayton cycle is
The exergy destruction associated with process 6-1 for Brayton cycle is
The exergy of the exhaust gases at the exit of the regenerator is
Explanation of Solution
Draw
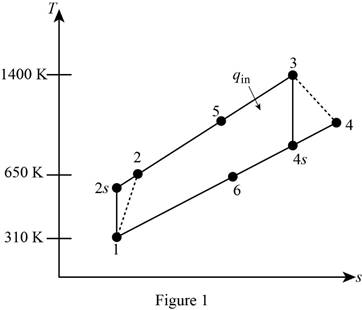
Write the expression of pressure ratio for the regenerative Brayton cycle
Here, pressure at state 2 is
Write the pressure ratio and pressure relation for the process 3-4.
Here, pressure at state 3 is
Write the expression of efficiency of the turbine
Here, enthalpy at state 3 is
Write the expression of heat added due to regeneration
Here, the effectiveness of the regenerator is
Write the expression of net work output of the regenerative Brayton cycle
Here, the work output by the turbine is
Write the expression of heat input to the regenerative Brayton cycle
Write the expression of heat rejected by the regenerative Brayton cycle
Write the expression of specific enthalpy at state 6
Write the specific enthalpy relation for the regenerator.
Write the expression of exergy destruction associated with the process 1-2 for Brayton cycle
Here, the gas constant of air is R, entropy of air at state 2 as a function of temperature only is
Write the expression of exergy destruction for process 3-4
Here, entropy of air at state 3 as a function of temperature is
Write the expression of exergy destruction for Brayton cycle
Here, entropy of air at state 5 as a function of temperature alone is
Write the expression of exergy destruction for process 5-3
Here, the temperature of the heat source is
Write the expression of exergy destruction for process 6-1
Here, the temperature of the sink is
Write the expression of stream exergy at the exit of the regenerator (state 6)
Here, the specific enthalpy of the surroundings is
Write the expression of change entropy for the exit of the regenerator
Here, entropy of air at the surroundings as a function of temperature alone is
Conclusion:
Refer Table A-17, “Ideal gas properties of air”, obtain the properties of air at 310 K
Substitute 900 kPa for
Substitute
Refer Table A-17, “Ideal gas properties of air”, obtain the properties of air at 50.06
Substitute
Substitute 0.80 for
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute 310.24
Substitute 659.84
Refer Table A-17, “Ideal gas properties of air”, obtain the properties of air at 310 K
Substitute 300 K for
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with process 1-2 for Brayton cycle is
Substitute 300 K for
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with process 3-4 for Brayton cycle is
Substitute 300 K for
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with regeneration process for Brayton cycle is
Substitute 300 K for
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with process 5-3 for Brayton cycle is
Substitute 300 K for
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with process 6-1 for Brayton cycle is
Refer Table A-17, “Ideal gas properties of air”, obtain the properties of air at 300 K
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the exergy of the exhaust gases at the exit of the regenerator is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
THERMODYNAMICS: ENG APPROACH LOOSELEAF
- S.4. Yandaki şekilde AB çubuğu pirinç ve CD çubuğu alüminyumdur. Sıcaklık 20°C iken iki çubuk arasında 0,5 mm boşluk bulunmaktadır. a) Sıcaklık 95°C'ye yükseldiğinde çubuklardaki normal gerilmeleri, b) Bu durumda AB ve CD çubuklarındaki deformasyonu bulunuz. AB çubuğu için: E 105 GPa, a = 20x 10 1/°C CD çubuğu için: E-70 GPa, a 23,6x 106 1/°C 0.5 300 250 mm Alüminyum Çap 50 mm Çap 75 mmarrow_forwardRecall the head loss equation developed in class for a sudden expansion (See section 7.7 in your textbook). h₁= (V1-V2)² 2g Show all the steps in going from this equation to equation 3 for the minor loss coefficient, K, above.arrow_forwardJust do Questions 7, 9, 11. Here are notes attached for reference. I prefer handwritten solutions. ONLY UPLOAD A SOLUTION IF YOU ARE SURE ABOUT THE ANSWER PLEASE. (If you have once answered this question don't answer it again I am looking for a difference solution)arrow_forward
- This is a tilt and rotation question. Here are notes attached for reference. I prefer handwritten solutions. ONLY UPLOAD A SOLUTION IF YOU ARE SURE ABOUT THE ANSWER PLEASE. I prefer handwritten solutions.arrow_forwardHomework#7arrow_forwardHomework#7arrow_forwardQ3. Consider an inlet flow for an engine with a supersonic inlet Mach number as shown in Figure. below, calculate the total pressure loss between point 1 and 3 if the flow passes first an oblique shock wave and then a reflected shock wave. (30 pts) Моо M∞ = 2.0 && = 30°arrow_forwardJust do Questions 7, 9, 11. Here are notes attached for reference. I prefer handwritten solutions. ONLY UPLOAD A SOLUTION IF YOU ARE SURE ABOUT THE ANSWER PLEASE. (If you have once answered this question don't answer it again)arrow_forwardThis is a tilt and rotation question. Here are notes attached for reference. I prefer handwritten solutions. ONLY UPLOAD A SOLUTION IF YOU ARE SURE ABOUT THE ANSWER PLEASE. I prefer handwritten solutions.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_iosRecommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY